tune_grid() 为一组预定义的调整参数计算一组性能指标(例如,准确性或 RMSE),这些参数对应于一次或多次数据重采样的模型或配方。
用法
tune_grid(object, ...)
# S3 method for model_spec
tune_grid(
object,
preprocessor,
resamples,
...,
param_info = NULL,
grid = 10,
metrics = NULL,
control = control_grid()
)
# S3 method for workflow
tune_grid(
object,
resamples,
...,
param_info = NULL,
grid = 10,
metrics = NULL,
control = control_grid()
)参数
- object
-
parsnip模型规范或workflows::workflow()。 - ...
-
目前未使用。
- preprocessor
-
使用
recipes::recipe()创建的传统模型公式或配方。 - resamples
-
rset()对象。 - param_info
-
dials::parameters()对象或NULL。如果没有给出,则从其他参数派生参数集。当需要自定义参数范围时,传递此参数可能很有用。 - grid
-
调谐组合或正整数的 DataFrame 。 DataFrame 应具有用于调整每个参数的列和用于调整候选参数的行。整数表示要自动创建的候选参数集的数量。
- metrics
-
一个
yardstick::metric_set()或NULL。 - control
-
用于修改调整过程的对象。
值
resamples 的更新版本,带有 .metrics 和 .notes 的额外列表列(可选列是 .predictions 和 .extracts )。 .notes
包含执行期间发生的警告和错误。
细节
假设有 m 个调整参数组合。 tune_grid() 可能不需要每次重采样都适合所有 m 个模型/配方。例如:
-
如果可以使用单个模型拟合来预测网格中的不同参数值,则仅使用一种拟合。例如,对于某些提升树,如果请求 100 次提升迭代,则可以使用 100 次迭代的模型对象对小于 100 次的迭代进行预测(如果所有其他参数都相等)。
-
当结合预处理和/或后处理参数调整模型时,将使用最小拟合次数。例如,如果配方步骤中的 PCA 组件数量在三个值(以及模型调整参数)上进行调整,则仅训练三个配方。另一种方法是为每个模型调整参数多次重新训练相同的配方。
这里使用foreach包。要并行执行重采样迭代,请注册并行后端函数。有关示例,请参阅 foreach::foreach() 的文档。
大多数情况下,训练期间生成的警告会在发生时显示,并与 control_grid(verbose = TRUE) 时的特定重新采样相关联。它们(通常)直到处理结束才聚合。
参数网格
如果未提供调整网格,则会使用 10 个候选参数组合创建半随机网格(通过 dials::grid_latin_hypercube() )。
如果提供,网格应具有每个参数的列名称,并且这些名称应由参数名称或 id 命名。例如,如果使用 penalty = tune() 将参数标记为优化,则应该有一个名为 penalty 的列。如果使用可选标识符,例如 penalty = tune(id = 'lambda') ,则相应的列名称应为 lambda 。
在某些情况下,调整参数值取决于数据的维度。例如,随机森林模型中的mtry 取决于预测变量的数量。在这种情况下,默认调整参数对象需要一个上限。 dials::finalize() 可用于导出数据相关参数。否则,可以创建参数集(通过 dials::parameters() ),并使用 dials update() 函数来更改值。此更新的参数集可以通过 param_info 参数传递给函数。
性能指标
要使用您自己的性能指标,可以使用 yardstick::metric_set() 函数来选择每个模型应测量的内容。如果需要多个指标,可以将它们捆绑在一起。例如,要估计 ROC 曲线下的面积以及灵敏度和特异性(在典型概率截止值 0.50 下),可以给出 metrics 参数:
metrics = metric_set(roc_auc, sens, spec)每个指标都是针对每个候选模型计算的。
如果未提供指标集,则会创建一个指标集:
-
对于回归模型,计算均方根误差和确定系数。
-
对于分类,计算 ROC 曲线下的面积和总体准确度。
请注意,这些指标还决定了调整期间估计的预测类型。例如,在分类问题中,如果使用的度量全部与硬类预测相关,则不会创建分类概率。
这些指标的 out-of-sample 估计值包含在名为 .metrics 的列表列中。该小标题包含每个指标的行和值、估计器类型等的列。
