数据可视化是分析数据的重要部分,因为绘制图形有助于更好地了解和理解问题。 Matplotlib.pyplot是执行此操作的最常用的库之一。它有助于创建有吸引力的数据,并且超级易于使用。
Matplotlib.pyplot.semilogx()函数
此函数用于以x轴转换为对数格式的方式显示数据。当参数之一非常大并因此最初以紧凑方式存储时,此函数特别有用。它支持plot()和matplotlib.axes.Axes.set_xscale()的所有关键字参数。其他参数是basex,subsx和nonposx。
用法:Matplotlib.pyplot.semilogx(x, y, )
参数:一些重要的参数是:
- x:X轴上的值。
- y:Y轴上的值。
- color:(可选)线条或符号的颜色。
- linewidth:(可选)线的宽度。
- label:(可选)指定图的标签
- basex:(可选)x对数的底数。标量应大于1。
- subsx:(可选)次要ticks的位置;没有默认值是自动订阅,这取决于情节中的十年数。
- nonposx:(可选)可以将x中的非正值掩盖为无效值,或将其裁剪为非常小的正数。
- marker:(可选)将点显示为上述符号。
- markersize:(可选)更改所有标记的大小。
Return:X轴上的log-scaled图。
范例1:简单的情节。
Python3
#import required library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# defining the values
# at X and Y axis
x = [1, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6]
y = [100, 200, 300,
400, 500, 600]
# plotting the given graph
plt.semilogx(x, y, marker = ".",
markersize = 15,
color = "green")
# plot with grid
plt.grid(True)
# show the plot
plt.show()输出:
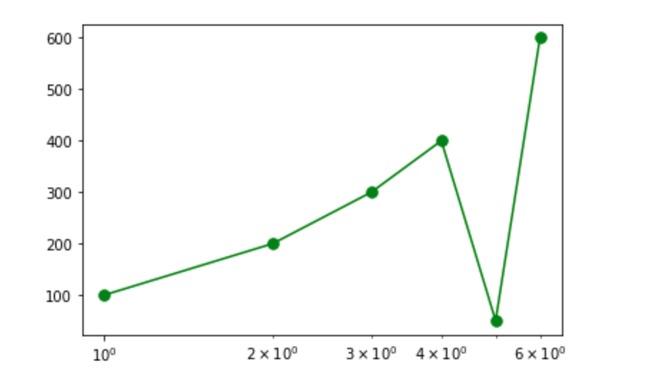
一个简单的情节
示例2:在X和Y轴上使用负值和零值。
由于X轴包含在对数函数中,因此很明显,如nonposx参数所指定的,负值或正值将被裁剪或屏蔽。默认情况下,将裁剪负值或零值。
Python3
# importing required libraries
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# defining the values
# at X and Y axis
x = [-1, -2, 0]
y = [5, -2, 0]
# plotting the given graph
plt.semilogx(x,y)
# show the plot
plt.show()输出:
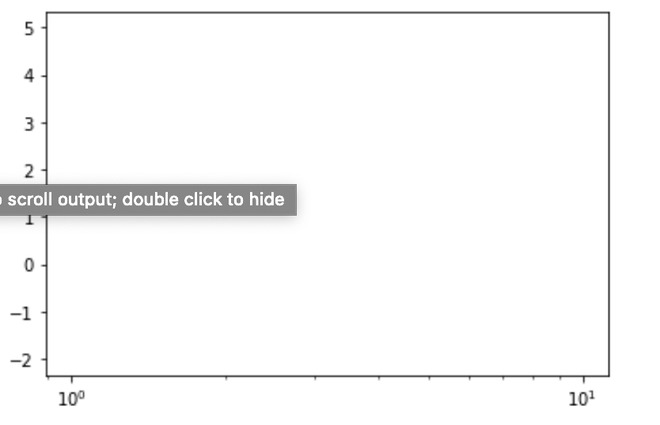
由于所有值均为负x值,因此未绘制任何值
范例3:如果使用符号,则仅删除负值或零值,仅绘制正值。
Python3
#import required library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# defining the values at X and Y axis
x = [-10, 30, 0, 20,
-50, 25, 29, -3
, 23, 25, 29, 31]
y = [-3, 30, -10, 0,
-40, 3, 8, 0,
-24, 40, 43, 25]
# plotting the graph
plt.semilogx(x,y,'g^', color = "red")
# plot with grid
plt.grid(True)
# set y axis label
plt.ylabel('---y---')
# set x axis label
plt.xlabel('---x---')
# show the plot
plt.show()输出:
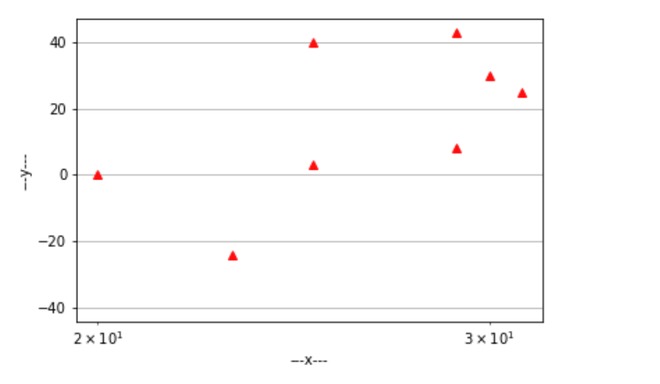
仅绘制正值
范例4:如果使用这些行,则将剪切值。
Python3
