notify() 和notifyAll() 方法以及wait() 方法用于线程之间的通信。通过调用 wait() 方法进入等待状态的线程将处于等待状态,直到任何其他线程在同一对象上调用 notify() 或 notifyAll() 方法。
notify(): notify()方法定义在对象类,这是Java的顶级类。它只用于唤醒一个线它正在等待一个对象,然后该线程开始执行。线程类notify()方法用于唤醒单个线程。
notifyAll():notifyAll() 唤醒在此对象监视器上等待的所有线程。线程通过调用其中之一来等待对象的监视器等待方法。被唤醒的线程将无法继续,直到当前线程放弃该对象上的锁。
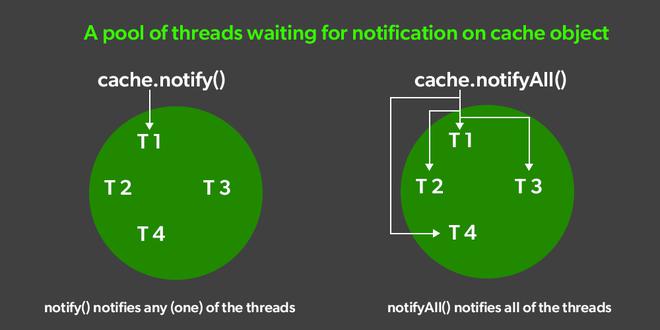
现在的问题是notify()和notifyAll()方法都用于向等待线程发出通知,那么它们之间有什么区别或者我们应该在哪里使用notify()方法以及我们应该在哪里使用notifyAll()方法?
| 先生。没有。 | 钥匙 | notify() | notifyAll() |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Notifications | 在 multiThreading 的情况下,notify() 方法仅将通知发送到等待发送锁的多个等待线程中的一个线程。 | 而同一上下文中的 notifyAll() 方法将通知发送给所有等待线程而不是单个线程。 |
| 2 | 线程标识 | 与notify()方法的情况一样,通知被发送到多个等待线程中的单个线程,因此可以确定哪些等待线程将接收锁。 | 另一方面,notifyAll() 向所有等待线程发送通知。因此,不清楚哪个线程将接收锁。 |
| 3 | 风险因子 | 在notify()方法的情况下,线程丢失的风险很高,因为通知仅发送给单个线程,如果它丢失了,那么其他线程将不会收到通知,从而获得锁。 | 而在 notifyAll() 的情况下,它会向所有等待线程发送通知,因此如果任何线程错过了通知,就会有其他线程来完成这项工作。因此风险较小。 |
| 4 | Performance | 与 notifyAll() 方法相比,Memory 和 CPU 在 notify() 方法中消耗更少,因为通知发送到单个线程,因此与 notifyAll() 相比性能更好。 | 另一方面,没有通知的成本被降低,通知被发送到所有等待线程,与 notify() 相比,内存和 CPU 消耗更多,因此 notifyAll() 的性能较低。 |
| 5 | Interchangeable | 在notify()方法的情况下,图中只有一个线程,因此不可能存在线程可互换的概念。 | 如果所有等待线程都可以互换(它们唤醒的顺序并不重要),那么我们应该选择notifyAll()。 |
让我们了解notify()方法的行为方式:
Java
// Java program to illustrate the
// behaviour of notify() method
class Geek1 extends Thread {
public void run()
{
synchronized (this)
{
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "...starts");
try {
this.wait();
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "...notified");
}
}
}
class Geek2 extends Thread {
Geek1 geeks1;
Geek2(Geek1 geeks1){
this.geeks1 = geeks1;
}
public void run()
{
synchronized (this.geeks1)
{
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "...starts");
try {
this.geeks1.wait();
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "...notified");
}
}
}
class Geek3 extends Thread {
Geek1 geeks1;
Geek3(Geek1 geeks1) { this.geeks1 = geeks1; }
public void run()
{
synchronized (this.geeks1)
{
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "...starts");
this.geeks1.notify();
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "...notified");
}
}
}
class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws InterruptedException
{
Geek1 geeks1 = new Geek1();
Geek2 geeks2 = new Geek2(geeks1);
Geek3 geeks3 = new Geek3(geeks1);
Thread t1 = new Thread(geeks1, "Thread-1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(geeks2, "Thread-2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(geeks3, "Thread-3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
Thread.sleep(100);
t3.start();
}
}输出:
Thread-1...start Thread-2...starts Thread-3...starts Thread-3...notified Thread-1...notified
让我们了解notifyAll()方法的行为方式:
Java
// Java program to illustrate the
// behavior of notifyAll() method
class Geek1 extends Thread {
public void run()
{
