借助sympy.stats.ExGaussian()方法,我们可以获得代表 index 修正高斯分布的连续随机变量。
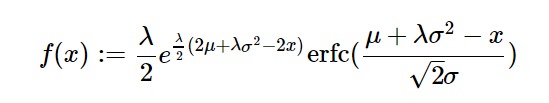
用法:sympy.stats.ExGaussian(name, mean, std, rate)
返回:Return continuous random variable.
范例1:
在这个例子中,我们可以通过使用sympy.stats.ExGaussian()通过使用该方法,我们能够获得代表 index 修正的高斯分布的连续随机变量。
# Import sympy and ExGaussian
from sympy.stats import ExGaussian, density
from sympy import Symbol
mean = Symbol("mean", integer = True, positive = True)
std = Symbol("std", integer = True, positive = True)
rate = Symbol("rate", integer = True, positive = True)
z = Symbol("z")
# Using sympy.stats.ExGaussian() method
X = ExGaussian("x", mean, std, rate)
gfg = density(X)(z)
pprint(gfg)输出:
/ 2 \
rate*\2*mean + rate*std - 2*z/
——————————- / ___ / 2 \\
2 |\/ 2 *\mean + rate*std - z/|
rate*e *erfc|—————————-|
\ 2*std /
————————————————————————
2
范例2:
# Import sympy and ExGaussian
from sympy.stats import ExGaussian, density
from sympy import Symbol
mean = 22
std = 21
rate = 7
z = 0.4
# Using sympy.stats.ExGaussian() method
X = ExGaussian("x", mean, std, rate)
gfg = density(X)(z)
pprint(gfg)输出:
/ ___\
3.50044639861837e+4758*erfc\74.0142857142857*\/ 2 /
相关用法
- Python zip()用法及代码示例
- Python abs()用法及代码示例
- Python pow()用法及代码示例
- Python gcd()用法及代码示例
- Python min() and max()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Jitender_1998大神的英文原创作品 sympy.stats.ExGaussian() in python。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
