d3.js中的geoConicEquidistant()函数用于从给定的geojson数据绘制圆锥等距投影。
用法:
d3.geoConicEquidistant()
参数:此方法不接受任何参数。
返回值:此方法返回圆锥等距投影。
范例1:下面的示例绘制中心在(0,0)且旋转0度的圆锥形等距投影。
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://d3js.org/d3.v4.js">
</script>
<script src=
"https://d3js.org/d3-geo-projection.v2.min.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width:700px; height:500px;">
<svg width="600" height="450"></svg>
</div>
<script>
var svg = d3.select("svg"),
width = +svg.attr("width"),
height = +svg.attr("height");
// ConicEquidistant projection
// with center at (0, 0) and
// rotation of 0 degrees
var gfg = d3.geoConicEquidistant()
.scale(width / 1.8 / Math.PI)
.rotate([0, 0])
.center([0, 0])
.translate([width / 2, height / 2]);
// Loading the json data
d3.json("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/" +
"janasayantan/datageojson/master/" +
"world.json",
function (data) {
// Drawing the map
svg.append("g")
.selectAll("path")
.data(data.features)
.enter().append("path")
.attr("fill", "Black")
.attr("d", d3.geoPath()
.projection(gfg)
)
.style("stroke", "#ffff")
});
</script>
</body>
</html>输出:
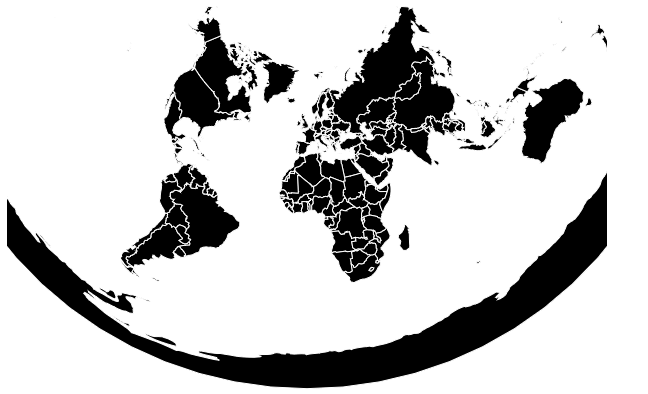
范例2:下面的示例绘制中心在(-10,0)且相对于y轴旋转90度的圆锥的等距投影。
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://d3js.org/d3.v4.js">
</script>
<script src=
"https://d3js.org/d3-geo-projection.v2.min.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width:700px; height:600px;">
<svg width="500" height="450"></svg>
</div>
<script>
var svg = d3.select("svg"),
width = +svg.attr("width"),
height = +svg.attr("height");
// ConicEquidistant projection
// center at (-10,0) and 90 degrees
// rotation w.r.t y-axis
var gfg = d3.geoConicEquidistant()
.scale(width / 1.8 / Math.PI)
.rotate([90, 0])
.center([-10, 0])
.translate([width / 2, height / 2]);
// Loading the json data
d3.json("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/" +
"janasayantan/datageojson/master/" +
"world.json",
function (data) {
// Draw the map
svg.append("g")
.selectAll("path")
.data(data.features)
.enter().append("path")
.attr("fill", "grey")
.attr("d", d3.geoPath()
.projection(gfg)
)
.style("stroke", "#ffff")
});
</script>
</body>
</html>输出:
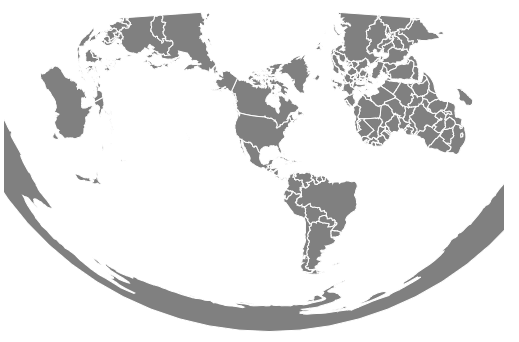
相关用法
- PHP imagecreatetruecolor()用法及代码示例
- p5.js year()用法及代码示例
- d3.js d3.utcTuesdays()用法及代码示例
- PHP ImagickDraw getTextAlignment()用法及代码示例
- PHP Ds\Sequence last()用法及代码示例
- PHP array_udiff_uassoc()用法及代码示例
- PHP geoip_continent_code_by_name()用法及代码示例
- d3.js d3.map.set()用法及代码示例
- PHP GmagickPixel setcolor()用法及代码示例
- PHP opendir()用法及代码示例
- PHP cal_to_jd()用法及代码示例
- d3.js d3.bisectLeft()用法及代码示例
- PHP stream_get_transports()用法及代码示例
- PHP Ds\Deque pop()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自jana_sayantan大神的英文原创作品 D3.js geoConicEquidistant() Function。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
