在 C++ 中,std::mutex 是一种机制,当其他线程正在处理共享资源时,该机制会锁定对共享资源的访问,从而可以避免竞争条件等错误,并且可以同步线程。但在某些情况下,多个线程需要同时从共享资源中读取数据。在这里,std::shared_mutex 发挥作用。在本文中,我们将讨论 std::shared_mutex、其关联方法,以及它与 C++ 中的 std::mutex 的不同之处。
先决条件: C++ 多线程,C++ 中的 std::mutex。
C++ 中的 std::shared_mutex
在 C++ 中,std::shared_mutex 是一个同步原语,它允许多个线程同时使用共享资源进行读取,同时保证独占写入访问。在许多线程需要对同一数据结构进行只读访问但不经常使用写入操作的情况下,它很有用。
std::shared_mutex 中的锁类型
std::shared_mutex 提供两种类型的锁:
- 独特的锁:它是一个唯一的锁,一次只能由单个线程获取。该锁只允许单个线程修改共享资源,同时阻塞其他线程。它类似于 std::mutex 提供的锁。
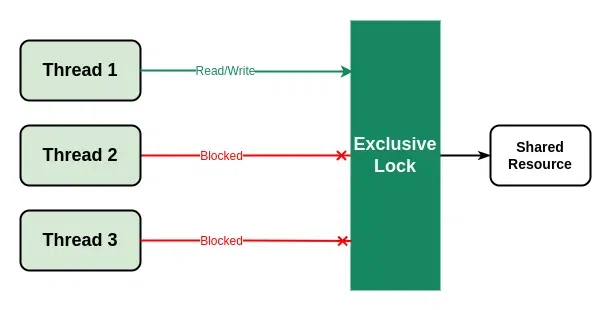
C++ 中的独占锁
- 共享锁:共享锁是多个线程可以同时获取的非独占锁。这为多个线程提供了对共享资源的只读访问权限。
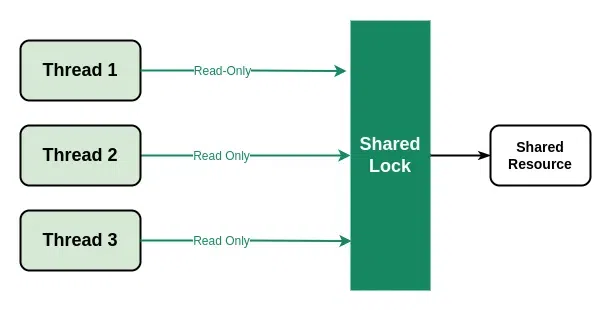
C++ 中的共享锁
Note: Multiple threads can aquire the shared lock simultaneously but only one thread can aquire the exclusive lock at a time.
与 std::shared_mutex 相关的方法
std::shared_mutex 包含执行不同操作所需的多个成员方法。一些常用的函数是:
|
S. 编号 |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
lock() | 独占锁定互斥锁,如果失败则阻塞。 |
|
2 |
unlock() | 解锁独占锁。 |
|
3 |
try_lock() | 尝试唯一锁定互斥体。如果互斥锁已被锁定以进行独占访问,则此函数不会阻塞并返回 false。 |
|
4 |
lock_shared() | 获取互斥体以使用共享锁。 |
|
5 |
unlock_shared() | 解锁当前线程的共享锁。 |
|
6 |
try_lock_shared() | 尝试共享锁。该函数不会阻塞,如果失败则返回 false。 |
std::shared_lock 的示例
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the use of shared_mutex
#include <iostream>
#include <shared_mutex>
#include <mutex>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
// creating a shared_mutex object
shared_mutex mutx;
int shared_data = 11;
// callable with shared lock
void readData() {
shared_lock<shared_mutex> lock(mutx);
cout << "Thread " << this_thread::get_id() << ": ";
cout << shared_data << endl;
}
// callable with unique_lock
void writeData(int n) {
unique_lock<shared_mutex> lock(mutx);
shared_data = n;
cout << "Thread" << this_thread::get_id() << ": \n";
}
// driver code
int main()
{
thread t1(readData);
thread t2(writeData, 128);
thread t3(writeData, 10);
thread t4 (readData);
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
t4.join();
return 0;
}输出
Read Thread 140122977658432: 11 Write Thread 140122960873024 Write Thread 140122969265728 Read Thread 140122952480320: 128
std::shared_mutex 与 std::mutex
与 std::mutex 类似,std::shared_mutex 是一个同步原语,可防止并发访问共享资源。两者都有各自的优点和缺点。
std::shared_mutex 相对于 std::mutex 的优点
与 std::mutex 相比,std::shared_mutex 具有以下优点:
- 增强并行性:多个线程可以同时访问共享数据进行读操作,增强了只需要读操作的程序的并行性。
std::shared_mutex 相对于 std::mutex 的优点
- 灵活性有限:std::shared_mutex 仅支持两种类型的锁:共享锁和唯一锁。通过 std::mutex 支持其他锁类型,例如递归锁和延迟锁。
- 增加复杂性:与 std::mutex 相比,std::shared_mutex 具有更大的复杂性。理解和应用可能会变得更具挑战性。
应用
以下是 std::shared_mutex 的一些主要应用:
- 当读取数据是主要操作并且写入数据不常见时,共享互斥体可以提供有效的并行性。
- 共享互斥体可用于缓存算法允许一个线程同时更新缓存,同时允许多个线程读取已缓存的数据。
- 数据库连接池允许多个线程同时读取和更新连接信息,但不允许同时修改。
结论
std::shared_mutex 是多线程环境中访问同步的有用机制之一。它在共享数据大多是只读的情况下尤其有效。但在使用 std::shared_mutex 之前,了解其局限性至关重要。
相关用法
- C++ std::swap()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::strncmp()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::sort()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::set_difference用法及代码示例
- C++ std::set_intersection用法及代码示例
- C++ std::set_union用法及代码示例
- C++ std::search用法及代码示例
- C++ std::stable_partition用法及代码示例
- C++ std::stof用法及代码示例
- C++ std::stol()、std::stoll()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::append()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::assign()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::back()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::clear用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::compare()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::data()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::erase用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::find_first_not_of用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::find_last_not_of用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::insert()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::push_back()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::resize()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::swap_ranges用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::rfind用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::find_last_of用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自ashish_rao_2373大神的英文原创作品 std::shared_mutex in C++。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
