在 C++ 中,std::mutex 是一種機製,當其他線程正在處理共享資源時,該機製會鎖定對共享資源的訪問,從而可以避免競爭條件等錯誤,並且可以同步線程。但在某些情況下,多個線程需要同時從共享資源中讀取數據。在這裏,std::shared_mutex 發揮作用。在本文中,我們將討論 std::shared_mutex、其關聯方法,以及它與 C++ 中的 std::mutex 的不同之處。
先決條件: C++ 多線程,C++ 中的 std::mutex。
C++ 中的 std::shared_mutex
在 C++ 中,std::shared_mutex 是一個同步原語,它允許多個線程同時使用共享資源進行讀取,同時保證獨占寫入訪問。在許多線程需要對同一數據結構進行隻讀訪問但不經常使用寫入操作的情況下,它很有用。
std::shared_mutex 中的鎖類型
std::shared_mutex 提供兩種類型的鎖:
- 獨特的鎖:它是一個唯一的鎖,一次隻能由單個線程獲取。該鎖隻允許單個線程修改共享資源,同時阻塞其他線程。它類似於 std::mutex 提供的鎖。
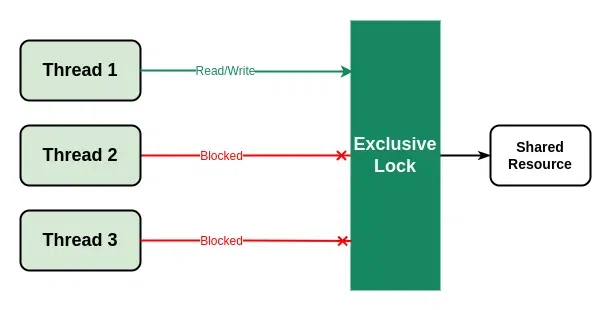
C++ 中的獨占鎖
- 共享鎖:共享鎖是多個線程可以同時獲取的非獨占鎖。這為多個線程提供了對共享資源的隻讀訪問權限。
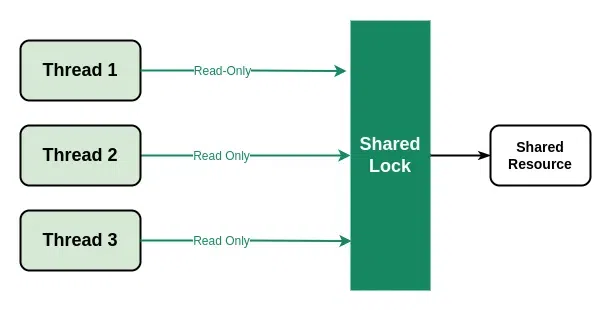
C++ 中的共享鎖
Note: Multiple threads can aquire the shared lock simultaneously but only one thread can aquire the exclusive lock at a time.
與 std::shared_mutex 相關的方法
std::shared_mutex 包含執行不同操作所需的多個成員方法。一些常用的函數是:
|
S. 編號 |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
lock() | 獨占鎖定互斥鎖,如果失敗則阻塞。 |
|
2 |
unlock() | 解鎖獨占鎖。 |
|
3 |
try_lock() | 嘗試唯一鎖定互斥體。如果互斥鎖已被鎖定以進行獨占訪問,則此函數不會阻塞並返回 false。 |
|
4 |
lock_shared() | 獲取互斥體以使用共享鎖。 |
|
5 |
unlock_shared() | 解鎖當前線程的共享鎖。 |
|
6 |
try_lock_shared() | 嘗試共享鎖。該函數不會阻塞,如果失敗則返回 false。 |
std::shared_lock 的示例
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the use of shared_mutex
#include <iostream>
#include <shared_mutex>
#include <mutex>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
// creating a shared_mutex object
shared_mutex mutx;
int shared_data = 11;
// callable with shared lock
void readData() {
shared_lock<shared_mutex> lock(mutx);
cout << "Thread " << this_thread::get_id() << ": ";
cout << shared_data << endl;
}
// callable with unique_lock
void writeData(int n) {
unique_lock<shared_mutex> lock(mutx);
shared_data = n;
cout << "Thread" << this_thread::get_id() << ": \n";
}
// driver code
int main()
{
thread t1(readData);
thread t2(writeData, 128);
thread t3(writeData, 10);
thread t4 (readData);
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
t4.join();
return 0;
}輸出
Read Thread 140122977658432: 11 Write Thread 140122960873024 Write Thread 140122969265728 Read Thread 140122952480320: 128
std::shared_mutex 與 std::mutex
與 std::mutex 類似,std::shared_mutex 是一個同步原語,可防止並發訪問共享資源。兩者都有各自的優點和缺點。
std::shared_mutex 相對於 std::mutex 的優點
與 std::mutex 相比,std::shared_mutex 具有以下優點:
- 增強並行性:多個線程可以同時訪問共享數據進行讀操作,增強了隻需要讀操作的程序的並行性。
std::shared_mutex 相對於 std::mutex 的優點
- 靈活性有限:std::shared_mutex 僅支持兩種類型的鎖:共享鎖和唯一鎖。通過 std::mutex 支持其他鎖類型,例如遞歸鎖和延遲鎖。
- 增加複雜性:與 std::mutex 相比,std::shared_mutex 具有更大的複雜性。理解和應用可能會變得更具挑戰性。
應用
以下是 std::shared_mutex 的一些主要應用:
- 當讀取數據是主要操作並且寫入數據不常見時,共享互斥體可以提供有效的並行性。
- 共享互斥體可用於緩存算法允許一個線程同時更新緩存,同時允許多個線程讀取已緩存的數據。
- 數據庫連接池允許多個線程同時讀取和更新連接信息,但不允許同時修改。
結論
std::shared_mutex 是多線程環境中訪問同步的有用機製之一。它在共享數據大多是隻讀的情況下尤其有效。但在使用 std::shared_mutex 之前,了解其局限性至關重要。
相關用法
- C++ std::swap()用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::strncmp()用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::sort()用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::set_difference用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::set_intersection用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::set_union用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::search用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::stable_partition用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::stof用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::stol()、std::stoll()用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::string::append()用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::string::assign()用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::string::back()用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::string::clear用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::string::compare()用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::string::data()用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::string::erase用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::string::find_first_not_of用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::string::find_last_not_of用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::string::insert()用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::string::push_back()用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::string::resize()用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::swap_ranges用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::string::rfind用法及代碼示例
- C++ std::string::find_last_of用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自ashish_rao_2373大神的英文原創作品 std::shared_mutex in C++。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
