Matplotlib是Python中的一个库,它是数字的-NumPy库的数学扩展。它是Python中令人惊叹的可视化库,用于数组的2D图,并用于与更广泛的SciPy堆栈配合使用。
matplotlib.axis.Axis.get_ticklabels()函数
matplotlib库的axis模块中的Axis.get_ticklabels()函数用于获取刻度标签作为Text实例列表。
用法: Axis.get_ticklabels(self, minor=False, which=None)
参数:此方法接受以下参数。
- minor:此参数包含布尔值。如果为True,则返回次要的ticklabel,否则返回主要的ticklabel。
- which:此参数选择要返回的刻度标签。
返回值:此方法返回“文本列表”实例。
以下示例说明了matplotlib.axis中的matplotlib.axis.Axis.get_ticklabels()函数:
范例1:
Python3
# Implementation of matplotlib function
from matplotlib.axis import Axis
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.patches import Polygon
def func(x):
return (x - 4) * (x - 6) * (x - 5) + 100
a, b = 2, 9 # integral limits
x = np.linspace(0, 10)
y = func(x)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, y, "k", linewidth = 2)
ax.set_ylim(bottom = 0)
# Make the shaded region
ix = np.linspace(a, b)
iy = func(ix)
verts = [(a, 0), *zip(ix, iy), (b, 0)]
poly = Polygon(verts, facecolor ='green',
edgecolor ='0.5', alpha = 0.4)
ax.add_patch(poly)
ax.text(0.5 * (a + b), 30,
r"$\int_a ^ b f(x)\mathrm{d}x$",
horizontalalignment ='center',
fontsize = 20)
fig.text(0.9, 0.05, '$x$')
fig.text(0.1, 0.9, '$y$')
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.set_xticks((a, b-a, b))
ax.set_xticklabels(('$a$', '$valx$', '$b$'))
fig.suptitle('Matplotlib.axis.Axis.get_ticklabels()\n\
Function Example', fontweight ="bold")
ax.grid()
print("Value of get_ticklabels():")
for i in ax.xaxis.get_ticklabels():
print(i)
plt.show()输出:
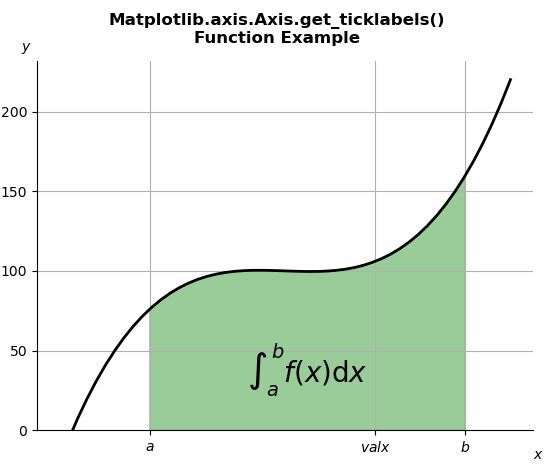
Value of get_ticklabels(): Text(0, 0, '$a$') Text(0, 0, '$valx$') Text(0, 0, '$b$')
范例2:
Python3
# Implementation of matplotlib function
from matplotlib.axis import Axis
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
y2 = y + 0.2 * np.random.normal(size = x.shape)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.plot(x, y2)
ax.set_xticks([0, np.pi, 2 * np.pi])
ax.set_xticklabels(['0', r'$\pi$', r'2$\pi$'])
ax.spines['left'].set_bounds(-1, 1)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
fig.suptitle('Matplotlib.axis.Axis.get_ticklabels()\n\
Function Example', fontweight ="bold")
ax.grid()
print("Value of get_ticklabels():")
for i in ax.xaxis.get_ticklabels():
print(i)
plt.show()输出:
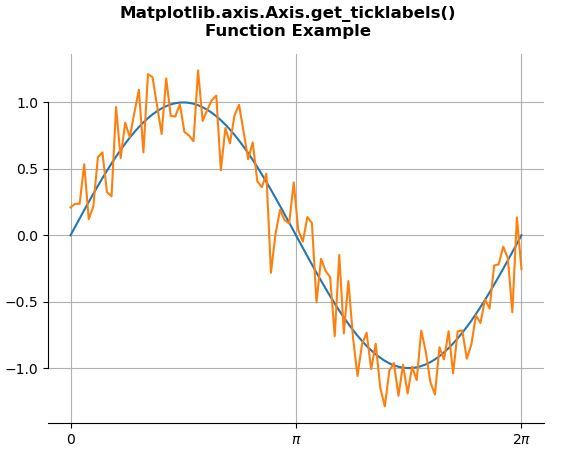
Value of get_ticklabels(): Text(0, 0, '0') Text(0, 0, '$\\pi$') Text(0, 0, '2$\\pi$')
相关用法
- Python Wand function()用法及代码示例
- Python map()用法及代码示例
- Python cmp()用法及代码示例
- Python oct()用法及代码示例
- Python ord()用法及代码示例
- Python str()用法及代码示例
- Python dir()用法及代码示例
- Python sum()用法及代码示例
- Python hex()用法及代码示例
- Python now()用法及代码示例
- Python tell()用法及代码示例
- Python int()用法及代码示例
- Python id()用法及代码示例
- Python cmath.sin()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自SHUBHAMSINGH10大神的英文原创作品 Matplotlib.axis.Axis.get_ticklabels() function in Python。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
