numpy.polyint(p,m):计算具有指定顺序的多项式的反导数。
多项式“ p”的反导数“ P”满足
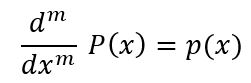
参数:
p: [array_like or poly1D] polynomial coefficients are given in decreasing order of powers. If the second parameter (root) is set to True then array values are the roots of the polynomial equation. For example, poly1d(3, 2, 6) = 3x2 + 2x + 6
m: [int, optional] Order of anti-derivative. Default is 1.
返回: Anti-Derivative of the polynomial.
代码1:
# Python code explaining
# numpy.polyint()
# importing libraries
import numpy as np
# Constructing polynomial
p1 = np.poly1d([1, 2])
p2 = np.poly1d([4, 9, 5, 4])
print ("P1:", p1)
print ("\n p2:\n", p2)
# Solve for x = 2
print ("\n\np1 at x = 2:", p1(2))
print ("p2 at x = 2:", p2(2))
a = np.polyint(p1, 1)
b = np.polyint(p2, 1)
print ("\n\nUsing polyint")
print ("p1 anti-derivative of order = 1:\n", a)
print ("p2 anti-derivative of order = 1:\n", b)
a = np.polyint(p1, 2)
b = np.polyint(p2, 2)
print ("\n\nUsing polyint")
print ("p1 anti-derivative of order = 2:\n", a)
print ("p2 anti-derivative of order = 2:\n", b) 输出:
P1:
1 x + 2
p2:
3 2
4 x + 9 x + 5 x + 4
p1 at x = 2: 4
p2 at x = 2: 82
Using polyint
p1 anti-derivative of order = 1:
2
0.5 x + 2 x
p2 anti-derivative of order = 1:
4 3 2
1 x + 3 x + 2.5 x + 4 x
代码2:
# Python code explaining
# numpy.polyint()
# importing libraries
import numpy as np
# Constructing polynomial
p1 = np.poly1d([1, 2])
p2 = np.poly1d([4, 9, 5, 4])
a = np.polyint(p1, 2)
b = np.polyint(p2, 2)
print ("\n\nUsing polyint")
print ("p1 anti-derivative of order = 2:\n", a)
print ("p2 anti-derivative of order = 2:\n", b) 输出:
Using polyint
p1 anti-derivative of order = 2:
3 2
0.1667 x + 1 x
p2 anti-derivative of order = 2:
5 4 3 2
0.2 x + 0.75 x + 0.8333 x + 2 x
相关用法
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自Mohit Gupta_OMG 大神的英文原创作品 numpy.polyint() in Python。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
