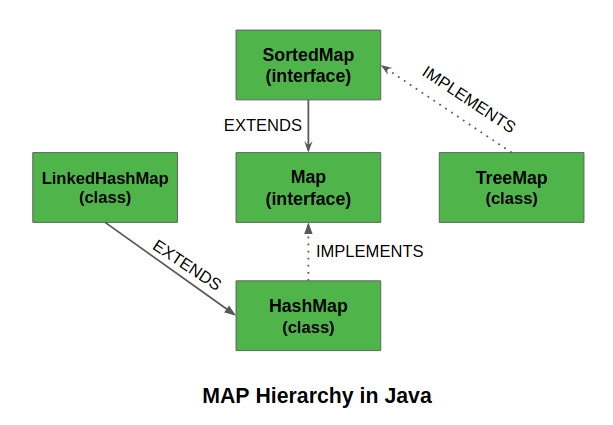
SortedMap 是 collection framework 中的接口。该接口扩展了Map interface并提供其元素的总排序(可以按键的排序顺序遍历元素)。实现该接口的类是TreeMap。
SortedMap 接口是 Java 中 java.util.Map 接口的子接口。它扩展了 Map 接口,以根据其键的自然顺序提供其元素的总排序。
SortedMap 和常规 Map 之间的主要区别在于 SortedMap 中的元素按排序顺序存储,而在 Map 中元素按任意顺序存储。排序顺序由键的自然顺序决定,键必须实现 java.lang.Comparable 接口,或者由传递给 SortedMap 构造函数的 Comparator 决定。
以下是如何使用 SortedMap 接口的示例:
Java
import java.util.SortedMap;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedMap<String, Integer> sortedMap = new TreeMap<>();
// Adding elements to the sorted map
sortedMap.put("A", 1);
sortedMap.put("C", 3);
sortedMap.put("B", 2);
// Getting values from the sorted map
int valueA = sortedMap.get("A");
System.out.println("Value of A: " + valueA);
// Removing elements from the sorted map
sortedMap.remove("B");
// Iterating over the elements of the sorted map
for (String key : sortedMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println("Key: " + key + ", Value: " + sortedMap.get(key));
}
}
} Value of A: 1 Key: A, Value: 1 Key: C, Value: 3
SortedMap 的主要特征是它按自然顺序或指定的比较器对键进行排序。因此,当您想要满足以下条件的Map时,请考虑使用TreeMap:
- 不允许使用 null 键或 null 值。
- 键按自然顺序或指定比较器排序。
类型参数:
- K - 该映射维护的键的类型
- V - 映射值的类型
SortedMap的父接口是Map<K, V>.
SortedMap的子接口是ConcurrentNavigableMap
SortedMap由ConcurrentSkipListMap实现,TreeMap.
声明:
public interface SortedMap<K, V> extends Map<K, V>
{
Comparator comparator();
SortedMap subMap(K fromKey, K toKey);
SortedMap headMap(K toKey);
SortedMap tailMap(K fromKey);
K firstKey();
K lastKey();
}
例子:
Java
// Java code to demonstrate SortedMap Interface
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.SortedMap;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class SortedMapExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedMap<Integer, String> sm
= new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
sm.put(new Integer(2), "practice");
sm.put(new Integer(3), "quiz");
sm.put(new Integer(5), "code");
sm.put(new Integer(4), "contribute");
sm.put(new Integer(1), "geeksforgeeks");
Set s = sm.entrySet();
// Using iterator in SortedMap
Iterator i = s.iterator();
// Traversing map. Note that the traversal
// produced sorted (by keys) output .
