response.reason返回与状态码相对应的文本。例如,“确定”为200,“未找到”为404。Python请求通常用于从特定资源URI中获取内容。每当我们通过Python向指定URI发出请求时,它都会返回一个响应对象。现在,此响应对象将用于访问某些函数,例如内容,标头等。本文围绕如何从响应对象中检查response.reason展开。
如何使用Python请求使用response.reason?
为了说明response.reason的用法,让我们ping github.com和geeksforgeeks.org。要运行此脚本,您需要在PC上安装Python和请求。
先决条件-
示例代码-
# import requests module
import requests
# Making a get request
response = requests.get('https://api.github.com/')
# print response
print(response)
# print the reason
print(response.reason)
# ping an incorrect url
response = requests.get('https://geeksforgeeks.org / naveen/')
# print response
print(response)
# print the reason now
print(response.reason)示例实现-
将以上文件另存为request.py并使用
Python request.py
输出-
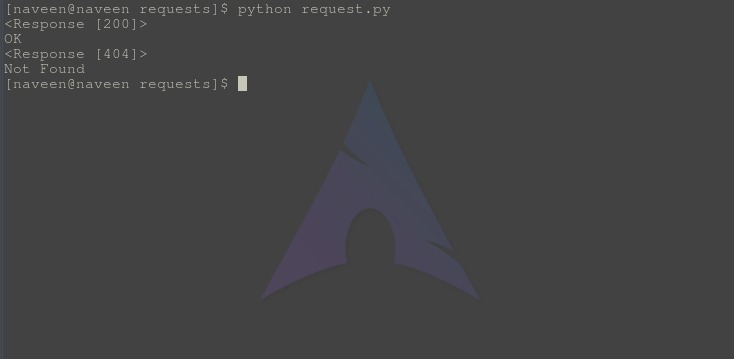
检查“确定”和“未找到”,它显示对应于特定status_code的文本。
先进概念
使用Python发出HTTP请求的库有很多,例如httplib,urllib,httplib2,treq等,但是请求是具有出色函数的最好的库之一。如果请求的任何属性显示为NULL,请使用以下属性检查状态代码。
requests.status_code
如果status_code不在200-29范围内。您可能需要检查开始用于请求的方法+您正在请求的URL的资源。
相关用法
- Python response.ok用法及代码示例
- Python response.url用法及代码示例
- Python response.encoding用法及代码示例
- Python response.cookies用法及代码示例
- Python response.elapsed用法及代码示例
- Python response.iter_content()用法及代码示例
- Python response.is_permanent_redirect用法及代码示例
- Python response.headers用法及代码示例
- Python response.close()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自NaveenArora大神的英文原创作品 response.reason – Python requests。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
