Python是進行數據分析的一種出色語言,主要是因為以數據為中心的python軟件包具有奇妙的生態係統。 Pandas是其中的一種,使導入和分析數據更加容易。
Pandas Index.searchsorted()函數查找索引,應在其中插入元素以保持順序。該函數在已排序的IndexOpsMixin自已中找到索引,這樣,如果將值中的相應元素插入到索引之前,則將保留self的順序。
用法: Index.searchsorted(value, side=’left’, sorter=None)
參數:
value:要插入自身的價值。
side:如果為“ left”,則給出找到的第一個合適位置的索引。如果為“正確”,則返回上一個這樣的索引。如果沒有合適的索引,則返回0或N(其中N是自身的長度)。
sorter:整數索引的可選數組,用於將自身按升序排序。它們通常是np.argsort的結果。
返回:[indices:int數組]具有與值相同形狀的插入點數組。
範例1:采用Index.searchsorted()函數查找插入元素的正確位置,以使Index保持排序。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the index
idx = pd.Index([1, 5, 8, 9, 11, 24, 56, 81])
# Print the Index
idx輸出:
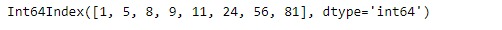
如果要插入的元素為10,請找出插入位置
# to find the position of inseretion
idx.searchsorted(10)輸出:

從輸出中可以看到,該函數已返回4,指示如果要保留順序,則在索引中插入10的正確位置是4。
範例2:采用Index.searchsorted()函數可以為索引中的多個元素找到正確的插入位置。插入時應保持順序。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the index
idx = pd.Index([1, 5, 8, 9, 11, 24, 56, 81])
# Print the Index
idx輸出:
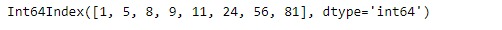
如果要插入的元素是7和29,讓我們找到插入位置
# to find the position of inseretion
idx.searchsorted([7, 29])輸出:
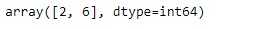
正如我們在輸出中看到的那樣,該函數返回了2和6,指示如果要保持順序,則在索引中插入7和29的正確位置是2nd和6th位置。
相關用法
- Python pandas.map()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.tz用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.str.contains()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.std()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.dst用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.sem()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas DataFrame.ix[ ]用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas.Categorical()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas.apply()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas TimedeltaIndex.contains用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.now用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.str.pad()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.take()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.all()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas series.str.get()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自Shubham__Ranjan大神的英文原創作品 Python | Pandas Index.searchsorted()。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
