Java中的List接口提供了一种存储有序集合的方法。它是一个子接口集合。它是一个有序的对象集合,其中可以存储重复的值。由于 List 保留插入顺序,因此它允许位置访问和插入元素。
表中的内容
Java中的列表接口
List接口位于java.util包中,并继承了Collection接口。它是ListIterator接口的工厂。通过ListIterator,我们可以向前和向后迭代列表。 List接口的实现类有ArrayList、LinkedList、Stack和Vector。 ArrayList 和 LinkedList 在 Java 编程中广泛使用。 Vector 类自 Java 5 起已被弃用。
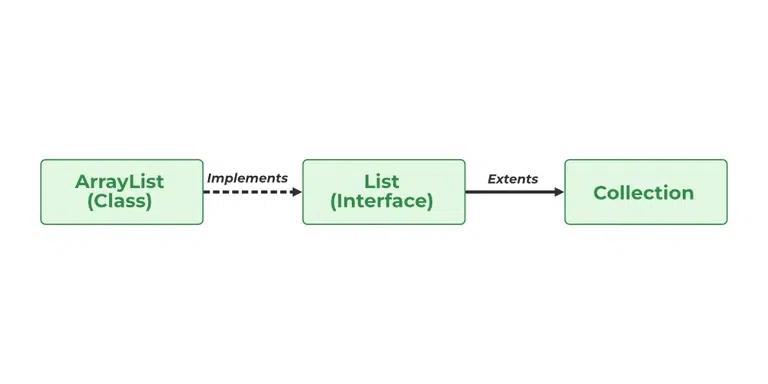
Java 集合框架中的列表和ArrayList
Java列表接口声明
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> ;
让我们详细说明在 List 类中创建对象或实例。自从List是一个接口,不能创建列表类型的对象。我们总是需要一个类来实现这个List为了创建一个对象。而且,推出后泛型在Java 1.5中,可以限制List中可以存储的对象类型。就像用户自定义‘classes’实现的其他几个用户自定义‘interfaces’一样,List是‘interface’,由ArrayList类,预定义在java.util包。
Java列表的语法
这种类型的安全列表可以定义为:
List<Obj> list = new ArrayList<Obj> ();
Note: Obj is the type of the object to be stored in List
Java 列表示例
Java
// Java program to Demonstrate List Interface
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// ListDemo class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object of List interface
// implemented by the ArrayList class
List<Integer> l1 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// Adding elements to object of List interface
// Custom inputs
l1.add(0, 1);
l1.add(1, 2);
// Print the elements inside the object
System.out.println(l1);
// Now creating another object of the List
// interface implemented ArrayList class
// Declaring object of integer type
List<Integer> l2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// Again adding elements to object of List interface
// Custom inputs
l2.add(1);
l2.add(2);
l2.add(3);
// Will add list l2 from 1 index
l1.addAll(1, l2);
System.out.println(l1);
// Removes element from index 1
l1.remove(1);
// Printing the updated List 1
System.out.println(l1);
// Prints element at index 3 in list 1
// using get() method
System.out.println(l1.get(3));
// Replace 0th element with 5
// in List 1
l1.set(0, 5);
// Again printing the updated List 1
System.out.println(l1);
}
}[1, 2] [1, 1, 2, 3, 2] [1, 2, 3, 2] 2 [5, 2, 3, 2]
现在让我们使用列表接口执行各种操作,以更好地理解它。我们将讨论下面列出的以下操作,稍后将通过干净的 Java 代码实现它们。
Java 列表接口中的操作
由于 List 是一个接口,因此它只能与实现该接口的类一起使用。现在,我们来看看如何对 List 进行一些常用的操作。
- 操作1:使用 add() 方法向 List 类添加元素
- 操作2:使用set()方法更新List类中的元素
- 操作3:使用 indexOf()、lastIndexOf 方法搜索元素
- 操作4:使用remove()方法删除元素
- 操作5:使用get()方法访问List类中的元素
- 操作6:使用 contains() 方法检查 List 类中是否存在元素
现在让我们单独讨论这些操作,并在代码中实现相同的操作,以便更好地掌握它。
1.使用以下方法将元素添加到 List 类add()方法
为了将元素添加到列表中,我们可以使用 List add()List get()方法。该方法被重载以根据不同的参数执行多个操作。
参数:它需要2个参数,即:
- add(Object):该方法用于在List的末尾添加一个元素。
- add(int index, Object):该方法用于在List中的特定索引处添加元素
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Add Elements to a List
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an object of List interface,
// implemented by ArrayList class
List<String> al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to object of List interface
// Custom elements
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
al.add(1, "For");
// Print all the elements inside the
// List interface object
System.out.println(al);
}
}[Geeks, For, Geeks]
2. 更新元素
添加元素后,如果我们想更改元素,可以使用 AbstractList set() 方法。由于 List 是有索引的,因此我们希望更改的元素是通过元素的索引来引用的。因此,该方法需要一个索引和需要在该索引处插入的更新元素。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Update Elements in a List
// Importing utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an object of List interface
List<String> al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to object of List class
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
al.add(1, "Geeks");
// Display theinitial elements in List
System.out.println("Initial ArrayList " + al);
// Setting (updating) element at 1st index
// using set() method
al.set(1, "For");
// Print and display the updated List
System.out.println("Updated ArrayList " + al);
}
}Initial ArrayList [Geeks, Geeks, Geeks] Updated ArrayList [Geeks, For, Geeks]
3.搜索元素
在List接口中搜索元素是Java编程中的常见操作。 List 接口提供了多种搜索元素的方法,例如List indexOf(), List lastIndexOf()方法。
indexOf() 方法返回列表中指定元素第一次出现的索引,而 lastIndexOf() 方法返回指定元素最后一次出现的索引。
参数:
- indexOf(element): 返回列表中指定元素第一次出现的索引,如果未找到该元素则返回 -1
- lastIndexOf(element): 返回列表中指定元素最后一次出现的索引,如果未找到该元素则返回 -1
例子:
Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ListExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create a list of integers
List<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<>();
// add some integers to the list
numbers.add(1);
numbers.add(2);
numbers.add(3);
numbers.add(2);
// use indexOf() to find the first occurrence of an
// element in the list
int index = numbers.indexOf(2);
System.out.println(
"The first occurrence of 2 is at index "
+ index);
// use lastIndexOf() to find the last occurrence of
// an element in the list
int lastIndex = numbers.lastIndexOf(2);
System.out.println(
"The last occurrence of 2 is at index "
+ lastIndex);
}
}The first occurrence of 2 is at index 1 The last occurrence of 2 is at index 3
4. 删除元素
为了从列表中删除一个元素,我们可以使用 List remove(Object obj)方法。该方法被重载以根据不同的参数执行多个操作。他们是:
参数:
- remove(Object):此方法用于简单地从列表中删除对象。如果存在多个此类对象,则删除第一个出现的对象。
- remove(int index):由于列表已建立索引,因此此方法采用一个整数值,该整数值仅删除列表中特定索引处存在的元素。删除元素后,所有元素都会向左移动以填充空间,并更新对象的索引。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Remove Elements from a List
// Importing List and ArrayList classes
// from java.util package
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating List class object
List<String> al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to the object
// Custom inputs
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
// Adding For at 1st indexes
al.add(1, "For");
// Print the initialArrayList
System.out.println("Initial ArrayList " + al);
// Now remove element from the above list
// present at 1st index
al.remove(1);
// Print the List after removal of element
System.out.println("After the Index Removal " + al);
// Now remove the current object from the updated
// List
al.remove("Geeks");
// Finally print the updated List now
System.out.println("After the Object Removal "
+ al);
}
}Initial ArrayList [Geeks, For, Geeks] After the Index Removal [Geeks, Geeks] After the Object Removal [Geeks]
5. 访问元素
为了访问列表中的元素,我们可以使用List get()方法,返回指定索引处的元素