while (i.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry)i.next();
int key = (Integer)m.getKey();
String value = (String)m.getValue();
System.out.println("Key : " + key
+ " value : " + value);
}
}
}Key : 1 value : geeksforgeeks Key : 2 value : practice Key : 3 value : quiz Key : 4 value : contribute Key : 5 value : code
创建SortedMap对象
由于 SortedMap 是 interface ,因此无法创建 SortedMap 类型的对象。我们总是需要一个扩展这个列表的类来创建一个对象。而且,在 Java 1.5 中引入泛型之后,可以限制可以存储在 SortedMap 中的对象的类型。这个类型安全的映射可以定义为:
// Obj1, Obj2 are the type of the object to be stored in SortedMap
SortedMap<Obj1, Obj2> set = new TreeMap<Obj1, Obj2> ();
对SortedMap执行各种操作
由于SortedMap 是一个接口,因此它只能与实现该接口的类一起使用。 TreeMap 是实现SortedMap 接口的类。现在,让我们看看如何在 TreeMap 上执行一些常用的操作。
1. 添加元素:为了向 SortedMap 添加元素,我们可以使用TreeMap put()方法。但是,插入顺序不会保留在 TreeMap 中。在内部,对于每个元素,都会对键进行比较并按升序排序。
Java
// Java program add the elements in the SortedMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Default Initialization of a
// SortedMap
SortedMap tm1 = new TreeMap();
// Initialization of a SortedMap
// using Generics
SortedMap<Integer, String> tm2
= new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
// Inserting the Elements
tm1.put(3, "Geeks");
tm1.put(2, "For");
tm1.put(1, "Geeks");
tm2.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
tm2.put(new Integer(2), "For");
tm2.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
System.out.println(tm1);
System.out.println(tm2);
}
}{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
2. 改变元素:添加元素后,如果我们想更改元素,可以通过再次添加元素来完成TreeMap put()方法。由于 SortedMap 中的元素是使用键进行索引的,因此只需插入我们希望更改的键的更新值即可更改键的值。
Java
// Java program to change
// the elements in SortedMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a SortedMap
// using Generics
SortedMap<Integer, String> tm
= new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
// Inserting the Elements
tm.put(3, "Geeks");
tm.put(2, "Geeks");
tm.put(1, "Geeks");
System.out.println(tm);
tm.put(2, "For");
System.out.println(tm);
}
}{1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks}
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
3. 移除元件:为了从 SortedMap 中删除元素,我们可以使用TreeMap remove()方法。此方法获取键值,并从 SortedMap 中删除键的映射(如果映射中存在该键的映射)。
Java
// Java program to remove the
// elements from SortedMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a SortedMap
// using Generics
SortedMap<Integer, String> tm
= new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
// Inserting the Elements
tm.put(3, "Geeks");
tm.put(2, "Geeks");
tm.put(1, "Geeks");
tm.put(4, "For");
System.out.println(tm);
tm.remove(4);
System.out.println(tm);
}
}{1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks, 4=For}
{1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks}
4. 迭代SortedMap:有多种方法可以迭代 Map。最著名的方法是使用增强的for循环并拿到钥匙。使用getValue()方法找到键的值。
Java
// Java program to iterate through SortedMap
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a SortedMap
// using Generics
SortedMap<Integer, String> tm
= new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
// Inserting the Elements
tm.put(3, "Geeks");
tm.put(2, "For");
tm.put(1, "Geeks");
for (Map.Entry mapElement : tm.entrySet()) {
int key = (int)mapElement.getKey();
// Finding the value
String value = (String)mapElement.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " : " + value);
}
}
}1 : Geeks 2 : For 3 : Geeks
实现SortedMap接口的类是TreeMap。
在集合框架中实现的TreeMap 类是SortedMap 接口和SortedMap 扩展Map 接口的实现。它的行为就像一个简单的映射,不同之处在于它以排序的格式存储键。 TreeMap采用树形数据结构进行存储。对象按升序存储。但我们也可以通过传递比较器来按降序存储。让我们看看如何使用此类创建SortedMap 对象。
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the
// creation of SortedMap object using
// the TreeMap class
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedMap<String, String> tm
= new TreeMap<String, String>(new Comparator<String>() {
public int compare(String a, String b)
{
return b.compareTo(a);
}
});
// Adding elements into the TreeMap
// using put()
tm.put("India", "1");
tm.put("Australia", "2");
tm.put("South Africa", "3");
// Displaying the TreeMap
System.out.println(tm);
// Removing items from TreeMap
// using remove()
