该类提供线程局部变量。这些变量与其正常对应变量的不同之处在于,访问一个变量(通过其 get 或 set 方法)的每个线程都有其自己的、独立初始化的变量副本。本质上,这是除了编写不可变类之外实现线程安全的另一种方法。由于对象不再共享,因此不需要同步,这可以提高应用程序的可扩展性和性能。 ThreadLocal提供线程限制,它是局部变量的扩展。 ThreadLocal仅在单个线程中可见。没有两个线程可以看到彼此的线程局部变量。这些变量通常是类中的私有静态字段,并在线程内维护它们的状态。
Note: ThreadLocal class extends Object class
构造函数:ThreadLocal():这将创建一个线程局部变量。
ThreadLocal类的方法
| 方法 | 执行的操作 |
|---|---|
| get() | 返回此线程局部变量的当前线程副本中的值。如果该变量对于当前线程没有值,则首先将其初始化为调用 initialValue() 方法返回的值 |
| initialValue() | 返回本地线程变量的当前线程初始值。 |
| remove() | 删除此线程局部变量的当前线程值。如果当前线程随后读取此线程局部变量,则将通过调用其 initialValue() 方法重新初始化其值,除非当前线程在此期间设置其值。这可能会导致当前线程中多次调用initialValue方法 |
| set() | 将此线程局部变量的当前线程副本设置为指定值。大多数子类不需要重写此方法,仅依靠initialValue()方法来设置线程局部变量的值。 |
示例 1:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate ThreadLocal Class
// Via get() and set() Method
// Class
// ThreadLocalDemo
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating objects of ThreadLocal class
ThreadLocal<Number> gfg_local
= new ThreadLocal<Number>();
ThreadLocal<String> gfg = new ThreadLocal<String>();
// Now setting custom value
gfg_local.set(100);
// Returns the current thread's value
System.out.println("value = " + gfg_local.get());
// Setting the value
gfg_local.set(90);
// Returns the current thread's value of
System.out.println("value = " + gfg_local.get());
// Setting the value
gfg_local.set(88.45);
// Returns the current thread's value of
System.out.println("value = " + gfg_local.get());
// Setting the value
gfg.set("GeeksforGeeks");
// Returning the current thread's value of
System.out.println("value = " + gfg.get());
}
}输出
value = 100 value = 90 value = 88.45 value = GeeksforGeeks
示例 2:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate ThreadLocal Class
// Via Illustrating remove() Method
// Class
// ThreadLocalDemo
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating objects of ThreadLocal class
ThreadLocal<Number> gfg_local
= new ThreadLocal<Number>();
ThreadLocal<String> gfg = new ThreadLocal<String>();
// Setting the value
gfg_local.set(100);
// Returning the current thread's value
System.out.println("value = " + gfg_local.get());
// Setting the value
gfg_local.set(90);
// Returns the current thread's value of
System.out.println("value = " + gfg_local.get());
// Setting the value
gfg_local.set(88.45);
// Returning the current thread's value of
System.out.println("value = " + gfg_local.get());
// Setting the value
gfg.set("GeeksforGeeks");
// Returning the current thread's value of
System.out.println("value = " + gfg.get());
// Removing value using remove() method
gfg.remove();
// Returning the current thread's value of
System.out.println("value = " + gfg.get());
// Removing value
gfg_local.remove();
// Returns the current thread's value of
System.out.println("value = " + gfg_local.get());
}
}输出
value = 100 value = 90 value = 88.45 value = GeeksforGeeks value = null value = null
示例 3:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate ThreadLocal Class
// Via initialValue() Method
// Importing required classes
import java.lang.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class extending Thread class
class NewThread extends Thread {
private static ThreadLocal gfg = new ThreadLocal() {
protected Object initialValue()
{
return new Integer(question--);
}
};
private static int question = 15;
NewThread(String name)
{
// super keyword refers to parent class instance
super(name);
start();
}
// Method
// run() method for Thread
public void run()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
System.out.println(getName() + " " + gfg.get());
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
// ThreadLocalDemo
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating threads inside main() method
NewThread t1 = new NewThread("quiz1");
NewThread t2 = new NewThread("quiz2");
}
}输出:
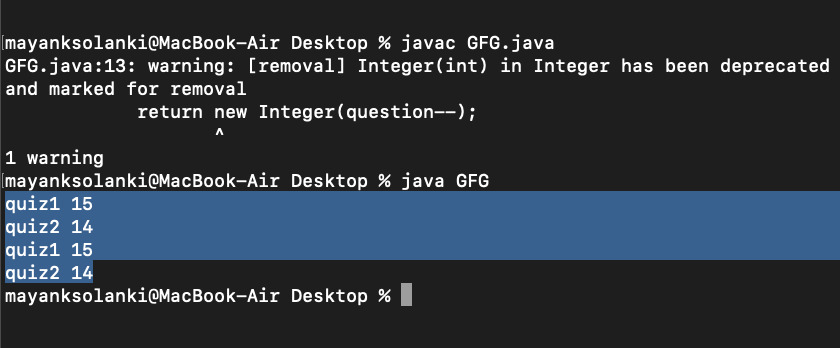
相关用法
- Java Java.lang.ThreadLocal.get()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.ThreadLocal.initialValue()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.ThreadLocal.remove()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.ThreadLocal.set()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.activeCount()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.checkAccess()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.currentThread()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.dumpStack()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.enumerate()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.getAllStackTraces()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.getContextClassLoader()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.getId()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.getName()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.getPriority()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.getStackTrace()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.getState()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.getThreadGroup()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.holdsLock()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.interrupt()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.interrupted()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.isAlive()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.isDaemon()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.isInterrupted()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.join()用法及代码示例
- Java Java.lang.Thread.run()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自佚名大神的英文原创作品 Java.lang.ThreadLocal Class in Java。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