#import required library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# defining the values
# at X and Y axis
x = [1, 2, -3,
-4, 5, 6]
y = [100, 200, 300,
400, 500, 600]
# plotting the graph
plt.semilogx(x, y, marker = ".",
markersize = 15)
# plot with grid
plt.grid(True)
# show the plot
plt.show()输出:
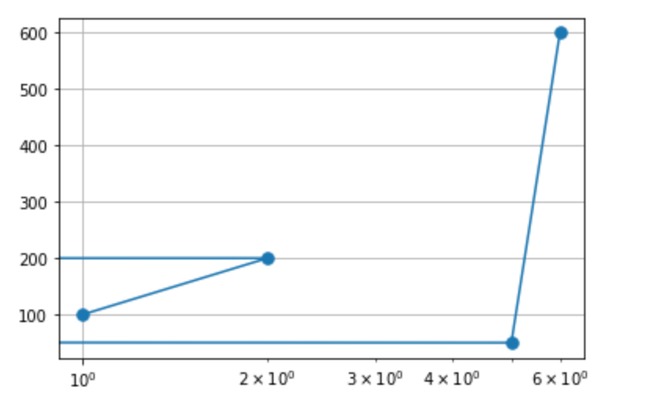
裁剪对应于-3和-4的值
范例5:以下子图将使区别更加清楚。
Python3
#import required library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# specifing the subplot
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows = 4,
ncols = 4,
figsize = (10,10))
# Or equivalently,
# "plt.tight_layout()"
fig.tight_layout()
# subplot 1
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
x2 = [0.1, 10, -30]
y2 = [40, -10, 45]
# plotting the given graph
plt.semilogx(x2, y2,
color = "blue",
linewidth = 4)
# set the title
plt.title("USING LINE")
# set y axis label
plt.ylabel('-----------y-----------')
# set x axis label
plt.xlabel('-----------x-----------')
# plot with grid
plt.grid(True)
# subplot 2
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
x2 = [0.1, 10, -30]
y2 = [40, -10, 45]
# plotting the given graph
plt.semilogx(x2, y2,
'g^',
markersize = 20,
color = "black")
# set the title
plt.title("USING SYMBOL")
# set y axis label
plt.ylabel('-----------y-----------')
# set x axis label
plt.xlabel('-----------x-----------')
# plot with grid
plt.grid(True)
# subplot 3
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
x2 = [0.1, 10, -30]
y2 = [40, -10 ,45]
# plotting the given graph
plt.semilogx(x2, y2,
nonposx = "clip",
color = "red",
linewidth = 4)
# set the title
plt.title("CLIPPED")
# set y axis label
plt.ylabel('-----------y-----------')
# set x axis label
plt.xlabel('-----------x-----------')
# plot with grid
plt.grid(True)
# subplot 4
plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
x2 = [0.1, 10, -30]
y2 = [40, -10, 45]
# plotting the given graph
plt.semilogx(x2, y2,
nonposx = "mask",
color = "green",
