C++ 算法 transform() 函數有兩種不同的使用方式:
1.一元運算:- 該方法對[first1, last1]範圍內的元素執行一元運算op,並將結果存儲在從結果開始的範圍內。
此 transform() 將函數應用於範圍的每個元素:

2.二元運算:- 該方法對[first1, last1]範圍內的元素進行二元運算binary_op,範圍內的元素以迭代器first2開始,並將結果存儲在從result開始的範圍內。
這個 transform() 需要兩個 2 範圍,並在輸入範圍的每對元素上應用一個帶有 2 個參數的函數:
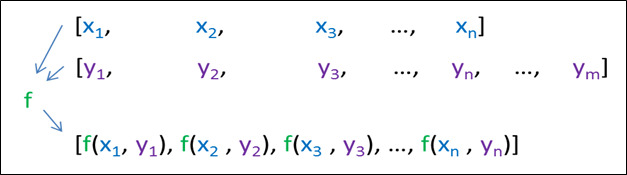
用法
一元運算(1)
template <class InputIterator, class OutputIterator, class UnaryOperation>
OutputIterator transform (InputIterator first1, InputIterator last1,
OutputIterator result, UnaryOperation op);二元運算(2)
template <class InputIterator1, class InputIterator2,
class OutputIterator, class BinaryOperation>
OutputIterator transform (InputIterator1 first1, InputIterator1 last1,
InputIterator2 first2, OutputIterator result,
BinaryOperation binary_op);參數
first1:一個輸入迭代器,指向要操作的第一個範圍的第一個元素的位置。
last1:一個迭代器,指向要操作的第一個範圍的最後一個元素之後的位置。
first2:輸入迭代器指向要操作的第二個範圍中的第一個元素。
result:一個輸出迭代器到存儲操作結果的範圍的初始位置。
op:一元函數應用於範圍的每個元素。
binary_op:兩個元素作為參數傳遞的二進製函數。
返回值
transform() 返回一個指向轉換範圍末尾的迭代器。
複雜度
複雜性在 first1 和 last1 之間的距離上是線性的。
數據競爭
範圍 [first1, last1) 中的對象被訪問,其中每個對象隻被訪問一次。
從結果開始的範圍內的對象被修改。
異常安全
如果任何函數調用賦值或迭代器上的操作拋出異常,則拋出異常。
請注意,無效參數會導致未定義的行為。
例子1
讓我們看一個簡單的例子來演示 transform() 的使用:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> v = { 3,1,4 };
vector<string> result;
transform(v.begin(), v.end(), back_inserter(result),
[](int x) { return to_string(x * 2); });
for_each(result.begin(), result.end(),
[](const string& s) { cout << s << endl; });
}輸出:
6 2 8
例子2
讓我們看另一個簡單的例子:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<char> v1 = { 'a','b','c' };
vector<int> v2 = { 3,1,4 };
vector<string> result;
transform(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), back_inserter(result),
[](char a, int b) { return string(b, a); });
for_each(result.begin(), result.end(),
[](const string& s) { cout << s << endl; });
return 0;
}輸出:
aaa b cccc
例子3
讓我們看另一個簡單的例子:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
#include <iterator>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef const vector <int>& vecref;
int power(int a, int b)
{
return pow(a, b);
}
void print(vecref a, vecref b, vecref c)
{
cout << "b[i] a[i] c[i]" << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++)
{
cout << setw(2) << setfill(' ') << a[i] << " ^ "
<< setw(1) << setfill(' ') << b[i] << " = "
<< setw(2) << setfill(' ') << c[i] << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
vector <int> a(10), b(10), c(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10 ;i++)
{
a[i] = (i % 2 + 1);
b[i] = (i % 3 + 1);
}
// Save the result in vector c
cout << "Transform operation" << endl;
transform(b.begin(), b.end(), a.begin(), c.begin(), power);
print(b, a, c);
return 0;
}輸出:
Transform operation b[i] a[i] c[i] 1 ^ 1 = 1 2 ^ 2 = 4 3 ^ 1 = 3 1 ^ 2 = 1 2 ^ 1 = 2 3 ^ 2 = 9 1 ^ 1 = 1 2 ^ 2 = 4 3 ^ 1 = 3 1 ^ 2 = 1
上麵的例子說明了 transform() 算法。該程序創建了兩個向量,並通過插入一個值來轉換第三個向量,該值等於第一個向量上升到第二個向量中元素的冪。函數 power 作為謂詞傳遞給函數 transform()。
示例 4
讓我們看另一個簡單的例子:
#include <iostream> // cout
#include <algorithm> // transform
#include <vector> // vector
#include <functional> // plus
using namespace std;
int op_increase (int i) { return ++i; }
int main () {
vector<int> foo;
vector<int> bar;
// set some values:
for (int i=1; i<6; i++)
foo.push_back (i*10); // foo:10 20 30 40 50
bar.resize(foo.size()); // allocate space
transform (foo.begin(), foo.end(), bar.begin(), op_increase);
// bar:11 21 31 41 51
// plus adds together its two arguments:
transform (foo.begin(), foo.end(), bar.begin(), foo.begin(), plus<int>());
// foo:21 41 61 81 101
cout << "foo contains:";
for (vector<int>::iterator it=foo.begin(); it!=foo.end(); ++it)
cout << ' ' << *it;
cout << '\n';
return 0;
}輸出:
foo contains:21 41 61 81 101
相關用法
- C++ Algorithm remove_if()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm remove()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm max_element()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm set_union()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm next_permutation()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm upper_bound()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm minmax()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm remove_copy_if()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm random_shuffle()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm pop_heap()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm replace()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm set_intersection()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm lower_bound()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm set_difference()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm is_sorted()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm equal_range()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm minmax_element()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm stable_sort()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm min()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Algorithm stable_partition()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自 C++ Algorithm transform()。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
