在 Java 中,Scanner 和 BufferedReader 類是用作讀取輸入的方式的源。 Scanner class 是一個簡單的文本掃描器,可以解析原始類型和字符串。它內部使用正則表達式來讀取不同類型,而另一方麵 BufferedReader class 從 character-input 流中讀取文本,緩衝字符以便高效讀取字符序列
奇怪的差異在於通過 next() 方法讀取不同的輸入方式,該方法在下麵的程序中通過類似的輸入集得到了證明。
示例 1:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Scanner Class
// Importing Scanner class from
// java.util package
import java.util.Scanner;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating object of Scanner class to
// read input from keyboard
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter an integer & a String");
// Using nextInt() to parse integer values
int a = scn.nextInt();
// Using nextLine() to parse string values
String b = scn.nextLine();
// Display name and age entered above
System.out.printf("You have entered:- " + a + " "
+ "and name as " + b);
}
}輸出:
Enter an integer & a String 10 John You have entered:- 10 and name as John
讓我們嘗試使用 Buffer 類和下麵相同的輸入進行相同的操作,如下所示:
示例 2:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate BufferedReader Class
// Importing required class
import java.io.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
throws IOException
{
// Creating object of class inside main() method
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("Enter an integer");
// Taking integer input
int a = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.println("Enter a String");
String b = br.readLine();
// Printing input entities above
System.out.printf("You have entered:- " + a
+ " and name as " + b);
}
}輸出:
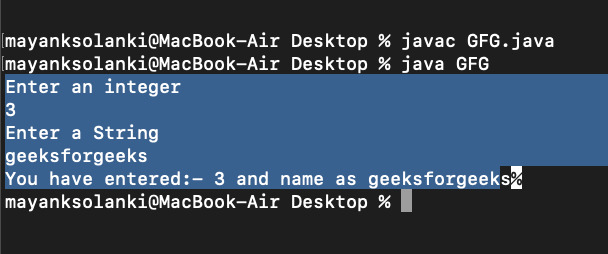
輸出說明:在 Scanner 類中,如果我們調用 nextLine()方法在七個中的任何一個之後nextXXX()方法那麽nextLine()不會從控製台讀取值,並且光標不會進入控製台,它將跳過該步驟。 nextXXX()方法為nextInt()、nextFloat()、nextByte()、nextShort()、nextDouble()、nextLong()、next()。
在BufferReader課程中不存在此類問題。此問題僅發生在 Scanner 類中,因為 nextXXX() 方法忽略換行符,而 nextLine() 隻讀取第一個換行符。如果我們在nextXXX()和nextLine()之間再調用一次nextLine()方法,那麽就不會出現這個問題,因為nextLine()會消耗換行符。
Tip: See this for the corrected program. This problem is same as scanf() followed by gets() in C/C++. This problem can also be solved by using next() instead of nextLine() for taking input of strings as shown 這裏.
以下是 Java 中 Scanner 和 BufferedReader 類之間的主要區別
- BufferedReader 是同步的,而掃描儀不是同步的。如果我們使用多個線程,則應使用BufferedReader。
- BufferedReader 的緩衝存儲器比掃描儀大得多。
- 掃描儀有一個小緩衝區(1KB 字符緩衝區),而不是 BufferedReader(8KB 字節緩衝區),但它已經足夠了。
- BufferedReader 與 Scanner 相比要快一些,因為 Scanner 會解析輸入數據,而 BufferedReader 隻是讀取字符序列。
相關用法
- Java Scanner findWithinHorizon()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner hasNext()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner next()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner remove()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner tokens()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner close()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner delimiter()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner findInLine()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner hasNextBigDecimal()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner hasNextBoolean()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner hasNextDouble()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner hasNextFloat()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner hasNextLine()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner hasNextShort()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner ioException()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner locale()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner match()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner nextBigDecimal()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner nextBigInteger()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner nextBoolean()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner nextByte()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner nextDouble()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner nextFloat()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner nextInt()用法及代碼示例
- Java Scanner nextLine()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自佚名大神的英文原創作品 Difference Between Scanner and BufferedReader Class in Java。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