linewidth = 4)
# set the title
plt.title("MASKED")
# set y axis label
plt.ylabel('-----------y-----------')
# set x axis label
plt.xlabel('-----------x-----------')
# plot with grid
plt.grid(True)
# show the plot
plt.show()输出:
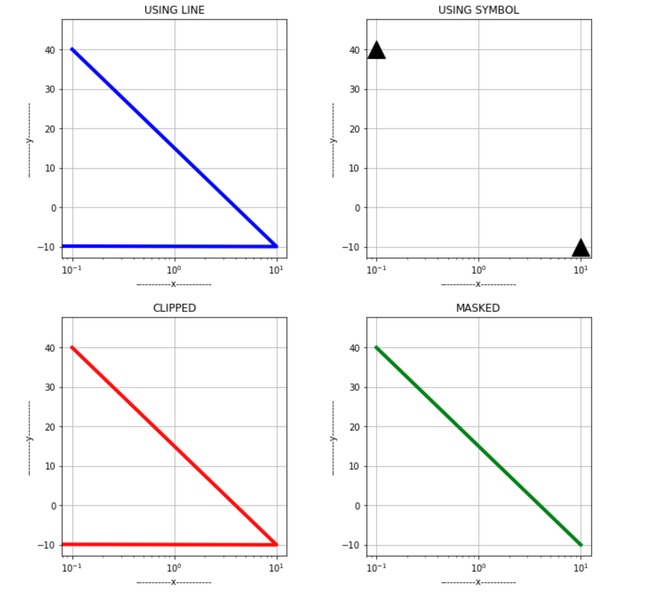
所有情节之间的差异。
示例6:使用nonposx参数。
遮罩会删除无效值,而剪裁会将其设置为非常低的可能值。
下图将更清楚地显示裁剪和遮罩之间的区别。
Python3
# import required library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows = 1,
ncols = 2,
figsize = (15,9))
# Or equivalently, "plt.tight_layout()"
fig.tight_layout()
# subplot 1
x1 = [-1, 2, 0,
-3, 5, 9,
10, -3, -8,
15, 12, 0.1,0.9]
y1 = [5, -2, 0,
10, 20, 30,
25, 28, 16,
25, 28, 3, 5]
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
# plotting the graph
plt.semilogx(x1, y1,
marker = ".",
markersize = 20,
nonposx = "clip",
color = "green" )
# set the y-axis label
plt.ylabel('---y---')
# set the x-axis label
plt.xlabel('---x---')
# set the title
plt.title('CLIP')
# plot with grid
plt.grid(True)
# subplot 2
x2 = [-1, 2, 0,
-3, 5, 9,
10, -3, -8,
15, 12, 0.1, 0.9]
y2 = [5, -2, 0,
10, 20, 30,
25, 28, 16,
25, 28, 3, 5]
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.semilogx(x2, y2,
nonposx = "mask",
color ="green",
linewidth = 4,
marker = ".",
markersize = 20)
# set the title
plt.title('MASK')
# set the y-axis label
plt.ylabel('---y---')
# set the x-axis label
plt.xlabel('---x---')
# plot with grid
plt.grid(True)
# show the plot
plt.show()输出:
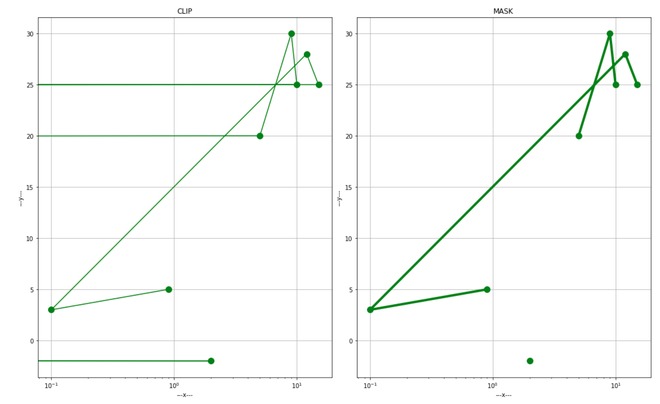
遮罩和夹子之间的区别
例7:更换底座。
可以根据方便设置底数,并且应该大于1才能满足对数性质。
Python3
# importing the required libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# function that will
# ouput the values
def function(t):
return np.exp(-t)*np.sin(2*np.pi.t)/2 + np.tan(t)
# define the x-axis values
t1 = np.arange(-0.01, 1.0, 0.08)
t2 = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.02)
# subplot 1
plt.figure(figsize = (10,10))
plt.subplot(211)
# plot the graph
plt.semilogx(t1, f(t1),
'bo', t2, f(t2),
