Matplotlib是Python中令人驚歎的可視化庫,用於數組的二維圖。 Matplotlib是一個基於NumPy數組的多平台數據可視化庫,旨在與更廣泛的SciPy堆棧配合使用。
matplotlib.colors.Normalize
matplotlib.colors.Normalize類屬於matplotlib.colors模塊。 matplotlib.colors模塊用於將顏色或數字參數轉換為RGBA或RGB。此模塊用於將數字映射到顏色或以一維顏色數組(也稱為colormap)進行顏色規格轉換。
matplotlib.colors.Normalize類用於將數據規範化為[0.0,1.0]的間隔。
用法:
class matplotlib.colors.Normalize(vmin=None, vmax=None, clip=False)
如果未設置vmin或vmax,則它將分別從處理的第一個輸入的最小值和最大值進行初始化。換句話說,__call __(Data)調用autoscale_None(Data)。如果clip的值設置為True且給定值超出範圍,則它將返回0或1,以最接近的值為準。如果vmax == vmin,則返回0。它與標量或包含掩碼數組的數組一起運行。如果clip為True,則將蒙版值設置為1,否則它們將保持蒙版。
方法:
- autoscale(self, A):此方法將vmin設置為A的最小值,並將vmax設置為A的最大值。
- autoscale_None(self, A):此方法僅自動縮放具有無值的vmin和vmax。
- inverse(self, value):它交換vmin和vmax的值。
- static process_value(value):此方法中的value參數可以是標量或序列。它用於均化輸入值,以進行有效而簡單的標準化。此方法返回匹配值的掩碼數組。將保留所有浮點數據類型,並將具有兩個或更少字節的整數數據類型轉換為np.float32,而將較大字節類型的數據轉換為np.float64。這樣做是為了通過使用就地操作盡可能保留float32值來提高大型數組的速度。
- scaled(self):它返回一個布爾值以檢查是否設置了vmin或vmax。
範例1:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import colors
from matplotlib.ticker import PercentFormatter
# set a random state for
# reproducibility
np.random.seed(19687581)
total_points = 500000
total_bins = 100
# Centering at a = 0 and b = 5
# generate normal distributions
a = np.random.randn(total_points)
b = .4 * a + np.random.randn(500000) + 5
figure, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2,
tight_layout = True)
# C is the count in each bin
C, bins, patches = axes[0].hist(a,
bins = total_bins)
# We'll color code by height,
# but you could use any scalar
fracs = C / C.max()
# Normalize of the data to 0..1
# for covering the full range of
# the colormap
norm = colors.Normalize(fracs.min(), fracs.max())
# looping through the objects and
# setting the color of each accordingly
for thisfrac, thispatch in zip(fracs, patches):
color = plt.cm.viridis(norm(thisfrac))
thispatch.set_facecolor(color)
# normalize the inputs by C
axes[1].hist(a, bins = total_bins, density = True)
# formating the y-axis for displaying
# percentage
axes[1].yaxis.set_major_formatter(PercentFormatter(xmax = 1))輸出:
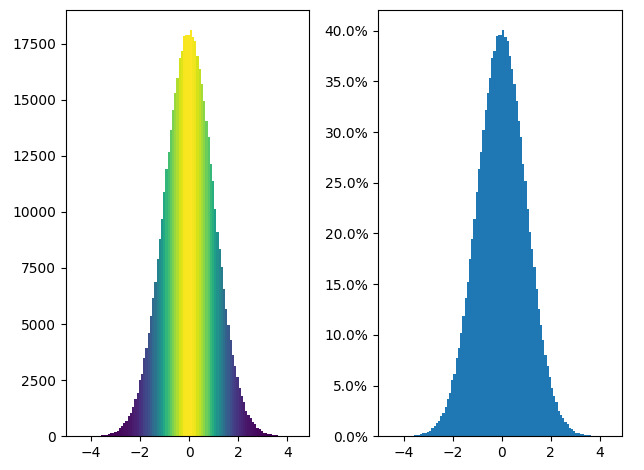
範例2:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
figure, axes = plt.subplots(figsize =(6, 1))
figure.subplots_adjust(bottom = 0.5)
color_map = mpl.cm.cool
normlizer = mpl.colors.Normalize(vmin = 0, vmax = 5)
figure.colorbar(mpl.cm.ScalarMappable(norm = normlizer,
cmap = color_map),
cax = axes, orientation ='horizontal',
label ='Arbitary Units')輸出:
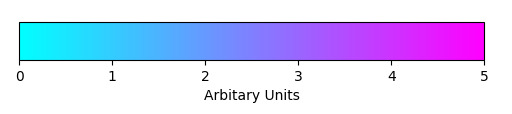
相關用法
- Python Matplotlib.ticker.MultipleLocator用法及代碼示例
- Python Matplotlib.gridspec.GridSpec用法及代碼示例
- Python Matplotlib.patches.CirclePolygon用法及代碼示例
- Python Matplotlib.colors.LogNorm用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自RajuKumar19大神的英文原創作品 Matplotlib.colors.Normalize class in Python。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
