集合接口是一个成员Java集合框架。它是一部分java.util包。它是集合层次结构的根接口之一。 Collection 接口不直接由任何类实现。但是,它是通过其子类型或子接口间接实现的,例如List Interface,Queue, 和放。
例如, HashSet类实现 Set 接口,它是 Collection 接口的子接口。如果集合实现没有实现特定操作,则应该定义相应的方法来抛出UnsupportedOperationException.
集合的层次结构
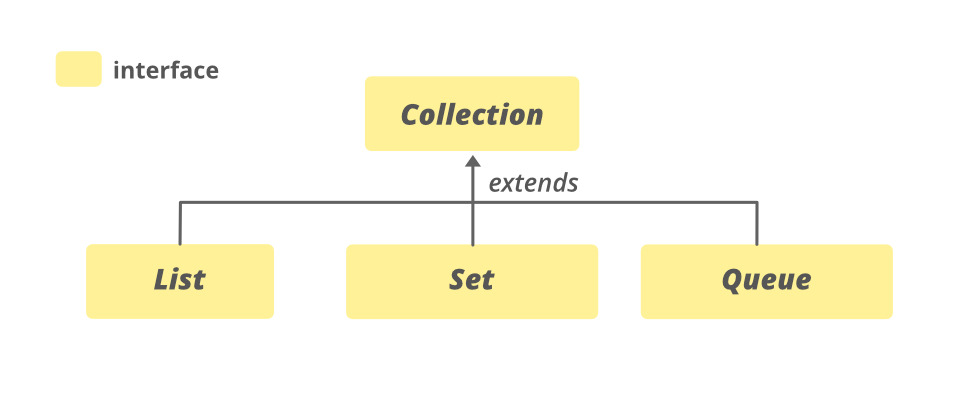
它实现了可迭代<E>接口。集合的 sub-interfaces 是BeanContext,BeanContextServices,阻塞双端队列<E>,BlockingQueue,双端队列<E>,EventSet,List Interface,导航集<E>,Queue,设置<E>,SortedSet Interface,传输队列<E>.
采集接口SubInterfaces
集合框架的所有类都实现集合接口的子接口。 Collection接口的所有方法也包含在它的子接口中。这些子接口有时称为集合类型或集合的SubTypes。其中包括以下内容:
List:这是集合接口的子接口。该接口专用于列表类型的数据,我们可以在其中存储所有对象的有序集合。这也允许其中存在重复数据。该列表接口由各种类实现,例如ArrayList,Vector,Stack等等。由于所有子类都实现了列表,因此我们可以使用这些类中的任何一个来实例化列表对象。例如,
List <T> al = new ArrayList<> ();
List <T> ll = new LinkedList<> ();
List <T> v = new Vector<> ();
Where T is the type of the object
放:集合是对象的无序集合,其中不能存储重复值。当我们希望避免对象的重复并希望仅存储唯一的对象时,可以使用此集合。这个集合接口由各种类实现,例如HashSet,TreeSet,LinkedHashSet等等。由于所有子类都实现了集合,因此我们可以使用这些类中的任何一个来实例化集合对象。例如,
Set<T> hs = new HashSet<> ();
Set<T> lhs = new LinkedHashSet<> ();
Set<T> ts = new TreeSet<> ();
Where T is the type of the object.
SortedSet:这个接口和设置接口很相似。唯一的区别是这个接口有额外的方法来维护元素的顺序。 Sorted Set接口扩展了Set接口,用于处理需要排序的数据。实现该接口的类是TreeSet。由于此类实现了 SortedSet,因此我们可以使用此类实例化 SortedSet 对象。例如,
SortedSet<T> ts = new TreeSet<> ();
Where T is the type of the object.
队列:顾名思义,队列接口维护 FIFO(先进先出)顺序,类似于 real-world 队列。该接口专用于存储元素顺序重要的所有元素。例如,每当我们尝试预订机票时,门票都是按照先到先得的原则出售的。因此,请求最先到达队列的人将获得票证。有各种各样的课程,例如PriorityQueue,双端队列,ArrayDeque等等。由于所有这些子类都实现了队列,因此我们可以使用这些类中的任何一个来实例化队列对象。例如,
Queue <T> pq = new PriorityQueue<> ();
Queue <T> ad = new ArrayDeque<> ();
Where T is the type of the object.
