C++是一种强大的语言。在C++中,我们可以编写结构化程序面向对象程序还。在这篇文章中,我们将重点关注dynamic_cast在C++中。现在在开始 C++ 中的 dynamic_cast 之前,首先了解什么是C++ 中的类型转换.’
类型铸造:
转换是将一种数据类型转换为另一种数据类型的技术。用于此目的的运算符称为强制转换运算符。它是一个一元运算符,强制将一种数据类型转换为另一种数据类型。它采用以下格式:
用法:
(Cast type) expression;
or
Cast type (expression)
程序1:
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the use
// of typecasting
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Variable declaration
int a, b;
float c;
a = 20;
b = 40;
// Typecasting
c = (float)a * b;
cout << "Result: " << c;
return 0;
}Result: 800
说明:在上面的例子中,首先将变量a转换为float然后乘以b,现在结果也是浮点float然后将结果赋给变量c。现在,c 的值为 800。
程序2:
C++
// C++ program to read the values of two
// variables and stored the result in
// third one
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Variable declaration and
// initialization
int a = 7, b = 2;
float c;
c = a / b;
cout << "Result:" << c;
return 0;
}Result:3
解释:在上面的例子中,变量c是3,而不是3.5,因为变量a和b都是整数类型,所以a/b也是整数类型。计算完a/b后,即int类型被分配给float类型的变量c。但 a/b 是 int 类型,即 7/2 是 3,而不是 3.5。因此,变量c的值为3。
程序3:
C++
// C++ program to read two variable value
// (a, b) and perform typecasting
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Variable declaration and
// initialization
int a = 7, b = 2;
float c;
// Type Casting
c = (float)a / b;
cout << "Result :" << c;
return 0;
}Result :3.5
解释:现在变量c为3.5,因为上面的表达式中首先将a转换为float,因此a/b也是float类型。 7.0/2 是 3.5。然后将其分配给变量 c。
C++ 支持四种类型的转换:
1.Static Cast
2. Dynamic Cast
3. Const Cast
4. Reinterpret Cast
静态投射:这是可以使用的最简单的转换类型。这是一个编译时投掷。它执行类型之间的隐式转换(例如 int 到 float,或指向 void* 的指针)之类的操作,并且还可以调用显式转换函数(或隐式转换函数)。
动态转换:转换是将数据从一种类型转换为另一种类型的运算符。在C++中,动态转换主要用于运行时的安全向下转换。要处理dynamic_cast,基类中必须有一个虚函数。 dynamic_cast 仅适用于多态基类,因为它使用此信息来决定安全向下转型。
用法:
dynamic_cast <new_type>(Expression)
- Downcasting:将基类指针(或引用)转换为派生类指针(或引用)称为向下转换。在图 1 中,从基类指针/引用转换为“派生类 1”指针/引用,显示向下转换(基类 -> 派生类)。
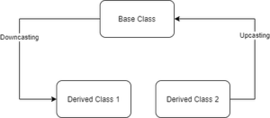
- Upcasting:将派生类指针(或引用)转换为基类指针(或引用)称为向上转换。在图 1 中,从派生类 2 指针/引用转换为 “Base class” 指针/引用,显示向上转换(派生类 2 -> 基类)。
正如我们上面提到的动态转换必须有一个虚函数。假设如果我们不使用虚函数,那么结果会是什么呢?
