fs.promises.lstat()方法定义在 Node.js 的文件系统模块中。文件系统模块本质上是与用户计算机的硬盘进行交互。 lstat() 方法使用 stats 对象上定义的方法(由 lstat 提供的数据)提供一些特定于文件和文件夹的信息。 fs.promises.lstat() 方法返回已解决或拒绝的 Promise,从而避免 fs.readdir() 方法中可能出现的回调嵌套或回调地狱问题。
用法
fs.promises.lstat(path, options)
参数:该方法接受如上所述和如下所述的两个参数:
path:它是一个字符串、缓冲区或 url,指定我们尝试读取其内容的目录路径。
options:它是一个可选参数。其中一个选项参数是‘bigint’,它是一个布尔值。在这里,我们通过 fs.lstat() 方法指定返回的 stats 对象中的数值是否为 bigint (default-false)。
返回值:它返回已解决或已拒绝的承诺。如果成功读取目录,则使用 stats 对象解决承诺,否则如果发生任何错误(example-specified 目录不存在或没有读取文件的权限等),则使用错误对象拒绝。
从已解决的 Promise 返回的 stats 对象中定义了一些属性和方法,这有助于获取有关目标文件或文件夹的一些特定详细信息。下面指定了一些方法。
- 统计数据.isDirectory():如果 stats 对象说明文件系统目录,则返回 true。
- 统计数据.isFile():如果 stats 对象说明常规文件,则返回 true。
- 统计数据.isSocket():如果 stats 对象说明了一个套接字,则返回 true。
- 统计数据.isSymbolicLink():如果 stats 对象说明了符号链接,则返回 true。
- 统计数据.isFile():如果 stats 对象说明常规文件,则返回 true。
- 统计数据.isFIFO():如果 stats 对象说明先进先出管道,则返回 true。
- 统计数据大小:指定文件的大小(以字节为单位)。
- 统计数据块:指定为文件分配的块数。
示例 1:
javascript
// Node.js program to demonstrate the
// Buffer.from() Method
// Importing File System module
const fs = require('fs')
// fs.readdir() reads contents of
// target directory
// process.cwd() gives current
// working directory
fs.readdir(process.cwd(), (err, filenames) => {
if (err) {
console.log(err)
return
}
for (let filename of filenames) {
// Calling lstat method to give the
// stats object for every directory
fs.promises.lstat(filename)
// If promise resolved and data
// are fetched
.then(stats => {
if (stats.isFile()) {
console.log(`${filename} ---------> File`)
} else {
console.log(`${filename} ---------> Folder`)
}
})
// If promise is rejected
.catch(err => {
console.log(err)
})
}
}) 输出:
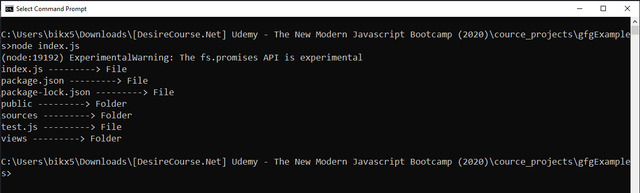
示例 2:
javascript
// Node.js program to demonstrate the
// Buffer.from() Method
// Importing File System module
const fs = require('fs')
// The fs.readdir() method reads the
// contents of target directory
// The process.cwd() method gives the
// current working directory
fs.readdir(process.cwd(), async (err, filenames) => {
if (err) {
console.log(err)
return
}
for (let filename of filenames) {
// Calling lstat method to give the
// stats object for every directory
fs.promises.lstat(filename)
// If promise resolved and datas
// are fetched
.then(stats => {
console.log(
`${filename} --------> ${stats.size} bytes`)
})
// If promise is rejected
.catch(err => {
console.log(err)
})
}
}) 输出:
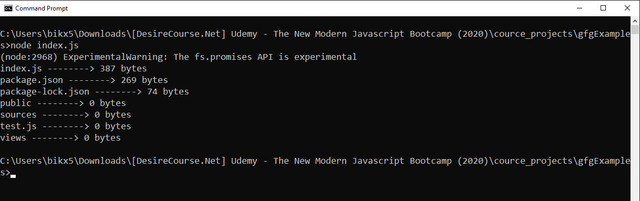
参考: https://nodejs.org/api/fs.html#fs_fspromises_lstat_path_options
相关用法
- Node.js fsPromises.lchmod()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.lchown()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.opendir()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.truncate()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.symlink()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.utimes()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.chmod()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.copyFile()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.rename()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.writeFile()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.readFile()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.access()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.mkdtemp()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.open()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.appendFile()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.mkdir()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.stat()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.realpath()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.chown()用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.access(path[, mode])用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.copyFile(src, dest[, mode])用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.mkdtemp(prefix[, options])用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.opendir(path[, options])用法及代码示例
- Node.js fsPromises.readdir(path[, options])用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自hunter__js大神的英文原创作品 Node.js fsPromises.lstat() Method。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