双端队列: 这是一个非常微小的变化队列数据结构.双端队列也称为双端队列,是一种可以在队列两端添加和删除元素的数据结构。该接口扩展了队列接口。实现该接口的类是ArrayDeque。由于该类实现了双端队列,因此我们可以用该类实例化一个双端队列对象。例如,
Deque<T> ad = new ArrayDeque<> ();
Where T is the type of the object.
声明:
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E>
这里,E是集合中存储的元素的类型。
例子:
Java
// Java program to illustrate Collection interface
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class CollectionDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// creating an empty LinkedList
Collection<String> list = new LinkedList<String>();
// use add() method to add elements in the list
list.add("Geeks");
list.add("for");
list.add("Geeks");
// Output the present list
System.out.println("The list is: " + list);
// Adding new elements to the end
list.add("Last");
list.add("Element");
// printing the new list
System.out.println("The new List is: " + list);
}
}The list is: [Geeks, for, Geeks] The new List is: [Geeks, for, Geeks, Last, Element]
实现类
Collection接口的实现是AbstractCollection,AbstractList,AbstractQueue,AbstractSequentialList,AbstractSet Class,ArrayBlockingQueue,ArrayDeque,ArrayList,AttributeList,BeanContextServicesSupport,BeanContextSupport, ConcurrentHashMap.KeySetView,ConcurrentLinkedDeque,ConcurrentLinkedQueue,ConcurrentSkipListSet,CopyOnWriteArrayList,CopyOnWriteArraySet,DelayQueue Class,EnumSet,HashSet,JobStateReasons,LinkedBlockingDeque,LinkedBlockingQueue,LinkedHashSet,LinkedList,LinkedTransferQueue,PriorityBlockingQueue,PriorityQueue,RoleList,RoleUnresolvedList,堆,SynchronousQueue,TreeSet,Vector.
用法:
Collection<E> objectName = new ArrayList<E>();
这里,E是集合中存储的元素的类型。
注意:在上面的语法中,如果任何类实现了 Collection 接口,我们可以用 ArrayList 替换该类。
Basic Operations
1. 添加元素
Collection提供的add(E e)和addAll(Collection c)方法可用于添加元素。
Java
// Java code to illustrate adding
// elements to the Collection
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class AddingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create an empty array list with an initial
// capacity
Collection<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<Integer>(5);
// use add() method to add elements in the list
list1.add(15);
list1.add(20);
list1.add(25);
// prints all the elements available in list
for (Integer number : list1) {
System.out.println("Number = " + number);
}
// Creating an empty ArrayList
Collection<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// Appending the collection to the list
list2.addAll(list1);
// displaying the modified ArrayList
System.out.println("The new ArrayList is: " + list2);
}
}Number = 15 Number = 20 Number = 25 The new ArrayList is: [15, 20, 25]
2. 删除元素
remove(E e) 和removeAll(Collection c) 方法可用于从集合中删除特定元素或元素集合。
Java
// Java program to demonstrate removing
// elements from a Collection
import java.util.*;
public class RemoveElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception
{
// Creating object of HashSet<Integer>
Collection<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<Integer>();
// Populating arrset1
set1.add(1);
set1.add(2);
set1.add(3);
set1.add(4);
set1.add(5);
// print set1
System.out.println("Initial set1 : " + set1);
// remove a particular element
set1.remove(4);
// print modified set1
System.out.println("set1 after removing 4 : " + set1);
// Creating another object of HashSet<Integer>
Collection<Integer> set2 = new HashSet<Integer>();
set2.add(1);
set2.add(2);
set2.add(3);
// print set2
System.out.println("Collection Elements to be removed : " + set2);
// Removing elements from set1
// specified in set2
// using removeAll() method
set1.removeAll(set2);
// print arrset1
System.out.println("set 1 after removeAll() operation : " + set1);
}
