C++ 中的sinh() 函数返回以弧度为单位的角度的双曲正弦值。
该函数在<cmath> 头文件中定义。
[Mathematics] sinh x = sinh(x) [In C++ Programming]
sinh() 原型 [从 C++ 11 标准开始]
double sinh(double x); float sinh(float x); long double sinh(long double x); double sinh(T x); // For integral type.
sinh() 函数接受一个以弧度表示的参数,并以 double , float 或 long double 类型返回该角度的双曲正弦值。
x 的双曲正弦由下式给出,
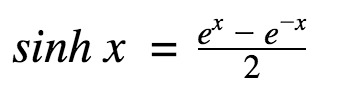
参数:
sinh() 函数采用一个强制参数,以弧度表示双曲角。
返回:
sinh() 函数返回参数的双曲正弦值。
如果结果的幅度太大而无法用返回类型的值表示,则函数返回带有正确符号的HUGE_VAL,并发生溢出范围错误。
示例 1:sinh() 函数如何工作?
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double x = 3.55, result;
result = sinh(x);
cout << "sinh(x) = " << result << endl;
// x in Degrees
double xDegrees = 90;
x = xDegrees * 3.14159/180;
result = sinh(x);
cout << "sinh(x) = " << result << endl;
return 0;
}
运行程序时,输出将是:
sinh(x) = 17.3923 sinh(x) = 2.3013
示例 2:sinh() 具有整数类型的函数
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = -3;
double result;
result = sinh(x);
cout << "sinh(x) = " << result << endl;
return 0;
}
运行程序时,输出将是:
sinh(x) = -10.0179
相关用法
- C++ sinh()用法及代码示例
- C++ complex sinh()用法及代码示例
- C++ sin()用法及代码示例
- C++ signbit()用法及代码示例
- C++ signal()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::max()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::push_back()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::less_equal用法及代码示例
- C++ set rbegin()用法及代码示例
- C++ string::length()用法及代码示例
- C++ set upper_bound()用法及代码示例
- C++ set crbegin用法及代码示例
- C++ std::is_member_object_pointer模板用法及代码示例
- C++ std::copy_n()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::string::insert()用法及代码示例
- C++ std::is_sorted_until用法及代码示例
- C++ std::iota用法及代码示例
- C++ set size用法及代码示例
- C++ std::numeric_limits::digits用法及代码示例
- C++ sscanf()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自 C++ sinh()。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