参数:
get(int index):此方法返回列表中指定索引处的元素。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Access Elements of a List
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an object of List interface,
// implemented by ArrayList class
List<String> al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to object of List interface
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("For");
al.add("Geeks");
// Accessing elements using get() method
String first = al.get(0);
String second = al.get(1);
String third = al.get(2);
// Printing all the elements inside the
// List interface object
System.out.println(first);
System.out.println(second);
System.out.println(third);
System.out.println(al);
}
}Geeks For Geeks [Geeks, For, Geeks]
6. 检查列表中是否存在元素
为了检查列表中是否存在某个元素,我们可以使用List contains() 方法。如果指定的元素存在于列表中,则此方法返回 true,否则返回 false。
参数:
contains(Object):此方法采用单个参数,即要检查的对象是否存在于列表中。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Check if an Element is Present in a List
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an object of List interface,
// implemented by ArrayList class
List<String> al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to object of List interface
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("For");
al.add("Geeks");
// Checking if element is present using contains()
// method
boolean isPresent = al.contains("Geeks");
// Printing the result
System.out.println("Is Geeks present in the list? "
+ isPresent);
}
}Is Geeks present in the list? true
Java中List接口的复杂性
|
操作 |
时间复杂度 |
空间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|
|
列表接口添加元素 |
O(1) |
O(1) |
|
从列表接口中删除元素 |
O(N) |
O(N) |
|
替换列表接口中的元素 |
O(N) |
O(N) |
|
遍历列表接口 |
O(N) |
O(N) |
Java 中列表接口的迭代
到目前为止,我们的输入大小非常小,并且我们正在为每个实体手动执行操作。现在让我们讨论迭代列表以使它们适用于更大的样本集的各种方法。
方法:有多种方法可以迭代列表。最著名的方法是使用基本的for循环结合一个List get()获取特定索引处的元素循环高级.
例子:
Java
// Java program to Iterate the Elements
// in an ArrayList
// Importing java utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an empty Arraylist of string type
List<String> al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to above object of ArrayList
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
// Adding element at specified position
// inside list object
al.add(1, "For");
// Using for loop for iteration
for (int i = 0; i < al.size(); i++) {
// Using get() method to
// access particular element
System.out.print(al.get(i) + " ");
}
// New line for better readability
System.out.println();
// Using for-each loop for iteration
for (String str : al)
// Printing all the elements
// which was inside object
System.out.print(str + " ");
}
}Geeks For Geeks Geeks For Geeks
列表接口的方法
由于不同类型列表背后的主要概念是相同的,因此列表接口包含以下方法:
|
方法 |
说明 |
|---|---|
| List add(int index, E element) | 此方法与 Java 列表接口一起使用,以在列表中的特定索引处添加元素。当传递单个参数时,它只是将元素添加到列表末尾。 |
| List addAll() | 此方法与 Java 中的列表接口一起使用,将给定集合中的所有元素添加到列表中。当传递单个参数时,它会将给定集合的所有元素添加到列表末尾。 |
| List size() | 此方法与 Java 列表接口一起使用以返回列表的大小。 |
| List clear() | 该方法用于删除列表中的所有元素。但是,所创建的列表的引用仍然被存储。 |