collect_metrics() 可用于这些对象来折叠重采样的结果(以获得每个调整参数组合的最终重采样估计)。
获取预测
当 control_grid(save_pred = TRUE) 时,输出 tibble 包含一个名为 .predictions 的列表列,其中包含网格和每个折叠中每个参数组合的 out-of-sample 预测(可能非常大)。
tibble 的元素是 tibbles,其中包含调整参数的列、原始数据对象 ( .row ) 的行号、结果数据(与原始数据具有相同的名称)以及由的预测。例如,对于简单的回归问题,此函数会生成一个名为.pred 的列,依此类推。如上所述,返回的预测列由请求的度量类型确定。
此列表列可以是 unnested 使用 tidyr::unnest() 或使用便利函数 collect_predictions() 。
提取信息
extract 控制选项将导致返回一个名为 .extracts 的附加函数。这是一个列表列,其中包含每个调整参数组合的用户函数结果的标题。这可以允许返回在重采样期间创建的每个模型和/或配方对象。请注意,这可能会导致返回对象很大,具体取决于返回的内容。
控制函数包含一个选项 (extract),可用于保留在重采样中创建的任何模型或配方。该参数应该是具有单个参数的函数。每次重新采样中赋予函数的参数值是工作流对象(有关更多信息,请参阅workflows::workflow())。可以使用多个辅助函数轻松地从工作流程中提取预处理和/或模型信息,例如 extract_preprocessor() 和 extract_fit_parsnip() 。
例如,如果有兴趣恢复每个防风草模型,可以使用:
extract = function (x) extract_fit_parsnip(x)请注意,赋予 extract 参数的函数是在每个适合的模型上评估的(而不是在评估的每个模型上)。如上所述,在某些情况下,可以针对 sub-models 导出模型预测,因此在这些情况下,并非调整参数网格中的每一行都有与其关联的单独 R 对象。
例子
library(recipes)
library(rsample)
library(parsnip)
library(workflows)
library(ggplot2)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
set.seed(6735)
folds <- vfold_cv(mtcars, v = 5)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# tuning recipe parameters:
spline_rec <-
recipe(mpg ~ ., data = mtcars) %>%
step_ns(disp, deg_free = tune("disp")) %>%
step_ns(wt, deg_free = tune("wt"))
lin_mod <-
linear_reg() %>%
set_engine("lm")
# manually create a grid
spline_grid <- expand.grid(disp = 2:5, wt = 2:5)
# Warnings will occur from making spline terms on the holdout data that are
# extrapolations.
spline_res <-
tune_grid(lin_mod, spline_rec, resamples = folds, grid = spline_grid)
spline_res
#> # Tuning results
#> # 5-fold cross-validation
#> # A tibble: 5 × 4
#> splits id .metrics .notes
#> <list> <chr> <list> <list>
#> 1 <split [25/7]> Fold1 <tibble [32 × 6]> <tibble [0 × 3]>
#> 2 <split [25/7]> Fold2 <tibble [32 × 6]> <tibble [0 × 3]>
#> 3 <split [26/6]> Fold3 <tibble [32 × 6]> <tibble [0 × 3]>
#> 4 <split [26/6]> Fold4 <tibble [32 × 6]> <tibble [0 × 3]>
#> 5 <split [26/6]> Fold5 <tibble [32 × 6]> <tibble [0 × 3]>
show_best(spline_res, metric = "rmse")
