Python也支持文件处理,并提供了用于创建,写入和读取文件的内置函数。可以在python中处理的文件有两种类型,普通文本文件和二进制文件(以二进制语言0s和1s编写)。
- 文字档:在这种类型的文件中,每行文本都以称为EOL(行尾)的特殊字符结尾,默认情况下,该字符是python中的换行符(\ n)。
- 二进制文件:在这种类型的文件中,一行没有终结符,并且在将数据转换为机器可理解的二进制语言后将其存储。
Refer the below articles to get the idea about basics of File handling.
tell()方法:
访问方式控制打开的文件中可能的操作类型。它指的是文件打开后的使用方式。这些模式还定义了文件句柄在文件中的位置。文件句柄就像一个游标,它定义了必须从何处读取或写入文件中的数据。有时对我们来说了解文件汉德的位置就变得很重要。tell() 方法可用于获取文件句柄的位置。tell()方法返回文件对象的当前位置。此方法不带参数,并返回一个整数值。最初,文件指针指向文件的开头(如果未在追加模式下打开)。所以,初始值tell()是零。
用法:
file_object.tell()
让我们假设名为“myfile”的文本文件如下所示:
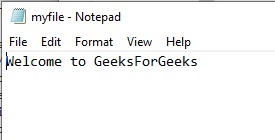
#示例1:在读取或写入文件之前文件句柄的位置。
# Python program to demonstrate
# tell() method
# Open the file in read mode
fp = open("myfile.txt", "r")
# Print the position of handle
print(fp.tell())
#Closing file
fp.close()输出:
0
#示例2:从文件读取数据后,文件句柄的位置。
# Python program to demonstrate
# tell() method
# Opening file
fp = open("sample.txt", "r")
fp.read(8)
# Print the position of handle
print(fp.tell())
# Closing file
fp.close()输出:
8
#示例3:用于二进制文件。让我们创建一个二进制文件,在写入二进制文件之前和之后,我们都会注意到句柄的位置。
# Python program to demonstrate
# tell() method
# for reading binary file we
# have to use "wb" in file mode.
fp = open("sample2.txt", "wb")
print(fp.tell())
# Writing to file
fp.write(b'1010101')
print(fp.tell())
# Closing file
fp.close()输出:
0 7
相关用法
- Python now()用法及代码示例
- Python cmp()用法及代码示例
- Python map()用法及代码示例
- Python ord()用法及代码示例
- Python int()用法及代码示例
- Python dir()用法及代码示例
- Python hex()用法及代码示例
- Python sum()用法及代码示例
- Python id()用法及代码示例
- Python oct()用法及代码示例
- Python globals()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自shaikameena大神的英文原创作品 Python tell() function。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
