根據 indices 將 updates 分散到現有張量中。
用法
tf.tensor_scatter_nd_update(
tensor, indices, updates, name=None
)參數
-
tensor要複製/更新的張量。 -
indices要更新的 index 。 -
updates適用於 index 的更新。 -
name操作的可選名稱。
返回
- 具有給定形狀的新張量,並根據索引應用更新。
此操作通過將稀疏的 updates 應用於輸入 tensor 來創建一個新的張量。這類似於索引分配。
# Not implemented: tensors cannot be updated inplace.
tensor[indices] = updates如果在 CPU 上發現超出範圍的索引,則返回錯誤。
警告:此操作有一些特定於 GPU 的語義。
- 如果發現超出範圍的索引,則忽略該索引。
- 應用更新的順序是不確定的,因此如果
indices包含重複項,則輸出將是不確定的。
此操作與 非常相似,隻是更新分散在現有張量上(而不是 zero-tensor)。如果無法重新使用現有張量的內存,則製作並更新副本。tf.scatter_nd
一般來說:
indices是一個整數張量 - 要在tensor中更新的索引。indices已至少兩個軸,最後一個軸是索引向量的深度。- 對於
indices中的每個索引向量,在updates中都有相應的條目。 - 如果索引向量的長度與
tensor的等級匹配,則索引向量每個都指向tensor中的標量,並且每次更新都是一個標量。 - 如果索引向量的長度小於
tensor的秩,則每個索引向量都指向tensor的切片,並且更新的形狀必須與該切片匹配。
總體而言,這導致以下形狀約束:
assert tf.rank(indices) >= 2
index_depth = indices.shape[-1]
batch_shape = indices.shape[:-1]
assert index_depth <= tf.rank(tensor)
outer_shape = tensor.shape[:index_depth]
inner_shape = tensor.shape[index_depth:]
assert updates.shape == batch_shape + inner_shape典型用法通常比這種一般形式簡單得多,從簡單的例子開始可以更好地理解:
標量更新
最簡單的用法是按索引將標量元素插入張量。在這種情況下,index_depth 必須等於輸入 tensor 的等級,切片 indices 的每一列是輸入 tensor 軸的索引。
在這個最簡單的情況下,形狀約束是:
num_updates, index_depth = indices.shape.as_list()
assert updates.shape == [num_updates]
assert index_depth == tf.rank(tensor)`例如,在 8 個元素的 rank-1 張量中插入 4 個分散元素。
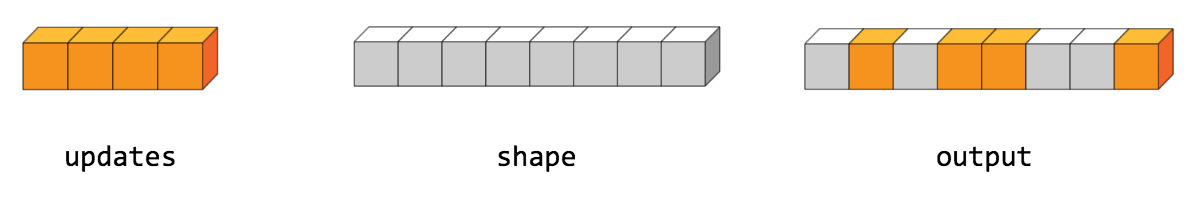
這個分散操作看起來像這樣:
tensor = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] # tf.rank(tensor) == 1
indices = [[1], [3], [4], [7]] # num_updates == 4, index_depth == 1
updates = [9, 10, 11, 12] # num_updates == 4
print(tf.tensor_scatter_nd_update(tensor, indices, updates))
tf.Tensor([ 0 9 0 10 11 0 0 12], shape=(8,), dtype=int32)updates 的長度(第一軸)必須等於 indices 的長度:num_updates。這是插入的更新數。每個標量更新都插入到索引位置的tensor。
對於更高等級的輸入 tensor 標量更新可以通過使用匹配 的 tf.rank(tensor) index_depth 插入:
tensor = [[1, 1], [1, 1], [1, 1]] # tf.rank(tensor) == 2
indices = [[0, 1], [2, 0]] # num_updates == 2, index_depth == 2
updates = [5, 10] # num_updates == 2
print(tf.tensor_scatter_nd_update(tensor, indices, updates))
tf.Tensor(
[[ 1 5]
[ 1 1]
[10 1]], shape=(3, 2), dtype=int32)切片更新
當輸入tensor 具有多個軸散布時,可用於更新整個切片。
在這種情況下,將輸入tensor 視為兩級array-of-arrays 會很有幫助。這個兩級數組的形狀分為 outer_shape 和 inner_shape 。
indices 索引輸入張量的外層(outer_shape)。並將該位置的 sub-array 替換為 updates 列表中的相應項目。每次更新的形狀是 inner_shape 。
更新切片列表時,形狀約束為:
num_updates, index_depth = indices.shape.as_list()
inner_shape = tensor.shape[:index_depth]
outer_shape = tensor.shape[index_depth:]
assert updates.shape == [num_updates, inner_shape]例如,要更新 (6, 3) tensor 的行:
tensor = tf.zeros([6, 3], dtype=tf.int32)使用索引深度為 1。
indices = tf.constant([[2], [4]]) # num_updates == 2, index_depth == 1
num_updates, index_depth = indices.shape.as_list()outer_shape 是 6 ,內部形狀是 3 :
outer_shape = tensor.shape[:index_depth]
inner_shape = tensor.shape[index_depth:]正在索引 2 行,因此必須提供 2 updates。每個更新的形狀都必須與 inner_shape 相匹配。
# num_updates == 2, inner_shape==3
updates = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])總而言之,這給出了:
tf.tensor_scatter_nd_update(tensor, indices, updates).numpy()
array([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[1, 2, 3],
[0, 0, 0],
[4, 5, 6],
[0, 0, 0]], dtype=int32)更多切片更新示例
代表一批大小均勻的視頻剪輯的張量自然有 5 個軸:[batch_size, time, width, height, channels]。
例如:
batch_size, time, width, height, channels = 13,11,7,5,3
video_batch = tf.zeros([batch_size, time, width, height, channels])要替換選擇的視頻剪輯:
- 使用 1 的
index_depth(索引outer_shape:[batch_size]) - 為每個更新提供與
inner_shape匹配的形狀:[time, width, height, channels]。
用一個替換前兩個剪輯:
indices = [[0],[1]]
new_clips = tf.ones([2, time, width, height, channels])
tf.tensor_scatter_nd_update(video_batch, indices, new_clips)要替換視頻中的選定幀:
indices對於outer_shape的index_depth必須為 2:[batch_size, time]。updates的形狀必須像圖像列表。每個更新都必須有一個形狀,匹配inner_shape:[width, height, channels]。
要替換前三個視頻剪輯的第一幀:
indices = [[0, 0], [1, 0], [2, 0]] # num_updates=3, index_depth=2
new_images = tf.ones([
# num_updates=3, inner_shape=(width, height, channels)
3, width, height, channels])
tf.tensor_scatter_nd_update(video_batch, indices, new_images)折疊索引
在簡單的情況下,將indices 和updates 視為列表很方便,但這不是嚴格的要求。 indices 和 updates 可以折疊成 batch_shape ,而不是平麵 num_updates 。這個 batch_shape 是 indices 的所有軸,除了最裏麵的 index_depth 軸。
index_depth = indices.shape[-1]
batch_shape = indices.shape[:-1]注意:一個例外是 batch_shape 不能是 [] 。您不能通過傳遞形狀為 [index_depth] 的索引來更新單個索引。
updates 必須具有匹配的 batch_shape(inner_shape 之前的軸)。
assert updates.shape == batch_shape + inner_shape注意:結果等效於展平 indices 和 updates 的 batch_shape 軸。當構造"folded" 索引和更新更自然時,這種概括隻是避免了重塑的需要。
通過這種概括,完整的形狀約束是:
assert tf.rank(indices) >= 2
index_depth = indices.shape[-1]
batch_shape = indices.shape[:-1]
assert index_depth <= tf.rank(tensor)
outer_shape = tensor.shape[:index_depth]
inner_shape = tensor.shape[index_depth:]
assert updates.shape == batch_shape + inner_shape例如,要在 (5,5) 矩陣上繪製 X,請從以下索引開始:
tensor = tf.zeros([5,5])
indices = tf.constant([
[[0,0],
[1,1],
[2,2],
[3,3],
[4,4]],
[[0,4],
[1,3],
[2,2],
[3,1],
[4,0]],
])
indices.shape.as_list() # batch_shape == [2, 5], index_depth == 2
[2, 5, 2]這裏 indices 的形狀不是 [num_updates, index_depth] ,而是 batch_shape+[index_depth] 的形狀。
由於 index_depth 等於 tensor 的等級:
outer_shape是(5,5)inner_shape是()- 每次更新都是標量updates.shape是batch_shape + inner_shape == (5,2) + ()
updates = [
[1,1,1,1,1],
[1,1,1,1,1],
]把它放在一起給出:
tf.tensor_scatter_nd_update(tensor, indices, updates).numpy()
array([[1., 0., 0., 0., 1.],
[0., 1., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 1., 0.],
[1., 0., 0., 0., 1.]], dtype=float32)相關用法
- Python tf.tensor_scatter_nd_max用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.tensor_scatter_nd_sub用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.tensor_scatter_nd_add用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.is_built_with_rocm用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.TestCase.assertLogs用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.is_gpu_available用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.TestCase.assertItemsEqual用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.TestCase.assertWarns用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.TestCase.create_tempfile用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.TestCase.cached_session用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.TestCase.captureWritesToStream用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.create_local_cluster用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.TestCase.assertRaises用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.TestCase.assertCountEqual用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.is_built_with_cuda用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.compute_gradient用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.gpu_device_name用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.TestCase.session用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.TestCase.create_tempdir用法及代碼示例
- Python tf.test.is_built_with_gpu_support用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自tensorflow.org大神的英文原創作品 tf.tensor_scatter_nd_update。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
