Pandas.apply允許用戶傳遞函數並將其應用於Pandas係列的每個單個值。這是對 Pandas 庫的一項重大改進,因為此函數有助於根據所需條件將數據隔離,從而有效地將其用於數據科學和機器學習。
安裝:
在終端上使用以下命令將Pandas模塊導入python文件:
pip install pandas
要讀取csv文件並將其壓縮為pandas係列,請使用以下命令:
import pandas as pd
s = pd.read_csv("stock.csv", squeeze=True)
用法:
s.apply(func, convert_dtype=True, args=())
參數:
-
func:.apply接受一個函數並將其應用於pandas係列的所有值。
convert_dtype:根據函數的操作轉換dtype。
args =():傳遞給函數而不是序列的其他參數。
返回類型:應用函數/操作後的 Pandas 係列。
對於數據集,請單擊此處下載。
範例1:
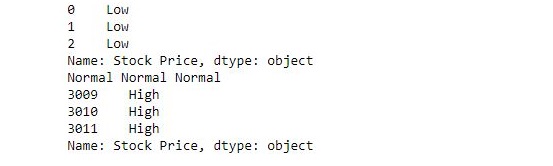
以下示例傳遞一個函數,並依次檢查每個元素的值,並相應地返回低,正常或高。
import pandas as pd
# reading csv
s = pd.read_csv("stock.csv", squeeze = True)
# defining function to check price
def fun(num):
if num<200:
return "Low"
elif num>= 200 and num<400:
return "Normal"
else:
return "High"
# passing function to apply and storing returned series in new
new = s.apply(fun)
# printing first 3 element
print(new.head(3))
# printing elements somewhere near the middle of series
print(new[1400], new[1500], new[1600])
# printing last 3 elements
print(new.tail(3))輸出:
範例2:
在以下示例中,使用lambda在.apply自身中製作了一個臨時匿名函數。它將每個序列的值加5,然後返回一個新的序列。
import pandas as pd
s = pd.read_csv("stock.csv", squeeze = True)
# adding 5 to each value
new = s.apply(lambda num : num + 5)
# printing first 5 elements of old and new series
print(s.head(), '\n', new.head())
# printing last 5 elements of old and new series
print('\n\n', s.tail(), '\n', new.tail())輸出:
0 50.12 1 54.10 2 54.65 3 52.38 4 52.95 Name: Stock Price, dtype: float64 0 55.12 1 59.10 2 59.65 3 57.38 4 57.95 Name: Stock Price, dtype: float64 3007 772.88 3008 771.07 3009 773.18 3010 771.61 3011 782.22 Name: Stock Price, dtype: float64 3007 777.88 3008 776.07 3009 778.18 3010 776.61 3011 787.22 Name: Stock Price, dtype: float64
觀察到,新值=舊值+ 5
相關用法
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自Kartikaybhutani大神的英文原創作品 Python | Pandas.apply()。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