synchronized (this)
{
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "...starts");
try {
this.wait();
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "...notified");
}
}
}
class Geek2 extends Thread {
Geek1 geeks1;
Geek2(Geek1 geeks1){
this.geeks1 = geeks1;
}
public void run()
{
synchronized (this.geeks1)
{
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "...starts");
try {
this.geeks1.wait();
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "...notified");
}
}
}
class Geek3 extends Thread {
Geek1 geeks1;
Geek3(Geek1 geeks1) { this.geeks1 = geeks1; }
public void run()
{
synchronized (this.geeks1)
{
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "...starts");
this.geeks1.notifyAll();
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "...notified");
}
}
}
class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws InterruptedException
{
Geek1 geeks1 = new Geek1();
Geek2 geeks2 = new Geek2(geeks1);
Geek3 geeks3 = new Geek3(geeks1);
Thread t1 = new Thread(geeks1, "Thread-1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(geeks2, "Thread-2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(geeks3, "Thread-3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
Thread.sleep(100);
t3.start();
}
}输出
Thread-1...starts Thread-2...starts Thread-3...starts Thread-3...notified Thread-1...notified Thread-2...notified
When to Use notify() method and notifyAll()?
- 在互斥锁定的情况下,只有一个等待线程在收到通知后可以执行一些有用的操作(在本例中获取锁)。在这种情况下,您宁愿使用notify()。如果实现得当,您也可以在这种情况下使用notifyAll(),但您会不必要地唤醒无论如何都无法执行任何操作的线程。
- 在某些情况下,一旦等待完成,所有等待线程都可以采取有用的操作。一个例子是一组线程等待某个任务完成;一旦任务完成,所有等待线程就可以继续其业务。在这种情况下,您可以使用notifyAll()同时唤醒所有等待线程。
Applications of notify() and notifyAll()
- 对共享资源的维护操作,其中多个线程在访问资源之前等待操作完成;对于这些,我们应该选择notifyAll()。
- 假设我们有一个生产者线程和一个消费者线程。生产者生产的每个 “packet” 都应该由消费者消费。消费者将一些东西放入队列中,然后调用notify()。
- 我们希望在漫长的过程完成时收到通知。您需要蜂鸣声和屏幕更新。该进程执行notifyAll()来通知蜂鸣线程和screen-update-thread。
相关用法
- Java notify()和notifyAll()的区别用法及代码示例
- Java next()和nextLine()的区别用法及代码示例
- Java String compareToIgnoreCase()用法及代码示例
- Java String compareTo()用法及代码示例
- Java String split()用法及代码示例
- Java String length()用法及代码示例
- Java String replace()用法及代码示例
- Java String replaceAll()用法及代码示例
- Java String substring()用法及代码示例
- Java String equals()用法及代码示例
- Java String equalsIgnoreCase()用法及代码示例
- Java String contains()用法及代码示例
- Java String indexOf()用法及代码示例
- Java String trim()用法及代码示例
- Java String charAt()用法及代码示例
- Java String toLowerCase()用法及代码示例
- Java String concat()用法及代码示例
- Java String valueOf()用法及代码示例
- Java String matches()用法及代码示例
- Java String startsWith()用法及代码示例
- Java String endsWith()用法及代码示例
- Java String isEmpty()用法及代码示例
- Java String intern()用法及代码示例
- Java String getBytes()用法及代码示例
- Java String contentEquals()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自佚名大神的英文原创作品 Difference Between notify() and notifyAll() in Java。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
