Python中的OS模块提供了与操作系统进行交互的函数。操作系统属于Python的标准实用程序模块。该模块提供了使用依赖于操作系统的函数的便携式方法。 os.path模块是Python中OS模块的子模块,用于通用路径名操作。
os.path.ismount()Python中的method方法用于检查给定的路径是否为安装点。
挂载点是文件系统中已挂载其他文件系统的点。
用法: os.path.ismount(path)
参数:
path:代表文件系统路径的path-like对象。 path-like对象是表示路径的字符串或字节对象。
返回类型:此方法返回布尔型的布尔值。如果给定路径是安装点,则此方法返回True,否则返回False。
在Linux系统上,可以使用df命令显示分区及其安装点信息。
例如:
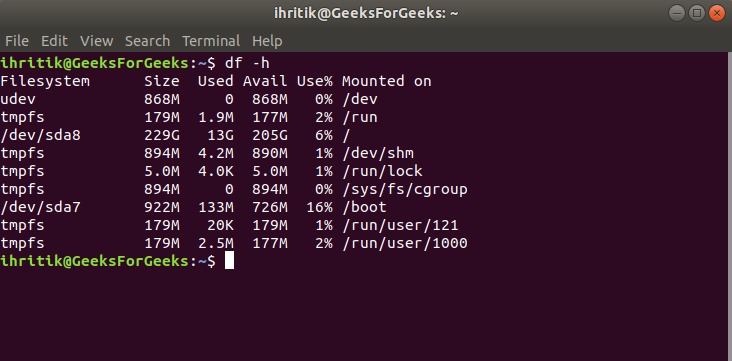
代码#1:使用os.path.ismount()方法检查给定路径是否为安装点(在Unix上)
# Python program to explain os.path.islink() method
# importing os.path module
import os.path
# Path
path = "/run"
# Check whether the
# given path is a
# mount point or not
ismount = os.path.ismount(path)
# Path
path = "/dev"
# Check whether the
# given path is a
# mount point or not
ismount = os.path.ismount(path)
print(ismount)
输出:
True True
代码2:使用os.path.ismount()方法检查给定路径是否为安装点(在Windows上)
# Python program to explain os.path.islink() method
# importing os.path module
import os.path
# On Windows, a drive letter root
# and a share UNC are always
# mount points Path
path = "C:"
# Check whether the
# given path is a
# mount point or not
ismount = os.path.ismount(path)
print(ismount)
输出:
True
参考: https://docs.python.org/3/library/os.path.html
相关用法
- Python os.dup()用法及代码示例
- Python next()用法及代码示例
- Python set()用法及代码示例
- Python object()用法及代码示例
- Python bytes()用法及代码示例
- Python os.times()用法及代码示例
- Python os.chmod用法及代码示例
- Python hash()用法及代码示例
- Python os.ftruncate()用法及代码示例
- Python os.truncate()用法及代码示例
- Python os.fsdecode()用法及代码示例
- Python dict pop()用法及代码示例
- Python os.abort()用法及代码示例
- Python os.WEXITSTATUS()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自ihritik大神的英文原创作品 Python | os.path.ismount() method。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