在这种情况下,它会生成错误消息“源类型不是多态的”。
C++
// C++ program demonstrate if there
// is no virtual function used in
// the Base class
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Base class declaration
class Base {
void print()
{
cout << "Base" << endl;
}
};
// Derived Class 1 declaration
class Derived1 : public Base {
void print()
{
cout << "Derived1" << endl;
}
};
// Derived class 2 declaration
class Derived2 : public Base {
void print()
{
cout << "Derived2" << endl;
}
};
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Derived1 d1;
// Base class pointer hold Derived1
// class object
Base* bp = dynamic_cast<Base*>(&d1);
// Dynamic casting
Derived2* dp2 = dynamic_cast<Derived2*>(bp);
if (dp2 == nullptr)
cout << "null" << endl;
return 0;
}输出
./Solution.cpp: In function 'int main()':
./Solution.cpp:42:47: error: cannot dynamic_cast 'bp' (of type 'class Base*') to type 'class Derived2*' (source type is not polymorphic)
Derived2* dp2 = dynamic_cast<Derived2*>(bp);
虚函数包含运行时类型信息,基类中没有虚函数。所以这段代码会产生错误。
情况1:以dynamic_cast为例,如果转换成功,则返回new_type类型的值。
C++
// C++ Program demonstrates successful
// dynamic casting and it returns a
// value of type new_type
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Base Class declaration
class Base {
virtual void print()
{
cout << "Base" << endl;
}
};
// Derived1 class declaration
class Derived1 : public Base {
void print()
{
cout << "Derived1" << endl;
}
};
// Derived2 class declaration
class Derived2 : public Base {
void print()
{
cout << "Derived2" << endl;
}
};
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Derived1 d1;
// Base class pointer holding
// Derived1 Class object
Base* bp = dynamic_cast<Base*>(&d1);
// Dynamic_casting
Derived1* dp2 = dynamic_cast<Derived1*>(bp);
if (dp2 == nullptr)
cout << "null" << endl;
else
cout << "not null" << endl;
return 0;
}not null
说明:在这个程序中,有一个基类和两个派生类(Derived1,Derived2),这里基类指针保存派生类1对象(d1)。在dynamic_casting基类时,指针持有Derived1对象并将其分配给派生类1,分配有效的dynamic_casting。
情况 2:现在,如果转换失败并且 new_type 是指针类型,则它返回该类型的空指针。
C++
// C++ Program demonstrate if the cast
// fails and new_type is a pointer type
// it returns a null pointer of that type
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Base class declaration
class Base {
virtual void print()
{
cout << "Base" << endl;
}
};
// Derived1 class declaration
class Derived1 : public Base {
void print()
{
cout << "Derived1" << endl;
}
};
// Derived2 class declaration
class Derived2 : public Base {
void print()
{
cout << "Derived2" << endl;
}
};
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Derived1 d1;
Base* bp = dynamic_cast<Base*>(&d1);
// Dynamic Casting
Derived2* dp2 = dynamic_cast<Derived2*>(bp);
if (dp2 == nullptr)
cout << "null" << endl;
return 0;
}null
说明:在此程序中,当 dynamic_casting 基类指针持有 Derived1 对象并将其分配给派生类 2 时,dynamic_casting 无效。因此,它在结果中返回该类型的空指针。
情况 3:现在再考虑 dynamic_cast 的情况,如果转换失败并且 new_type 是引用类型,则会抛出与 std::bad_cast 类型的处理程序匹配的异常,并给出警告:dynamic_cast “Derived d1”到“class Derived2&”永远不会成功。
C++
// C++ Program demonstrate if the cast
// fails and new_type is a reference
// type it throws an exception
#include <exception>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Base class declaration
class Base {
virtual void print()
{
cout << "Base" << endl;
}
};
// Derived1 class
class Derived1 : public Base {
void print()
{
cout << "Derived1" << endl;
}
};
// Derived2 class
class Derived2 : public Base {
void print()
{
cout << "Derived2" << endl;
}
};
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Derived1 d1;
Base* bp = dynamic_cast<Base*>(&d1);
// Type casting
Derived1* dp2 = dynamic_cast<Derived1*>(bp);
if (dp2 == nullptr)
cout << "null" << endl;
else
cout << "not null" << endl;
// Exception handling block
try {
Derived2& r1 = dynamic_cast<Derived2&>(d1);
}
catch (std::exception& e) {
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
return 0;
}输出:
warning: dynamic_cast of ‘Derived1 d1’ to ‘class Derived2&’ can never succeed Derived2& r1 = dynamic_cast<Derived2&>(d1);
注意:
- Dynamic_cast 具有运行时开销,因为它在运行时使用“Run-Time Type Information”检查对象类型。
- 如果可以保证我们永远不会转换为错误的对象,那么请始终避免dynamic_cast并使用static_cast。
相关用法
- C++ Deque assign()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque at()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque back()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque begin()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque cbegin()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque cend()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque clear()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque crbegin()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque crend()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque emplace()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque emplace_front()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque empty()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque end()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque erase()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque insert()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque max_size()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque pop_back()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque pop_front()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque push_back()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque push_front()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque rbegin()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque rend()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque resize()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque shrink_to_fit()用法及代码示例
- C++ Deque size()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自varshachoudhary大神的英文原创作品 Dynamic _Cast in C++。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
