Python是進行數據分析的一種出色語言,主要是因為以數據為中心的python軟件包具有奇妙的生態係統。 Pandas是其中的一種,使導入和分析數據更加容易。
Pandas Index.copy()函數複製此對象。該函數還將新對象的名稱和dtype屬性設置為原始對象的名稱和dtype屬性。如果我們希望新對象具有不同的數據類型,則可以通過設置函數的dtype屬性來實現。
用法: Index.copy(name=None, deep=False, dtype=None, **kwargs)
參數:
name:字符串,可選
deep:布爾值,默認為False
dtype:numpy dtype或pandas類型
返回:複製:索引
注意:在大多數情況下,使用Deep應該沒有函數上的區別,但是如果通過deep,它將嘗試進行深度複製。
範例1:采用Index.copy()複製索引值到新對象並將新對象的數據類型更改為“ int64”的函數
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Index
idx = pd.Index([17.3, 69.221, 33.1, 15.5, 19.3, 74.8, 10, 5.5])
# Print the Index
idx輸出:
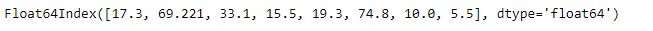
讓我們創建一個數據類型為“ int64”的對象的副本。
# Change the data type of newly
# created object to 'int64'
idx.copy(dtype ='int64')輸出:
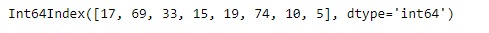
正如我們在輸出中看到的那樣,該函數返回了帶有'int64'dtype的原始索引的副本。
範例2:采用Index.copy()函數複製原始對象。還要設置新對象的名稱屬性,並將字符串dtype轉換為“ datetime”類型。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Index
idx = pd.Index(['2015-10-31', '2015-12-02', '2016-01-03',
'2016-02-08', '2017-05-05'])
# Print the Index
idx輸出:
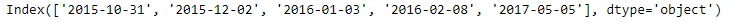
讓我們複製原始對象。
# to make copy and set data type in the datetime format.
idx_copy = idx.copy(dtype ='datetime64')
# Print the newly created object
idx_copy輸出:

從輸出中可以看到,新對象具有datatime格式的數據,並且其name屬性也已設置。
相關用法
- Python pandas.map()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.now用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.second用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas DataFrame.abs()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.lt()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.all()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas DataFrame.ix[ ]用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.pop()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas TimedeltaIndex.max用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.dst用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Timestamp.tz用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.mean()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas TimedeltaIndex.min用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas Series.ptp()用法及代碼示例
- Python Pandas dataframe.cov()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自Shubham__Ranjan大神的英文原創作品 Python | Pandas Index.copy()。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