tm.remove("Australia");
System.out.println("Map after removing "
+ "Australia:" + tm);
}
}{South Africa=3, India=1, Australia=2}
Map after removing Australia:{South Africa=3, India=1}
SortedMap接口的方法
| METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| SortedMap comparator() | 返回用于对该映射中的键进行排序的比较器,如果该映射使用其键的自然顺序,则返回 null。 |
| SortedMap entrySet() | 返回此映射中包含的映射的集合视图。 |
| SortedMap firstKey() | 返回当前此映射中的第一个(最低)键。 |
| SortedMap headMap() | 返回此映射的部分视图,其键严格小于 toKey。 |
| SortedMap keySet() | 返回此映射中包含的键的集合视图。 |
| SortedMap lastKey() | 返回当前此映射中的最后一个(最高)键。 |
| SortedMap subMap() | 返回此映射的部分视图,其键范围从 fromKey(包含)到 toKey(不包含)。 |
| SortedMap tailMap() | 返回此映射中键大于或等于 fromKey 的部分的视图。 |
| SortedMap values() | 返回此映射中包含的值的集合视图。 |
从接口 java.util.Map 继承的方法
| METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Map clear() | 此方法用于清除和删除指定 Map 集合中的所有元素或映射。 |
| Map containsKey() |
此方法用于检查特定键是否已映射到 Map 中。 它将关键元素作为参数,如果该元素已映射到映射中,则返回 True。 |
| Map containsValue() |
此方法用于检查 Map 中是否由单个或多个键映射特定值。 它将该值作为参数,如果该值由映射中的任何键映射,则返回 True。 |
| Map entrySet() | 此方法用于创建Map中包含的相同元素的集合。它本质上返回Map的集合视图,或者我们可以创建一个新集合并将Map元素存储到其中。 |
| Map equals() | 此方法用于检查两个映射之间的相等性。它验证作为参数传递的一个映射的元素是否等于该映射的元素。 |
| Map get() | 此方法用于检索或获取参数中提到的特定键映射的值。当映射不包含键的此类映射时,它返回 NULL。 |
| Map hashCode() | 此方法用于为包含键和值的给定映射生成 hashCode。 |
| Map isEmpty() | 此方法用于检查映射是否有任何键和值对的条目。如果不存在映射,则返回 true。 |
| Map keySet() | 此方法用于返回此映射中包含的键的 Set 视图。该集合由Map支持,因此对Map的更改会反映在集合中,反之亦然。 |
| Map put() | 该方法用于将指定的值与该映射中的指定的键关联起来。 |
| Map putAll() | 该方法用于将指定映射的所有映射复制到该映射。 |
| Map remove() | 此方法用于从该映射中删除键的映射(如果该键存在于映射中)。 |
| size() | 此方法用于返回映射中可用的键/值对的数量。 |
| values() | 此方法用于创建Map值的集合。它本质上返回 HashMap 中值的集合视图。 |
SortedMap的优点:
- 排序顺序:SortedMap 接口根据其键的自然顺序或传递给构造函数的自定义比较器提供其元素的排序顺序。这在您需要按特定顺序检索元素的情况下非常有用。
- 可预测的迭代顺序:由于 SortedMap 中的元素按排序顺序存储,因此您可以预测它们在迭代期间返回的顺序,从而更容易编写以特定顺序处理元素的算法。
- 搜索性能:SortedMap 接口提供了 Map 接口的高效实现,允许您在对数时间内检索元素,这使其在需要快速检索元素的搜索算法中非常有用。
SortedMap的缺点:
- 插入元素速度慢:将元素插入 SortedMap 可能比将元素插入常规 Map 慢,因为 SortedMap 需要维护其元素的排序顺序。
- 键限制:SortedMap 中的键必须实现 java.lang.Comparable 接口,或者必须提供自定义 Comparator。如果您需要使用未实现此接口的自定义键,这可能是一个限制。
相关书籍:
- “Java Collections” 作者:莫里斯·纳夫塔林和菲利普·瓦德勒。本书全面概述了 Java Collections 框架,包括 SortedMap 接口。
- David Flanagan 的《Java 简介》。本书提供了 Java 核心函数的快速参考,包括SortedMap 接口。
- Maurice Naftalin 和 Philip Wadler 的“Java 泛型和集合”。本书提供了 Java 中泛型和集合的全面指南,包括 SortedMap 接口。
相关用法
- Java SortedMap clear()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap comparator()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap conatinsKey()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap conatinsValue()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap entrySet()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap equals()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap firstKey()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap get()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap hashCode()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap headMap()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap isEmpty()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap keySet()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap lastKey()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap put()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap putAll()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap remove()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap size()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap subMap()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap tailMap()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedMap values()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedSet add()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedSet addAll()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedSet clear()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedSet contains()用法及代码示例
- Java SortedSet containsAll()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自佚名大神的英文原创作品 SortedMap Interface in Java with Examples。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
