Matplotlib是Python中的一个库,它是数字的-NumPy库的数学扩展。轴类包含大多数图形元素:Axis,Tick,Line2D,Text,Polygon等,并设置坐标系。 Axes实例通过callbacks属性支持回调。
matplotlib.axes.Axes.psd()函数
matplotlib库的axiss模块中的Axes.psd()函数用于绘制功率谱密度。
用法: Axes.psd(self, x, NFFT=None, Fs=None, Fc=None, detrend=None, window=None, noverlap=None, pad_to=None, sides=None, scale_by_freq=None, return_line=None, *, data=None, **kwargs)
参数:此方法接受以下描述的参数:
- x:此参数是数据序列。
- Fs:此参数是标量。默认值为2。
- window:此参数将数据段作为参数,并返回该段的窗口版本。其默认值为window_hanning()
- sides:此参数指定要返回光谱的哪一侧。它可以具有以下值:“默认”,“单面”和“双面”。
- pad_to:此参数包含填充数据段的整数值。
- NFFT:此参数包含每个块中用于FFT的数据点数。
- detrend:此参数包含应用于fft-ing之前的每个细分的函数,旨在删除均值或线性趋势{“无”,“平均值”,“线性”}。
- scale_by_freq:该参数允许对返回的频率值进行积分。
- noverlap:此参数是块之间的重叠点数。
- Fc:此参数是x的中心频率。
- return_line:此参数包括在返回值中绘制的线对象。
返回值:这将返回以下内容:
- Pxx:这将返回缩放之前的功率谱P_ {xx}的值。
- freqs:这将返回Pxx中元素的频率。
- line:这将返回此函数创建的行。
结果是(Pxx, freqs, line)
以下示例说明了matplotlib.axes中的matplotlib.axes.Axes.csd()函数:
示例1:
# Implementation of matplotlib function
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
dt = 0.01
t = np.arange(0, 30, dt)
nse1 = np.random.randn(len(t))
s1 = 1.5 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * 10 * t) + nse1 + np.cos(np.pi * t)
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots()
ax1.psd(s1**2, 512, 1./dt, color ="green")
ax1.set_xlabel('Frequency')
ax1.set_ylabel('PSD(db)')
ax1.set_title('matplotlib.axes.Axes.psd() Example')
plt.show()输出:
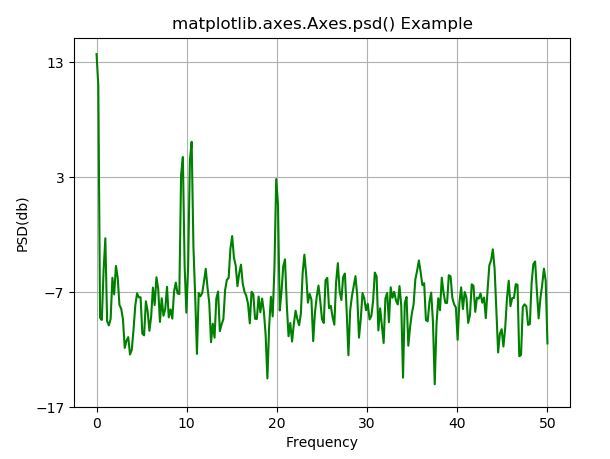
示例2:
# Implementation of matplotlib function
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
dt = 0.01
t = np.arange(0, 30, dt)
nse1 = np.random.randn(len(t))
r = np.exp(-t / 0.05)
cnse1 = np.convolve(nse1, r, mode ='same')*dt
s1 = np.cos(np.pi * t) + cnse1 + np.sin(2 * np.pi * 10 * t)
fig, [ax1, ax2] = plt.subplots(2, 1)
ax1.plot(t, s1)
ax1.set_xlim(0, 5)
ax1.set_ylabel('value s1')
ax1.grid(True)
ax2.psd(s1, 256, 1./dt)
ax2.set_ylabel('PSD(db)')
ax2.set_xlabel('Frequency')
ax1.set_title('matplotlib.axes.Axes.psd() Example')
plt.show()输出:
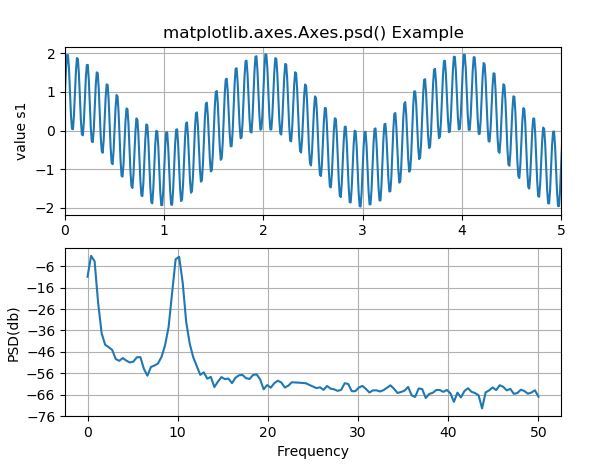
相关用法
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自SHUBHAMSINGH10大神的英文原创作品 Matplotlib.axes.Axes.psd() in Python。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
