random模块用于在Python中生成随机数。实际上不是随机的,而是用于生成伪随机数的。这意味着可以确定这些随机生成的数字。
expovariate()
expovariate() 是内置的方法random模块。它用于返回具有 index 分布的随机浮点数。
用法: random.expovariate(lambd)
参数:
lambd:非零值
返回:随机 index 分布浮点数
如果参数为正,则结果范围为0到正无穷大
如果参数为负,则结果范围为0到负无穷大
范例1:
# import the random module
import random
# determining the values of the parameter
lambd = 1.5
# using the expovariate() method
print(random.expovariate(lambd))输出:
0.22759592233982198
范例2:我们可以多次生成该数字并绘制图形以观察 index 分布。
# import the required libraries
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# store the random numbers in a
# list
nums = []
alpha = 3
for i in range(100):
temp = random.paretovariate(alpha)
nums.append(temp)
# plotting a graph
plt.plot(nums)
plt.show()输出:
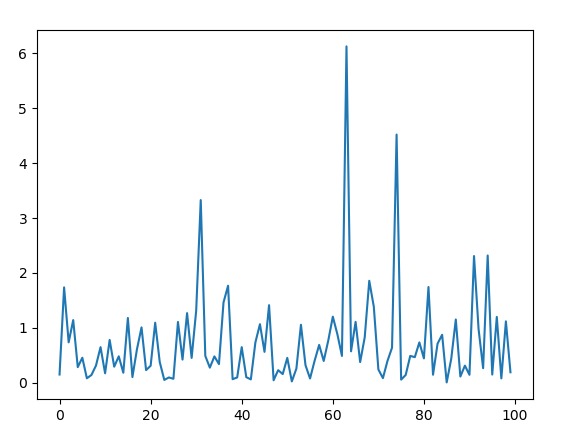
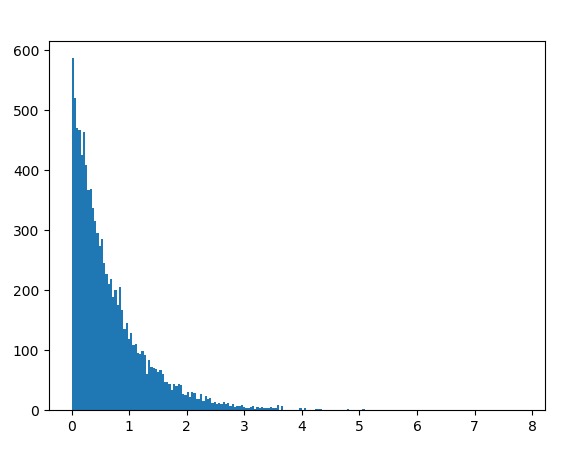
范例3:我们可以创建一个直方图来观察 index 分布的密度。
# import the required libraries
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# store the random numbers in a list
nums = []
lambd = 1.5
for i in range(10000):
temp = random.expovariate(lambd)
nums.append(temp)
# plotting a graph
plt.hist(nums, bins = 200)
plt.show()输出:
相关用法
- Python Wand function()用法及代码示例
- Python ord()用法及代码示例
- Python hex()用法及代码示例
- Python id()用法及代码示例
- Python dir()用法及代码示例
- Python int()用法及代码示例
- Python cmp()用法及代码示例
- Python now()用法及代码示例
- Python oct()用法及代码示例
- Python map()用法及代码示例
- Python sum()用法及代码示例
- Python tell()用法及代码示例
- Python fsum()用法及代码示例
- Python round()用法及代码示例
- Python reversed()用法及代码示例
- Python cmath.sin()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Yash_R大神的英文原创作品 random.expovariate() function in Python。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
