此几何管理器通过将小部件放置在父小部件中的特定位置来组织小部件。
用法
widget.place( place_options )
以下是可能的选项列表 -
anchor- 小部件的确切位置 其他选项参考:可能是 N、E、S、W、NE、NW、SE 或 SW,指示小部件角落和侧面的指南针方向;默认为 NW(小部件的左上角)
bordermode- INSIDE(默认)表示其他选项引用父级的内部(忽略父级的边框);否则外面。
height, width- 以像素为单位的高度和宽度。
relheight, relwidth- 高度和宽度作为 0.0 和 1.0 之间的浮点数,作为父小部件高度和宽度的一部分。
relx, rely- 水平和垂直偏移作为 0.0 和 1.0 之间的浮点数,作为父小部件的高度和宽度的一部分。
x, y- 以像素为单位的水平和垂直偏移。
示例
通过在不同按钮上移动光标来尝试以下示例 -
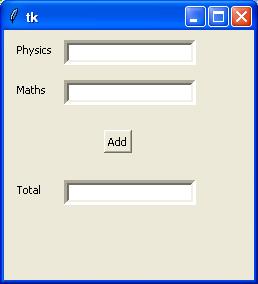
# !/usr/bin/python3
from tkinter import *
top = Tk()
L1 = Label(top, text = "Physics")
L1.place(x = 10,y = 10)
E1 = Entry(top, bd = 5)
E1.place(x = 60,y = 10)
L2 = Label(top,text = "Maths")
L2.place(x = 10,y = 50)
E2 = Entry(top,bd = 5)
E2.place(x = 60,y = 50)
L3 = Label(top,text = "Total")
L3.place(x = 10,y = 150)
E3 = Entry(top,bd = 5)
E3.place(x = 60,y = 150)
B = Button(top, text = "Add")
B.place(x = 100, y = 100)
top.geometry("250x250+10+10")
top.mainloop()执行上述代码时,会产生以下结果 -
相关用法
- Python 3 Tkinter pack()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 Tuple tuple()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 Tuple len()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 Tuple cmp()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 Tuple max()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 Tuple min()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 Number tan()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 os.fstatvfs()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 List pop()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 os.minor()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 dictionary cmp()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 String isupper()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 os.close()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 List index()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 String decode()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 os.unlink()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 os.major()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 Number atan()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 List len()用法及代码示例
- Python 3 String maketrans()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自 Python 3 - Tkinter place() Method。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