'k', color = "blue",
basex = 3)
# set the title
plt.title("BASE:3")
# subplot 2
plt.subplot(212)
# plot the graph
plt.semilogx(t2, np.cos(2*np.pi*t2),
'r--', color = "brown",
linewidth = 2, basex = 4)
# set the title
plt.title("BASE:4")
# show the plot
plt.show()输出:
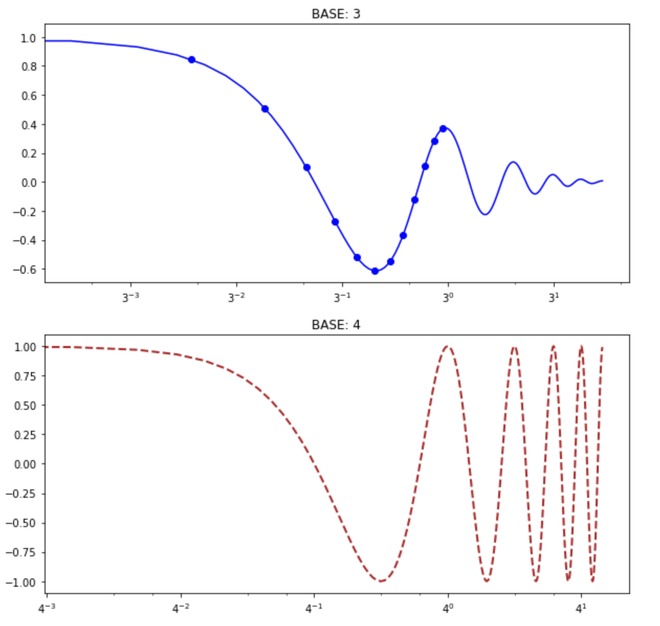
改变基础
示例8:使用subsx参数。
指定X轴上的次要Xticks。默认情况下,它取决于图中的几十年数。
Python3
# import required library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows = 2,
ncols = 2,
figsize = (10,7))
# Or equivalently, "plt.tight_layout()"
fig.tight_layout()
# subplot 1
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
x = [1, 11]
y = [4, 6]
# plot the graph
plt.semilogx(x, y, marker = ".",
markersize = 20,
color = "green")
# set the title
plt.title("Without subsx - line ")
# plot with grid
plt.grid(True)
# subplot 2
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
x = [1, 11]
y = [4, 6]
# plot the graph
plt.semilogx(x, y, subsx = [2, 3, 9, 10],
marker = ".", markersize = 20,
color = "green")
# set the title
plt.title("With subsx - line ")
plt.grid(True)
# subplot 3
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
x = [1, 11]
y = [4, 6]
plt.semilogx(x, y, 'g^', marker = ".",
markersize = 20,
color = "blue")
plt.title("Without subsx - symbol ")
plt.grid(True)
# subplot 4
plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
x = [1, 11]
y = [4, 6]
plt.semilogx(x, y, 'g^', subsx=[2, 3, 9, 10],
marker = ".", markersize = 20,
color = "blue")
plt.title("With subsx - symbol ")
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()输出:
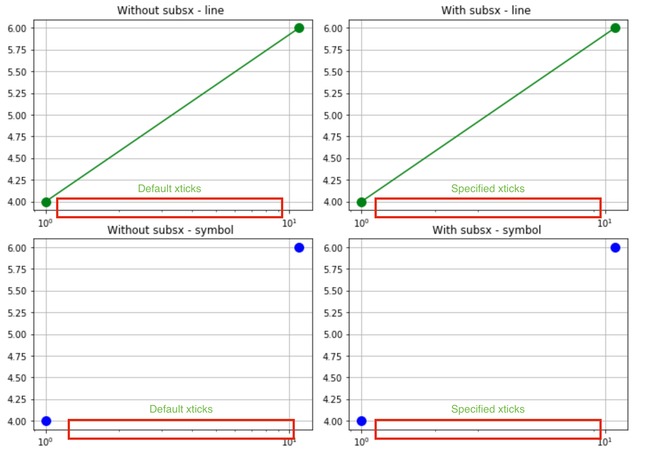
SUBSX参数
概要:
- X轴以对数方式绘制,并且可以通过定义basex属性来指定基数。基数应大于1
- 如果绘制线,则默认情况下会裁剪负值或零值。
- mask属性会删除负值/零值,而clip属性会将其设置为非常低的正值。
- 如果使用符号,则默认情况下会掩盖负数/零。
- 半对数遵循plot()和matplotlib.axes.Axes.set_xscale()的所有参数。
- s参数定义次要提要。
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自2001guljain大神的英文原创作品 Matplotlib.pyplot.semilogx() in Python。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