#> # A tibble: 5 × 8
#> disp wt .metric .estimator mean n std_err .config
#> <int> <int> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 3 2 rmse standard 2.54 5 0.207 Preprocessor02_Model1
#> 2 3 3 rmse standard 2.64 5 0.234 Preprocessor06_Model1
#> 3 4 3 rmse standard 2.82 5 0.456 Preprocessor07_Model1
#> 4 4 2 rmse standard 2.93 5 0.489 Preprocessor03_Model1
#> 5 4 4 rmse standard 3.01 5 0.475 Preprocessor11_Model1
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# tune model parameters only (example requires the `kernlab` package)
car_rec <-
recipe(mpg ~ ., data = mtcars) %>%
step_normalize(all_predictors())
svm_mod <-
svm_rbf(cost = tune(), rbf_sigma = tune()) %>%
set_engine("kernlab") %>%
set_mode("regression")
# Use a space-filling design with 7 points
set.seed(3254)
svm_res <- tune_grid(svm_mod, car_rec, resamples = folds, grid = 7)
svm_res
#> # Tuning results
#> # 5-fold cross-validation
#> # A tibble: 5 × 4
#> splits id .metrics .notes
#> <list> <chr> <list> <list>
#> 1 <split [25/7]> Fold1 <tibble [14 × 6]> <tibble [0 × 3]>
#> 2 <split [25/7]> Fold2 <tibble [14 × 6]> <tibble [0 × 3]>
#> 3 <split [26/6]> Fold3 <tibble [14 × 6]> <tibble [0 × 3]>
#> 4 <split [26/6]> Fold4 <tibble [14 × 6]> <tibble [0 × 3]>
#> 5 <split [26/6]> Fold5 <tibble [14 × 6]> <tibble [0 × 3]>
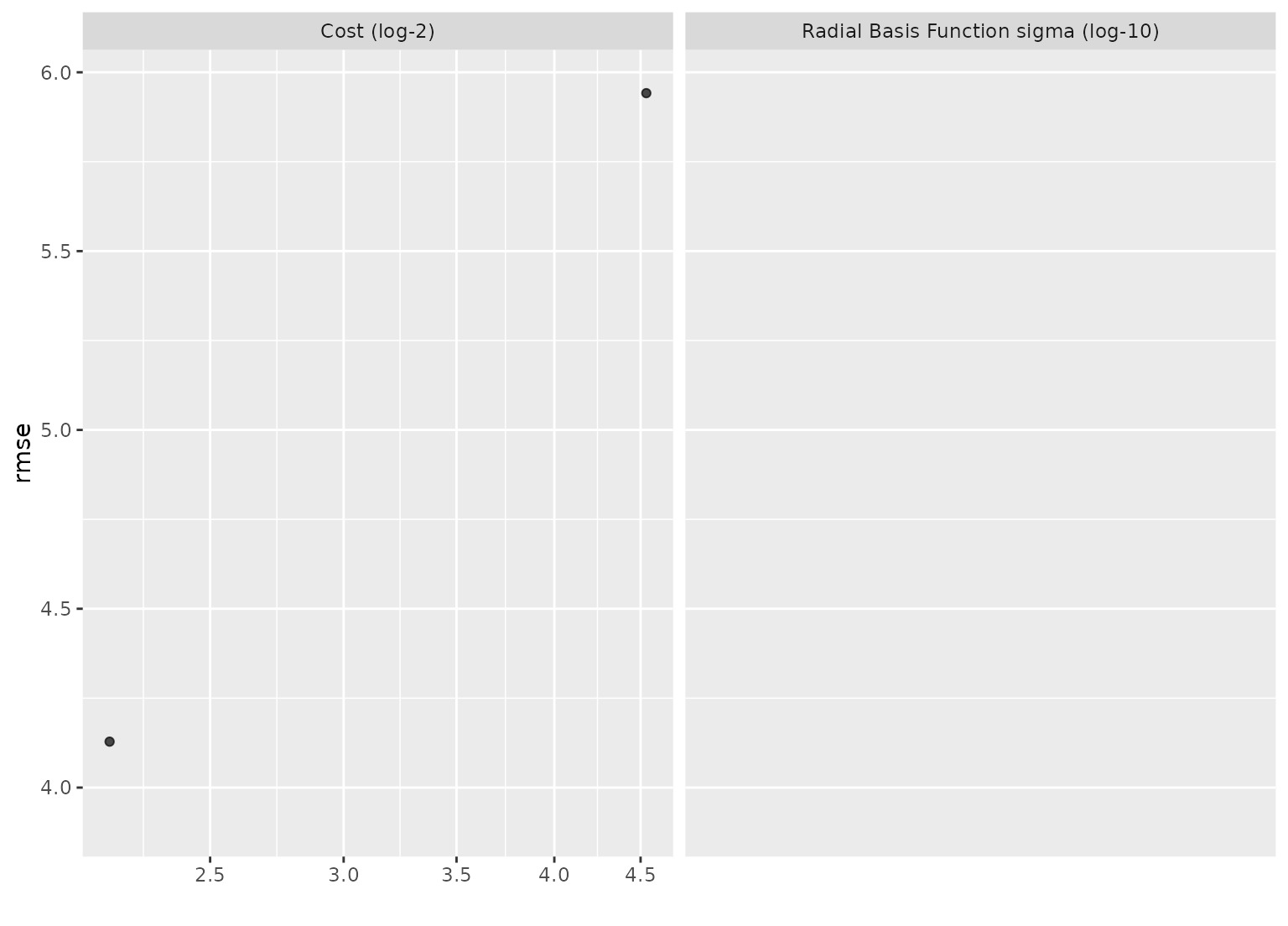
show_best(svm_res, metric = "rmse")
#> # A tibble: 5 × 8
#> cost rbf_sigma .metric .estimator mean n std_err .config
#> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 0.304 0.117 rmse standard 3.91 5 0.652 Preprocesso…
#> 2 4.53 0.000420 rmse standard 4.13 5 0.741 Preprocesso…
#> 3 0.00247 0.00931 rmse standard 5.94 5 0.966 Preprocesso…
#> 4 23.2 0.000000684 rmse standard 5.94 5 0.967 Preprocesso…
#> 5 0.0126 0.00000239 rmse standard 5.96 5 0.970 Preprocesso…
autoplot(svm_res, metric = "rmse") +
scale_x_log10()
#> Warning: NaNs produced
#> Warning: Transformation introduced infinite values in continuous x-axis
#> Warning: Removed 12 rows containing missing values (`geom_point()`).
 # ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Using a variables preprocessor with a workflow
# Rather than supplying a preprocessor (like a recipe) and a model directly
# to `tune_grid()`, you can also wrap them up in a workflow and pass
# that along instead (note that this doesn't do any preprocessing to
# the variables, it passes them along as-is).
wf <- workflow() %>%
add_variables(outcomes = mpg, predictors = everything()) %>%
add_model(svm_mod)
set.seed(3254)
svm_res_wf <- tune_grid(wf, resamples = folds, grid = 7)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Using a variables preprocessor with a workflow
# Rather than supplying a preprocessor (like a recipe) and a model directly
# to `tune_grid()`, you can also wrap them up in a workflow and pass
# that along instead (note that this doesn't do any preprocessing to
# the variables, it passes them along as-is).
wf <- workflow() %>%
add_variables(outcomes = mpg, predictors = everything()) %>%
add_model(svm_mod)
set.seed(3254)
svm_res_wf <- tune_grid(wf, resamples = folds, grid = 7)
相关用法
- R tune tune_bayes 模型参数的贝叶斯优化。
- R tune coord_obs_pred 对观察值与预测值的绘图使用相同的比例
- R tune extract-tune 提取调整对象的元素
- R tune filter_parameters 删除一些调整参数结果
- R tune fit_best 将模型拟合到数值最优配置
- R tune conf_mat_resampled 计算重采样的平均混淆矩阵
- R tune finalize_model 将最终参数拼接到对象中
- R tune collect_predictions 获取并格式化由调整函数产生的结果
- R tune show_best 研究最佳调整参数
- R tune expo_decay 指数衰减函数
- R tune fit_resamples 通过重采样拟合多个模型
- R tune merge.recipe 将参数网格值合并到对象中
- R tune autoplot.tune_results 绘图调整搜索结果
- R tune dot-use_case_weights_with_yardstick 确定案例权重是否应传递至标准
- R tune message_wrap 写一条尊重线宽的消息
- R tune prob_improve 用于对参数组合进行评分的获取函数
- R tune last_fit 将最终的最佳模型拟合到训练集并评估测试集
- R update_PACKAGES 更新现有的 PACKAGES 文件
- R textrecipes tokenlist 创建令牌对象
- R themis smotenc SMOTENC算法
- R print.via.format 打印实用程序
- R tibble tibble 构建 DataFrame 架
- R tidyr separate_rows 将折叠的列分成多行
- R textrecipes step_lemma 标记变量的词形还原
- R textrecipes show_tokens 显示配方的令牌输出
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Max Kuhn等大神的英文原创作品 Model tuning via grid search。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