| List remove(int index) | 此方法从指定索引中删除一个元素。它将后续元素(如果有)向左移动,并将其索引减 1。 |
| List remove(Object obj) | 此方法与 Java 列表接口一起使用,以删除列表中第一次出现的给定元素。 |
| List get() | 此方法返回指定索引处的元素。 |
| ArrayList set() | 此方法用新元素替换给定索引处的元素。该函数返回刚刚被新元素替换的元素。 |
| List indexOf() | 此方法返回给定元素的第一次出现或-1如果该元素不存在于列表中。 |
| List lastIndexOf() | 此方法返回给定元素的最后一次出现或-1如果该元素不存在于列表中。 |
| List equals() | 此方法与 Java 列表接口一起使用,以比较给定元素与列表元素的相等性。 |
| List hashCode() | 该方法与 Java 中的 List Interface 一起使用,返回给定列表的 hashcode 值。 |
| List isEmpty() | 此方法与 Java 列表接口一起使用来检查列表是否为空。如果列表为空,则返回 true,否则返回 false。 |
| List contains() | 此方法与 Java 中的列表接口一起使用,以检查列表是否包含给定元素。如果列表包含该元素,则返回 true。 |
| List containsAll() | 此方法与 Java 列表接口一起使用来检查列表是否包含所有元素的集合。 |
| sort(Comparator comp) | 该方法与 Java 中的 List Interface 一起使用,根据给定的值对列表的元素进行排序Comparator Interface. |
Java 列表与集合
List接口和Set接口都继承了Collection接口。然而,它们之间存在一些差异。
|
List |
放 |
|---|---|
| List 是一个有序序列。 | Set 是一个无序序列。 |
| 列表允许重复元素 | Set 不允许有重复的元素。 |
| 可以按元素的位置来访问元素。 | 不允许对元素进行位置访问。 |
| 可以存储多个空元素。 | null 元素只能存储一次。 |
| 列表的实现有ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector、Stack | Set的实现有HashSet、LinkedHashSet。 |
类与 Java 列表接口的关联
现在让我们讨论实现 List 接口的类,首先请参考下面的图示以更好地理解 List 接口。如下:
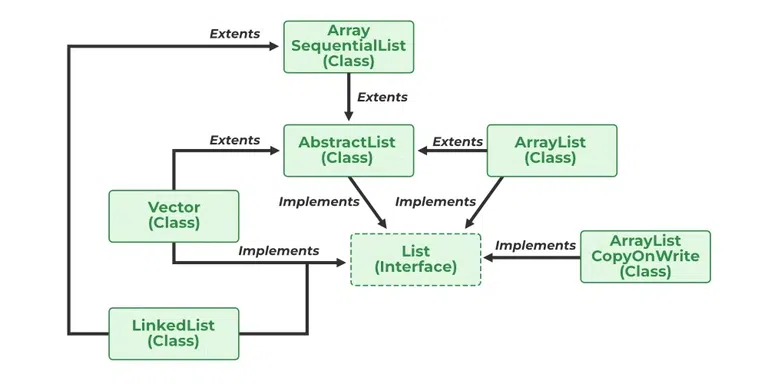
AbstractList,CopyOnWriteArrayList, 和AbstractSequentialList是实现 List 接口的类。在每个提到的类中都实现了单独的函数。它们如下:
- 摘要列表:该类用于实现一个不可修改的列表,只需扩展AbstractList类并仅实现get()和size()方法。
- 写入数组列表时复制:该类实现了列表接口。它是一个增强版本ArrayList其中所有修改(添加、设置、删除等)都是通过制作列表的新副本来实现的。
- 抽象顺序列表:这个类实现了采集接口和AbstractCollection 类。该类用于实现一个不可修改的列表,只需扩展AbstractList类并仅实现get()和size()方法。
我们将按照这种方式进行。
- ArrayList
- Vector
- Stack
- LinkedList
让我们按顺序讨论它们并实现相同的方法,以了解使用 List 接口的类的工作原理。
1.ArrayList
ArrayList集合框架中实现的类为我们提供了Java中的动态数组。虽然它可能比标准数组慢,但对于需要对数组进行大量操作的程序很有帮助。让我们看看如何使用此类创建列表对象。
例子:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the
// creation of list object using the
// ArrayList class
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Size of ArrayList
int n = 5;
// Declaring the List with initial size n
List<Integer> arrli = new ArrayList<Integer>(n);
// Appending the new elements
// at the end of the list
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
arrli.add(i);
// Printing elements
System.out.println(arrli);
// Remove element at index 3
arrli.remove(3);
// Displaying the list after deletion
System.out.println(arrli);
// Printing elements one by one
for (int i = 0; i < arrli.size(); i++)
System.out.print(arrli.get(i) + " ");
}
}[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] [1, 2, 3, 5] 1 2 3 5
2.矢量
Vector是在集合框架中实现的类,实现了可增长的对象数组。 Vector 实现了动态数组,这意味着它可以根据需要增长或缩小。与数组一样,它包含可以使用整数索引访问的组件。向量本质上属于遗留类,但现在它与集合完全兼容。让我们看看如何使用此类创建列表对象。
例子:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the
// creation of list object using the
// Vector class
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Size of the vector
int n = 5;
// Declaring the List with initial size n
List<Integer> v = new Vector<Integer>(n);
// Appending the new elements
// at the end of the list
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
v.add(i);
// Printing elements
