本文简要介绍 python 语言中 numpy.random.RandomState.gumbel 的用法。
用法:
random.RandomState.gumbel(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=None)从 Gumbel 分布中抽取样本。
从具有指定位置和比例的 Gumbel 分布中抽取样本。有关 Gumbel 分布的更多信息,请参阅下面的注释和参考。
注意
新代码应改为使用
default_rng()实例的gumbel方法;请参阅快速入门。- loc: float 或 数组 的浮点数,可选
分布模式的位置。默认值为 0。
- scale: float 或 数组 的浮点数,可选
分布的尺度参数。默认值为 1。必须为非负数。
- size: int 或整数元组,可选
输出形状。例如,如果给定的形状是
(m, n, k),则绘制m * n * k样本。如果 size 为None(默认),如果loc和scale都是标量,则返回单个值。否则,将抽取np.broadcast(loc, scale).size样本。
- out: ndarray 或标量
从参数化 Gumbel 分布中抽取样本。
参数:
返回:
注意:
Gumbel(或最小极值 (SEV) 或最小极值类型 I)分布是用于对极值问题建模的一类广义极值 (GEV) 分布。 Gumbel 是极值 I 型分布的一个特例,用于具有 “exponential-like” 尾部分布的最大值。
Gumbel 分布的概率密度为
其中是模式,位置参数,是比例参数。
Gumbel(以德国数学家 Emil Julius Gumbel 命名)很早就在水文学文献中用于模拟洪水事件的发生。它还用于模拟最大风速和降雨率。这是一个 “fat-tailed” 分布 - 分布尾部发生事件的概率比使用高斯分布的概率更大,因此 100 年洪水的发生令人惊讶地频繁。洪水最初被建模为高斯过程,它低估了极端事件的频率。
它是一类极值分布,即广义极值 (GEV) 分布,其中还包括 Weibull 和 Frechet。
该函数的平均值为 ,方差为 。
参考:
Gumbel, E. J.,“极端统计”,纽约:哥伦比亚大学出版社,1958 年。
赖斯,R.-D。和 Thomas, M.,“保险、金融、水文和其他领域极值的统计分析”,巴塞尔:Birkhauser Verlag,2001 年。
1:
2:
例子:
从分布中抽取样本:
>>> mu, beta = 0, 0.1 # location and scale >>> s = np.random.gumbel(mu, beta, 1000)显示样本的直方图以及概率密度函数:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s, 30, density=True) >>> plt.plot(bins, (1/beta)*np.exp(-(bins - mu)/beta) ... * np.exp( -np.exp( -(bins - mu) /beta) ), ... linewidth=2, color='r') >>> plt.show()
显示极值分布如何从高斯过程中产生并与高斯过程进行比较:
>>> means = [] >>> maxima = [] >>> for i in range(0,1000) : ... a = np.random.normal(mu, beta, 1000) ... means.append(a.mean()) ... maxima.append(a.max()) >>> count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(maxima, 30, density=True) >>> beta = np.std(maxima) * np.sqrt(6) / np.pi >>> mu = np.mean(maxima) - 0.57721*beta >>> plt.plot(bins, (1/beta)*np.exp(-(bins - mu)/beta) ... * np.exp(-np.exp(-(bins - mu)/beta)), ... linewidth=2, color='r') >>> plt.plot(bins, 1/(beta * np.sqrt(2 * np.pi)) ... * np.exp(-(bins - mu)**2 / (2 * beta**2)), ... linewidth=2, color='g') >>> plt.show()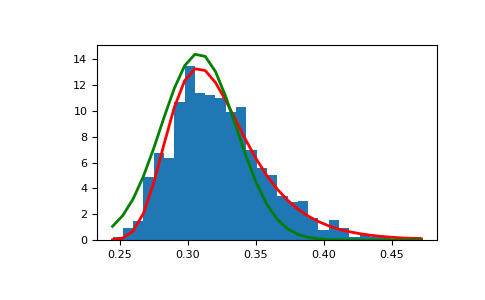
相关用法
- Python numpy RandomState.geometric用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.gamma用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.standard_exponential用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.bytes用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.uniform用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.standard_gamma用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.seed用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.power用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.standard_normal用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.random_sample用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.logseries用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.noncentral_chisquare用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.wald用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.chisquare用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.poisson用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.randn用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.vonmises用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.zipf用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.triangular用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.f用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.shuffle用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.rayleigh用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.randint用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.permutation用法及代码示例
- Python numpy RandomState.lognormal用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自numpy.org大神的英文原创作品 numpy.random.RandomState.gumbel。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
