JSON的完整形式是JavaScript Object Notation。這意味著將使用編程語言的文本組成的腳本(可執行)文件用於存儲和傳輸數據。 Python通過名為內置的軟件包支持JSONjson。要使用此函數,我們以Python腳本導入json包。 JSON中的文本是通過quoted-string完成的,其中包含鍵值映射中的值{ }。它類似於Python中的字典。
json.dump()
jsonPython模塊中的模塊提供了一種稱為dump()它將Python對象轉換為適當的json對象。它是dumps()方法。
dump()和dumps()之間的區別
| dump() | dumps() |
|---|---|
| 當必須將Python對象存儲在文件中時,可以使用dump()方法。 | 當對象必須為字符串格式時,可以使用dumps()並將其用於解析,打印等。 |
| dump()需要json文件名,在其中必須將輸出存儲為參數。 | dumps()不需要傳遞任何此類文件名。 |
| 該方法寫入內存,然後單獨執行寫入磁盤的命令 | 該方法直接寫入json文件 |
| 更快的方法 | 慢2倍 |
dump()及其參數
用法: json.dump(d, skipkeys=False, ensure_ascii=True, check_circular=True, allow_nan=True, cls=None, indent=None, separators=None)
參數:
- indent:它提高了json文件的可讀性。可以傳遞給此參數的可能值隻是雙引號(
""),任何整數值。簡單的雙引號使每個鍵值對都出現在換行符中。例:
import json # python object(dictionary) to be dumped dict1 ={ "emp1":{ "name":"Lisa", "designation":"programmer", "age":"34", "salary":"54000" }, "emp2":{ "name":"Elis", "designation":"Trainee", "age":"24", "salary":"40000" }, } # the json file where the output must be stored out_file = open("myfile.json", "w") json.dump(dict1, out_file, indent = 6) out_file.close()輸出:
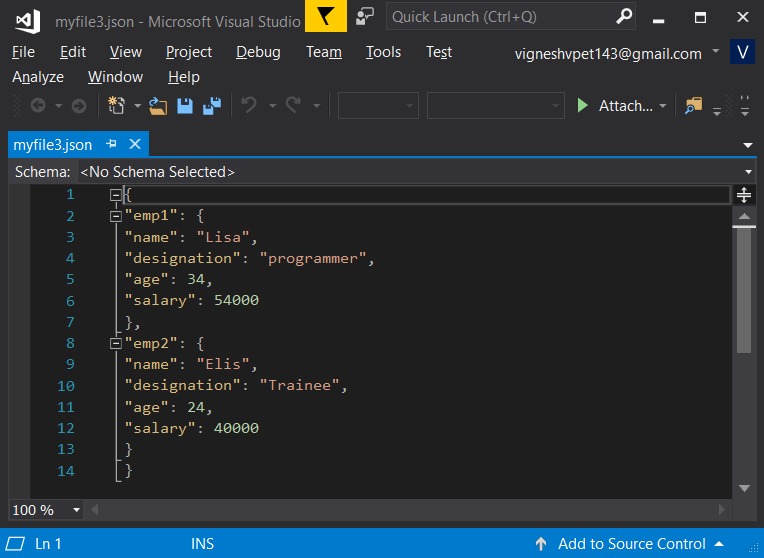
- skipkeys:如果 key 不是標準允許的類型,例如int,float,string,None或bool,則在轉儲它們時將產生錯誤。如果將此參數設置為true,則可以避免這種情況。
例:
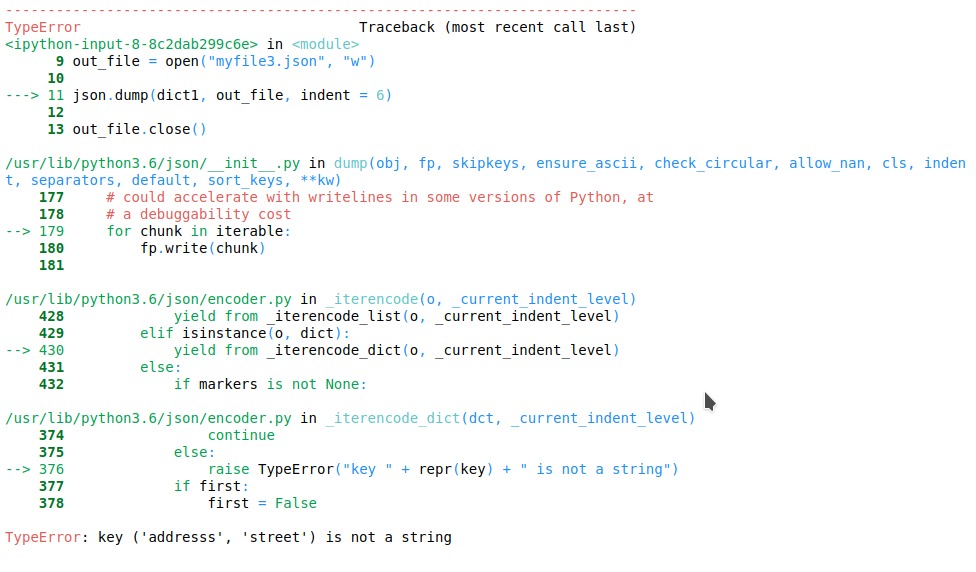
import json # python object(dictionary) to be dumped dict1 ={ ('addresss', 'street'):'Brigade road', } # the json file where the output must be stored out_file = open("myfile.json", "w") json.dump(dict1, out_file, indent = 6) out_file.close()輸出:
如果skipkeys未設置為true,則將生成以下錯誤:
- separator:此參數占用一個或兩個值。第一個值指定將一個鍵值對與另一個鍵值對分開的符號。下一個指定用於將值與其鍵分開的符號。
- sort_keys:此參數為布爾值。如果將其設置為True,則將按升序設置鍵,否則它們將顯示為Python對象
- ensure_ascii:此參數也僅采用布爾值。如果未將其設置為true,則將非ASCII字符原樣轉儲到輸出文件中。默認情況下,該值為true。
請參閱下麵的兩個代碼以獲取區別。
範例1:
# dictionary to be dumped d ={'lang':'??? ????'} with open('myfile.json', 'w', encoding ='utf8') as json_file: json.dump(d, json_file, ensure_ascii = False)輸出:
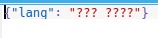
範例2:如果將其設置為True,則json文件的內容將為:
import json # dictionary to be dumped d ={'lang':'??? ????'} with open('myfile.json', 'w', encoding ='utf8') as json_file: json.dump(d, json_file, ensure_ascii = True)輸出:

- allow_nan:它有助於序列化float值的範圍。
範例1:
import json # dictionary to be dumped d ={ 'a':1, 'x':float('nan') } with open('myfile.json', 'w', encoding ='utf8') as json_file: json.dump(d, json_file, allow_nan=False)輸出:

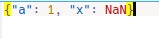
範例2:如果將其設置為True,則不會生成錯誤。 json文件中的內容將是:
import json # dictionary to be dumped d ={ 'a':1, 'x':float('nan') } with open('myfile.json', 'w', encoding ='utf8') as json_file: json.dump(d, json_file, allow_nan=True)輸出:
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自 json.dump() in Python。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
