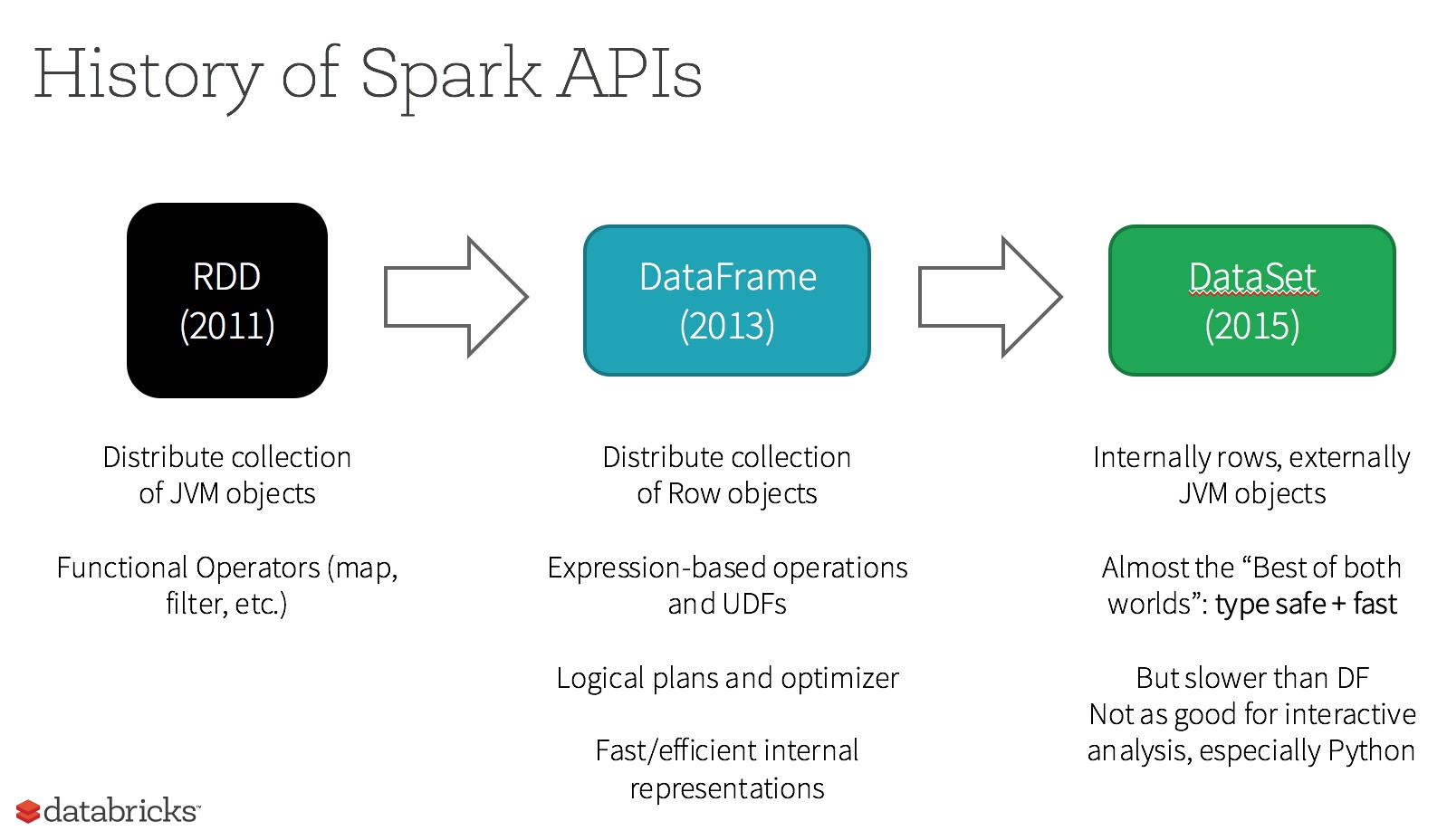
跟关系数据库的表(Table)一样,DataFrame是Spark中对带模式(schema)行列数据的抽象。DateFrame广泛应用于使用SQL处理大数据的各种场景。创建DataFrame有很多种方法,比如从本地List创建、从RDD创建或者从源数据创建,下面简要介绍创建DataFrame的三种方法。
方法一,Spark中使用toDF函数创建DataFrame
通过导入(importing)Spark sql implicits, 就可以将本地序列(seq), 数组或者RDD转为DataFrame。只要这些数据的内容能指定数据类型即可。
本地seq + toDF创建DataFrame示例:
import sqlContext.implicits._
val df = Seq(
(1, "First Value", java.sql.Date.valueOf("2010-01-01")),
(2, "Second Value", java.sql.Date.valueOf("2010-02-01"))
).toDF("int_column", "string_column", "date_column")
注意:如果直接用toDF()而不指定列名字,那么默认列名为”_1″, “_2”, …
通过case class + toDF创建DataFrame的示例
// sc is an existing SparkContext.
val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext(sc)
// this is used to implicitly convert an RDD to a DataFrame.
import sqlContext.implicits._
// Define the schema using a case class.
// Note: Case classes in Scala 2.10 can support only up to 22 fields. To work around this limit,
// you can use custom classes that implement the Product interface.
case class Person(name: String, age: Int)
// Create an RDD of Person objects and register it as a table.
val people = sc.textFile("examples/src/main/resources/people.txt").map(_.split(",")).map(p => Person(p(0), p(1).trim.toInt)).toDF()
people.registerTempTable("people")
// 使用 sqlContext 执行 sql 语句.
val teenagers = sqlContext.sql("SELECT name FROM people WHERE age >= 13 AND age <= 19")
// 注:sql()函数的执行结果也是DataFrame,支持各种常用的RDD操作.
// The columns of a row in the result can be accessed by ordinal.
teenagers.map(t => "Name: " + t(0)).collect().foreach(println)
方法二,Spark中使用createDataFrame函数创建DataFrame
在SqlContext中使用createDataFrame也可以创建DataFrame。跟toDF一样,这里创建DataFrame的数据形态也可以是本地数组或者RDD。
通过row+schema创建示例
import org.apache.spark.sql.types._
val schema = StructType(List(
StructField("integer_column", IntegerType, nullable = false),
StructField("string_column", StringType, nullable = true),
StructField("date_column", DateType, nullable = true)
))
val rdd = sc.parallelize(Seq(
Row(1, "First Value", java.sql.Date.valueOf("2010-01-01")),
Row(2, "Second Value", java.sql.Date.valueOf("2010-02-01"))
))
val df = sqlContext.createDataFrame(rdd, schema)
方法三,通过文件直接创建DataFrame
使用parquet文件创建
val df = sqlContext.read.parquet("hdfs:/path/to/file")
使用json文件创建
val df = spark.read.json("examples/src/main/resources/people.json")
// Displays the content of the DataFrame to stdout
df.show()
// +----+-------+
// | age| name|
// +----+-------+
// |null|Michael|
// | 30| Andy|
// | 19| Justin|
// +----+-------+
使用csv文件,spark2.0+之后的版本可用
//首先初始化一个SparkSession对象
val spark = org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession.builder
.master("local")
.appName("Spark CSV Reader")
.getOrCreate;
//然后使用SparkSessions对象加载CSV成为DataFrame
val df = spark.read
.format("com.databricks.spark.csv")
.option("header", "true") //reading the headers
.option("mode", "DROPMALFORMED")
.load("csv/file/path"); //.csv("csv/file/path") //spark 2.0 api
df.show()
补充:spark数据集的演变: