Matplotlib是Python中的一个库,它是数字的-NumPy库的数学扩展。轴类包含大多数图形元素:Axis,Tick,Line2D,Text,Polygon等,并设置坐标系。 Axes实例通过callbacks属性支持回调。
matplotlib.axes.Axes.get_adjustable()函数
matplotlib库的axiss模块中的Axes.get_adjustable()函数用于获取为实现给定方面而给定的Axes参数。
用法: Axes.get_adjustable(self)
参数:此方法不接受任何参数。
返回值:此方法返回可调值。
以下示例说明了matplotlib.axes中的matplotlib.axes.Axes.get_adjustable()函数:
范例1:
# ImpleIn Reviewtation of matplotlib function
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
ax1.set_xscale("log")
ax1.set_yscale("log")
ax1.set_xlim(1e1, 1e3)
ax1.set_ylim(1e2, 1e3)
ax1.set_aspect(1)
ax1.set_title("Axes 1")
ax2.set_xscale("log")
ax2.set_yscale("log")
ax2.set_adjustable("datalim")
ax2.plot([1, 113, 10], [1, 119, 100], "o-")
ax2.set_xlim(1e-1, 1e2)
ax2.set_ylim(1e-1, 1e3)
ax2.set_aspect(1)
ax2.set_title("Axes 2")
w = ax1.get_adjustable()
w1 = ax2.get_adjustable()
ax1.text(20, 400,
" Value return by\n get_adjustable():" +str(w))
ax2.text(1, 200,
" Value return by \nget_adjustable():\n " +str(w1))
fig.suptitle('matplotlib.axes.Axes.get_adjustable() function Example\n',
fontweight ="bold")
fig.canvas.draw()
plt.show()输出:
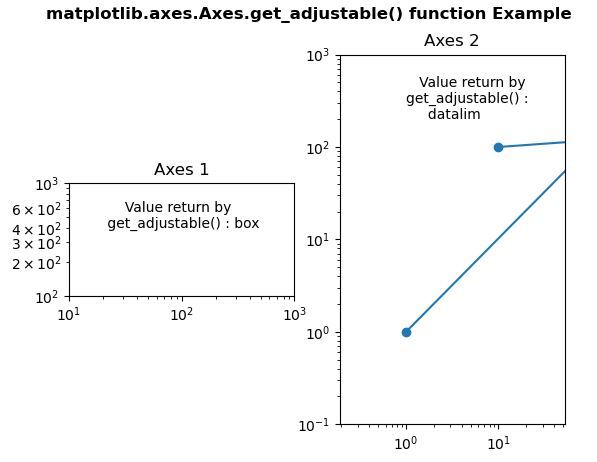
范例2:
# ImpleIn Reviewtation of matplotlib function
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.tri as tri
import numpy as np
n_angles = 40
n_radii = 10
min_radius = 2
radii = np.linspace(min_radius, 0.95, n_radii)
angles = np.linspace(0, 4 * np.pi, n_angles,
endpoint = False)
angles = np.repeat(angles[..., np.newaxis],
n_radii, axis = 1)
angles[:, 1::2] += np.pi / n_angles
x = (radii * np.cos(angles)).flatten()
y = (radii * np.sin(angles)).flatten()
triang = tri.Triangulation(x, y)
triang.set_mask(np.hypot(x[triang.triangles].mean(axis = 1),
y[triang.triangles].mean(axis = 1))
< min_radius)
fig, (ax, ax1) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
ax.triplot(triang, 'bo-', lw = 1, color = "green")
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.set_title("Axes 1")
ax1.set_aspect('equal')
ax1.set_adjustable("datalim")
ax1.triplot(triang, 'bo-', lw = 1, color = "green")
ax1.set_title("Axes 2")
w = ax.get_adjustable()
w1 = ax1.get_adjustable()
ax.text(-1.15, -3.5,
" Value return by\n get_adjustable():" +str(w))
ax1.text(-1, 2.5,
" Value return by \nget_adjustable():\n " +str(w1))
fig.suptitle('matplotlib.axes.Axes.get_adjustable() function \
Example\n', fontweight ="bold")
fig.canvas.draw()
plt.show()输出:
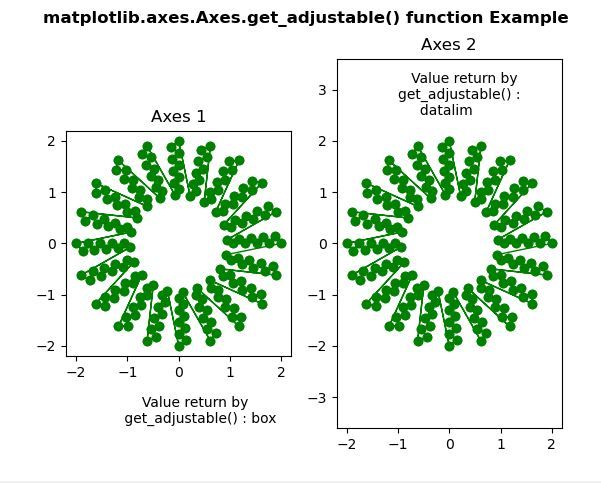
相关用法
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自SHUBHAMSINGH10大神的英文原创作品 Matplotlib.axes.Axes.get_adjustable() in Python。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
