对于同时执行多个线程的multi-threaded程序,我们需要获取并释放锁,以保持进程之间的同步。 java的FileChannel类还提供一种称为trylock()的方法,该方法用于获取对指定File的锁定。此方法用于获取在该方法的参数中指定的文件的任何区域上的锁定。
锁定可能是比标准同步块更灵活,更复杂的线程同步机制。锁可以是用于控制多个线程对共享资源的访问的工具。通常,锁提供对共享资源的独占访问:一次只有一个线程可以获取该锁,每个访问共享资源的人都需要先获取该锁。但是,某些锁可能允许并发访问共享资源,例如ReadWriteLock的读取锁。
此处的输出是FileLock类的对象,该对象提到已应用的锁定,如果未应用任何锁定(可能是由于某些其他进程正在保存或写入文件的原因),则此方法将返回null。 Position变量指定要从中获取锁的文件的标记,并且范围(要获取锁的程度)由‘size’变量给出。如果在第二个参数的位置未提及任何内容,则默认使用Long.MAX_VALUE的大小。 “shared”布尔变量表明是否共享锁。如果为假,则该锁是互斥的,否则将在其他进程之间共享。这些是同步方法的一些基础知识。其默认值为false。
这种方法的主要优点是它永远不会被阻塞。调用之后,它或者返回获取的锁,或者在文件由另一个进程处理的情况下返回null或引发异常。此方法通常与同一类的lock()方法不同,因为在同步过程中,该过程必须等待很长时间才能访问文件或资源并获取锁,但是此方法将永远不会等待,它将返回null或异常。
用法:方法声明
public abstract FileLock tryLock(long position, long size, boolean shared) throws IOException
示例
Java
// Java Program to illustarte FileChannel Class
// tryLock() method
// Importing libraries
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.FileLock;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
// save the file named as GFG.java
public class GFG extends Thread {
// content to be written in the file.
String input
= "geeks for geeks is a learning portal for computer sciences.";
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.wrap(input.getBytes());
// path of the file
String fp = "gfg.txt";
// file channel class object
Path pt = Paths.get(fp);
public void run()
{
try {
// the thread says if file is opened.
FileChannel fc = FileChannel.open(
pt, StandardOpenOption.WRITE,
StandardOpenOption.APPEND);
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getId()
+ "says:File channel is opened for writing");
// trying lock
fc.tryLock(0L, Long.MAX_VALUE, false);
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getId()
+ "says:acquiring lock");
// writing
fc.write(buf);
// release the Lock after writing
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getId()
+ "says:");
System.out.println(
"writing is done, closing the file");
// Closing the file connections
fc.close();
}
// Catch block to handle the exception
catch (Exception e) {
// Getting and printing current threads
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getId()
+ "says:Exception" + e);
}
// Here, one file raises exception since the file
// is being written by another thread.
}
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Creating an object in the main() method
GFG g1 = new GFG();
GFG g2 = new GFG();
// Calling start() methods over the objects
g1.start();
g2.start();
// Here Two thread in concurrency
// are trying to access the file
}
}输出:
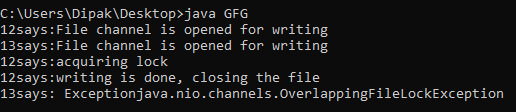
输出说明:
我们正在创建两个线程,它们将尝试访问文件并对其执行写操作。因为要保持同步,所以我们使用trylock()方法。当线程之一获取锁并对文件进行操作时,如果第二个线程调用要获取的锁,则该方法会引发异常,因为无法自由获取文件。在上面的代码中,我们已经明确获取了整个文件的锁定。如果需要,我们可以更改必须获取锁的文件部分的大小。
相关用法
- Java Java.util.concurrent.RecursiveAction用法及代码示例
- Java Java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask用法及代码示例
- Java Java.awt.image.RescaleOp用法及代码示例
- Java Java.util.concurrent.Phaser用法及代码示例
- Java Class getModule()用法及代码示例
- Java Class getPackage()用法及代码示例
- Java Class getPackageName()用法及代码示例
- Java Class getTypeParameters()用法及代码示例
- Java Class getDeclaredClasses()用法及代码示例
- Java Class getDeclaredMethods()用法及代码示例
- Java Class getDeclaredFields()用法及代码示例
- Java Class getConstructors()用法及代码示例
- Java Class getName()用法及代码示例
- Java Class getGenericSuperclass()用法及代码示例
- Java Class getClassLoader()用法及代码示例
- Java Class getSuperclass()用法及代码示例
- Java Class isEnum()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自harshkumarchoudhary144大神的英文原创作品 FileChannel Class tryLock() Method in Java with Examples。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