System.out.println(v);
// Remove element at index 3
v.remove(3);
// Displaying the list after deletion
System.out.println(v);
// Printing elements one by one
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
System.out.print(v.get(i) + " ");
}
}[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] [1, 2, 3, 5] 1 2 3 5
3. 堆栈
Stack是一个在集合框架中实现的类,它扩展了向量类模型并实现了栈数据结构。该类基于后进先出的基本原则。除了基本的入栈和出栈操作外,该类还提供了清空、搜索和查看三个函数。让我们看看如何使用此类创建列表对象。
例子:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the
// creation of list object using the
// Stack class
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Size of the stack
int n = 5;
// Declaring the List
List<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>();
// Appending the new elements
// at the end of the list
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
s.add(i);
// Printing elements
System.out.println(s);
// Remove element at index 3
s.remove(3);
// Displaying the list after deletion
System.out.println(s);
// Printing elements one by one
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
System.out.print(s.get(i) + " ");
}
}[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] [1, 2, 3, 5] 1 2 3 5
4.LinkedList
LinkedList 是一个在集合框架中实现的类,它本质上实现了链表数据结构。它是一种线性数据结构,其中元素不存储在连续位置,并且每个元素都是具有数据部分和地址部分的单独对象。这些元素使用指针和地址链接。每个元素称为一个节点。由于插入和删除的动态性和简便性,它们比数组更受青睐。让我们看看如何使用此类创建列表对象。
例子:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the
// creation of list object using the
// LinkedList class
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Size of the LinkedList
int n = 5;
// Declaring the List with initial size n
List<Integer> ll = new LinkedList<Integer>();
// Appending the new elements
// at the end of the list
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
ll.add(i);
// Printing elements
System.out.println(ll);
// Remove element at index 3
ll.remove(3);
// Displaying the list after deletion
System.out.println(ll);
// Printing elements one by one
for (int i = 0; i < ll.size(); i++)
System.out.print(ll.get(i) + " ");
}
}[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] [1, 2, 3, 5] 1 2 3 5
相关用法
- Java List sort()用法及代码示例
- Java List spliterator()用法及代码示例
- Java List toArray()用法及代码示例
- Java List add()用法及代码示例
- Java List addAll()用法及代码示例
- Java List clear()用法及代码示例
- Java List contains()用法及代码示例
- Java List containsAll()用法及代码示例
- Java List equals()用法及代码示例
- Java List get()用法及代码示例
- Java List hashCode()用法及代码示例
- Java List indexOf()用法及代码示例
- Java List isEmpty()用法及代码示例
- Java List lastIndexOf()用法及代码示例
- Java List listIterator()用法及代码示例
- Java List removeAll()用法及代码示例
- Java List retainAll()用法及代码示例
- Java List size()用法及代码示例
- Java List sublist()用法及代码示例
- Java List remove(Object obj)用法及代码示例
- Java List add(E ele)用法及代码示例
- Java List remove(int index)用法及代码示例
- Java List add(int index, E element)用法及代码示例
- Java ListIterator add()用法及代码示例
- Java ListIterator hasNext()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自佚名大神的英文原创作品 List Interface in Java with Examples。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
