java.nio.file.Path的normalize()方法用于从当前路径返回路径,在该路径中消除了所有冗余名称元素。
此方法的精确定义取决于实现,并且它派生出不包含冗余名称元素的路径。在许多文件系统中,“.”和“..”是表示当前目录和父目录的特殊名称。在那些情况下,所有出现的“.”都被认为是冗余的,并且如果“..”的前面带有非“..”名称,则这两个名称都被认为是冗余的。
用法:
Path normalize()
参数:此方法不接受任何内容。是少参数方法。
返回值:此方法返回结果路径;如果该路径不包含冗余名称元素,则返回此路径;否则,返回此路径。如果此路径没有根组件并且所有名称元素都是冗余的,则返回一个空路径。
以下示例程序旨在说明normalize()方法:
示例1:
// Java program to demonstrate
// java.nio.file.Path.normalize() method
import java.nio.file.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create object of Path
// In this example \\.. starts with non".."
// element
Path path
= Paths.get("D:\\..\\..\\.\\p2\\core"
+ "\\cache\\binary");
// print actual path
System.out.println("Actual Path : "
+ path);
// normalize the path
Path normalizedPath = path.normalize();
// print normalized path
System.out.println("\nNormalized Path : "
+ normalizedPath);
}
}
输出:


示例2:
// Java program to demonstrate
// java.nio.file.Path.normalize() method
import java.nio.file.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
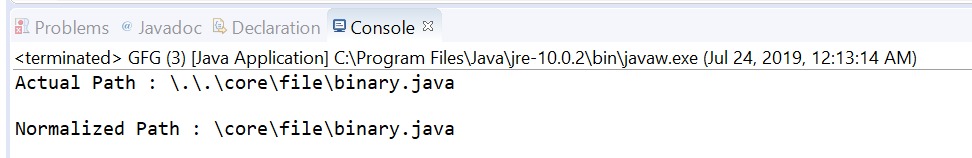
// create object of Path
Path path
= Paths.get("\\.\\.\\core"
+ "\\file\\binary.java");
// print actual path
System.out.println("Actual Path : "
+ path);
// normalize the path
Path normalizedPath = path.normalize();
// print normalized path
System.out.println("\nNormalized Path : "
+ normalizedPath);
}
}
输出:

参考文献: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/10/docs/api/java/nio/file/Path.html#normalize()
相关用法
- Java Path toAbsolutePath()用法及代码示例
- Java Path getRoot()用法及代码示例
- Java Path toString()用法及代码示例
- Java Path isAbsolute()用法及代码示例
- Java Path hashCode()用法及代码示例
- Java Path getFileName()用法及代码示例
- Java Path getNameCount()用法及代码示例
- Java Path compareTo()用法及代码示例
- Java Path getParent()用法及代码示例
- Java Path equals()用法及代码示例
- Java Path getName(int)用法及代码示例
- Java Path endsWith()用法及代码示例
- Java Path startsWith()用法及代码示例
- Java Path relativize()用法及代码示例
- Java Path iterator()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自AmanSingh2210大神的英文原创作品 Path normalize() method in Java with Examples。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
