JSON的完整形式是JavaScript Object Notation。这意味着将使用编程语言的文本组成的脚本(可执行)文件用于存储和传输数据。 Python通过名为内置的软件包支持JSONjson。要使用此函数,我们以Python脚本导入json包。 JSON中的文本是通过quoted-string完成的,其中包含键值映射中的值{ }。它类似于Python中的字典。
json.dump()
jsonPython模块中的模块提供了一种称为dump()它将Python对象转换为适当的json对象。它是dumps()方法。
dump()和dumps()之间的区别
| dump() | dumps() |
|---|---|
| 当必须将Python对象存储在文件中时,可以使用dump()方法。 | 当对象必须为字符串格式时,可以使用dumps()并将其用于解析,打印等。 |
| dump()需要json文件名,在其中必须将输出存储为参数。 | dumps()不需要传递任何此类文件名。 |
| 该方法写入内存,然后单独执行写入磁盘的命令 | 该方法直接写入json文件 |
| 更快的方法 | 慢2倍 |
dump()及其参数
用法: json.dump(d, skipkeys=False, ensure_ascii=True, check_circular=True, allow_nan=True, cls=None, indent=None, separators=None)
参数:
- indent:它提高了json文件的可读性。可以传递给此参数的可能值只是双引号(
""),任何整数值。简单的双引号使每个键值对都出现在换行符中。例:
import json # python object(dictionary) to be dumped dict1 ={ "emp1":{ "name":"Lisa", "designation":"programmer", "age":"34", "salary":"54000" }, "emp2":{ "name":"Elis", "designation":"Trainee", "age":"24", "salary":"40000" }, } # the json file where the output must be stored out_file = open("myfile.json", "w") json.dump(dict1, out_file, indent = 6) out_file.close()输出:
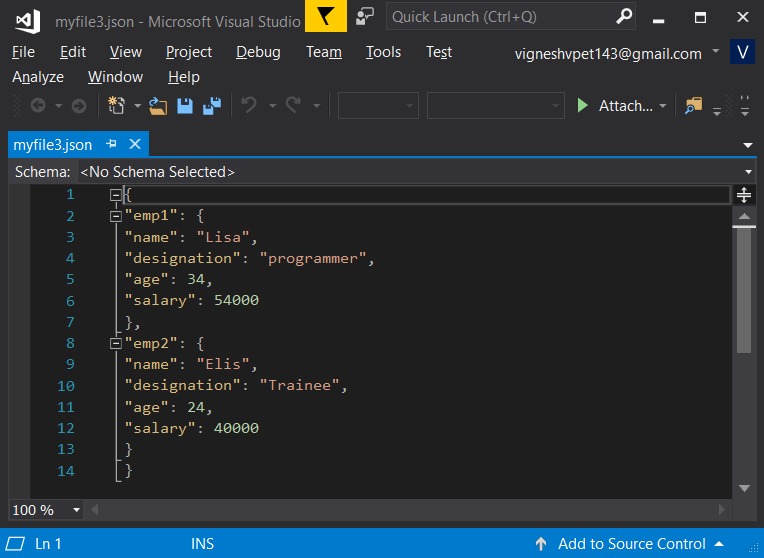
- skipkeys:如果 key 不是标准允许的类型,例如int,float,string,None或bool,则在转储它们时将产生错误。如果将此参数设置为true,则可以避免这种情况。
例:
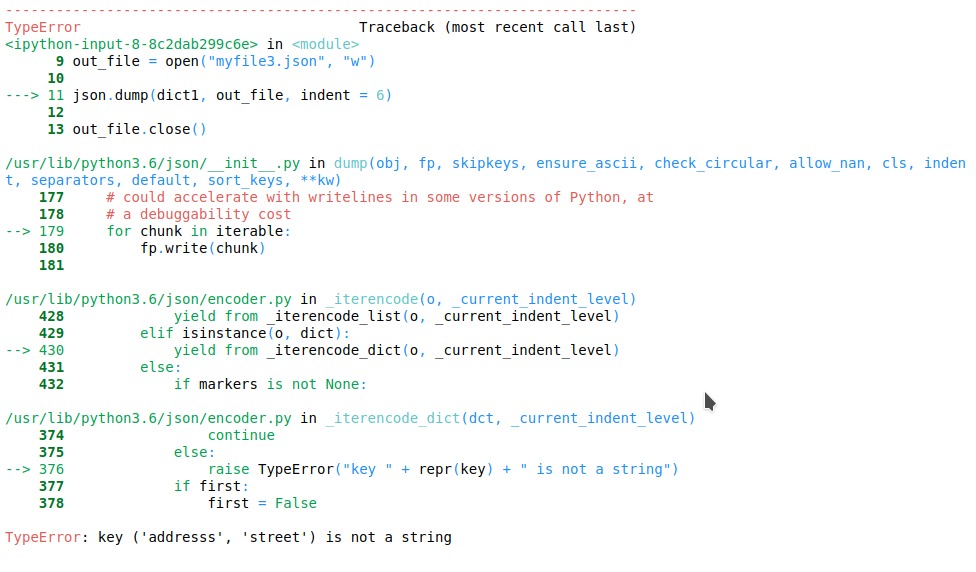
import json # python object(dictionary) to be dumped dict1 ={ ('addresss', 'street'):'Brigade road', } # the json file where the output must be stored out_file = open("myfile.json", "w") json.dump(dict1, out_file, indent = 6) out_file.close()输出:
如果skipkeys未设置为true,则将生成以下错误:
- separator:此参数占用一个或两个值。第一个值指定将一个键值对与另一个键值对分开的符号。下一个指定用于将值与其键分开的符号。
- sort_keys:此参数为布尔值。如果将其设置为True,则将按升序设置键,否则它们将显示为Python对象
- ensure_ascii:此参数也仅采用布尔值。如果未将其设置为true,则将非ASCII字符原样转储到输出文件中。默认情况下,该值为true。
请参阅下面的两个代码以获取区别。
范例1:
# dictionary to be dumped d ={'lang':'??? ????'} with open('myfile.json', 'w', encoding ='utf8') as json_file: json.dump(d, json_file, ensure_ascii = False)输出:
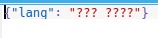
范例2:如果将其设置为True,则json文件的内容将为:
import json # dictionary to be dumped d ={'lang':'??? ????'} with open('myfile.json', 'w', encoding ='utf8') as json_file: json.dump(d, json_file, ensure_ascii = True)输出:

- allow_nan:它有助于序列化float值的范围。
范例1:
import json # dictionary to be dumped d ={ 'a':1, 'x':float('nan') } with open('myfile.json', 'w', encoding ='utf8') as json_file: json.dump(d, json_file, allow_nan=False)输出:

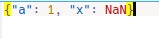
范例2:如果将其设置为True,则不会生成错误。 json文件中的内容将是:
import json # dictionary to be dumped d ={ 'a':1, 'x':float('nan') } with open('myfile.json', 'w', encoding ='utf8') as json_file: json.dump(d, json_file, allow_nan=True)输出:
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自 json.dump() in Python。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