}Initial set1 : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] set1 after removing 4 : [1, 2, 3, 5] Collection Elements to be removed : [1, 2, 3] set 1 after removeAll() operation : [5]
3. 迭代
要迭代 Collection 的元素,我们可以使用 iterator() 方法。
Java
// Java code to illustrate iterating
// over a Collection
import java.util.*;
public class IteratingExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create and populate the list
Collection<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add("Geeks");
list.add("for");
list.add("Geeks");
list.add("is");
list.add("a");
list.add("CS");
list.add("Students");
list.add("Portal");
// Displaying the list
System.out.println("The list is: " + list);
// Create an iterator for the list
// using iterator() method
Iterator<String> iter = list.iterator();
// Displaying the values after iterating
// through the list
System.out.println("\nThe iterator values" + " of list are: ");
while (iter.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iter.next() + " ");
}
}
}The list is: [Geeks, for, Geeks, is, a, CS, Students, Portal] The iterator values of list are: Geeks for Geeks is a CS Students Portal
Methods of Collection
|
METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Collection add() | 确保此集合包含指定的元素(可选操作)。 |
| addAll(集合 <? 扩展 E> c) | 将指定集合中的所有元素添加到此集合中(可选操作)。 |
| Collection clear() | 从此集合中删除所有元素(可选操作)。 |
| Collection contains() | 如果此集合包含指定元素,则返回 true。 |
| containsAll(集合<?> c) | 如果此集合包含指定集合中的所有元素,则返回 true。 |
| equals(Object o) | 比较指定对象与此集合是否相等。 |
| hashCode() | 返回此集合的哈希码值。 |
| isEmpty() | 如果此集合不包含任何元素,则返回 true。 |
| iterator() | 返回此集合中元素的迭代器。 |
| parallelStream() | 返回一个可能并行的 Stream 并以此集合作为其源。 |
| remove(Object o) | 从此集合中删除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)(可选操作)。 |
| 移除全部(集合<?> c) | 删除指定集合中也包含的所有该集合的元素(可选操作)。 |
| removeIf(Predicate<? super E> 过滤器) | 删除此集合中满足给定谓词的所有元素。 |
| keepAll(集合<?> c) | 仅保留此集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。 |
| size() | 返回此集合中的元素数量。 |
| spliterator() | 在此集合中的元素上创建一个 Spliterator。 |
| stream() | 返回以此集合作为源的顺序 Stream。 |
| toArray() | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组。 |
| toArray(IntFunction<T[]> 生成器) | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组,使用提供的生成器函数分配返回的数组。 |
| toArray(T[] a) | 返回一个包含该集合中所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型是指定数组的运行时类型。 |
接口 java.lang.Iterable 中声明的方法
|
METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Iterable forEach() | 对 Iterable 的每个元素执行给定的操作,直到处理完所有元素或该操作引发异常。 |
参考:https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/docs/api/java.base/java/util/Collection.html
相关用法
- Java Collection containsAll()用法及代码示例
- Java Collection equals()用法及代码示例
- Java Collection hashCode()用法及代码示例
- Java Collection iterator()用法及代码示例
- Java Collection remove()用法及代码示例
- Java Collection removeAll()用法及代码示例
- Java Collection removeIf()用法及代码示例
- Java Collection retainAll()用法及代码示例
- Java Collection size()用法及代码示例
- Java Collection spliterator()用法及代码示例
- Java Collection toArray()用法及代码示例
- Java Collection add()用法及代码示例
- Java Collection addAll()用法及代码示例
- Java Collection clear()用法及代码示例
- Java Collection contains()用法及代码示例
- Java Collection isEmpty()用法及代码示例
- Java Collections binarySearch()用法及代码示例
- Java Collections checkedNavigableMap()用法及代码示例
- Java Collections checkedNavigableSet()用法及代码示例
- Java Collections checkedQueue()用法及代码示例
- Java Collections disjoint()用法及代码示例
- Java Collections emptyEnumeration()用法及代码示例
- Java Collections emptyIterator()用法及代码示例
- Java Collections emptyList()用法及代码示例
- Java Collections emptyListIterator()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Ganeshchowdharysadanala大神的英文原创作品 Collection Interface in Java with Examples。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
