density.weight()函数用于设置密度轮廓估计器函数的权重访问器。如果给出了权重,则此函数将访问权设置为点权重,否则将访问器设置为默认值1。
用法:
d3.contourDensity.x().y().weight([weight]);
参数:此函数采用上面给出的一个参数,如下所述:
- weight:它使用一个数字来设置点权重的访问器。
返回值:此函数不返回任何内容。
下面给出了一些density.weight()函数的示例。
范例1:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="
width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<script type="text/javascript"
src="https://d3js.org/d3.v4.min.js">
</script>
<script src=
"https://d3js.org/d3-contour.v1.min.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1 style="color:green">GeeksforGeeks</h1>
<script>
// append the svg object to the body.
var svg = d3.select("body")
.append("svg")
.attr("width", 530)
.attr("height", 480)
.append("g")
.attr("transform",
"translate(" + 40 + ", " + -80 + ")");
// read data
d3.csv("./data.csv", function(data) {
var y = d3.scaleLinear()
.domain([2, 30])
.range([ 300, 100 ]);
var x = d3.scaleLinear()
.domain([2, 22])
.range([ 0, 200]);
svg.append("g")
.call(d3.axisLeft(y));
svg.append("g")
.attr("transform", "translate(0, " + 300 + ")")
.call(d3.axisBottom(x));
var density= d3.contourDensity()
.y(function(d) { return y(d.y); })
.bandwidth(15)
// Use of weight function
.weight(0.007)
.x(function(d) { return x(d.x); })(data)
svg.selectAll("path")
.data(density)
.enter()
.append("path")
.attr("d", d3.geoPath())
.attr("fill", "none")
.attr("stroke", "green")
});
// Data for csv file
// x, y, group
// 9.45, 14.14, H
// 9.1, 14.14, H
// 9.9, 9.9, H
// 9.6, 14.5, H
// 9.1, 9.7, H
// 14.7, 9.5, H
// 7.9, 9.6, H
// 14.7, 9.7, H
// 9.45, 14.14, H
// 12.1, 9.14, H
// 7.5, 9, H
// 14.5, 14.5, H
// 9.45, 9.7, H
// 14.45, 9.6, H
// 9.5, 7.6, H
// 9, 9.45, H
// 14.7, 12, H
// 9.7, 9.7, H
// 9.6, 9, H
// 12, 9, H
// 9.45, 14.5, H
// 9.9, 14.6, H
// 12.7, 9.9, H
// 9, 12.14, H
// 9, 14.9, H
// 9.5, 9.7, H
// 9.7, 14.7, H
// 9.9, 14.5, H
// 14, 14.5, H
// 7.9, 9, H
// 9.9, 9.45, H
// 9, 14.14, H
// 14.7, 9.7, H
// 14.5, 9.9, H
</script>
</body>
</html> 输出:
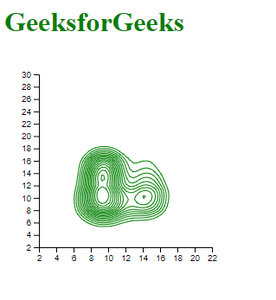
范例2:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="
width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<script type="text/javascript"
src="https://d3js.org/d3.v4.min.js">
</script>
<script src=
"https://d3js.org/d3-contour.v1.min.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1 style="color:green">GeeksforGeeks</h1>
<script>
// append the svg object to the body.
var svg = d3.select("body")
.append("svg")
.attr("width", 530)
.attr("height", 480)
.append("g")
.attr("transform",
"translate(" + 40 + ", " + -80 + ")");
// read data
d3.csv("./data.csv", function(data) {
var y = d3.scaleLinear()
.domain([2, 30])
.range([ 300, 100 ]);
var x = d3.scaleLinear()
.domain([2, 22])
.range([ 0, 200]);
svg.append("g")
.call(d3.axisLeft(y));
svg.append("g")
.attr("transform", "translate(0, " + 300 + ")")
.call(d3.axisBottom(x));
var density= d3.contourDensity()
.y(function(d) { return y(d.y); })
.bandwidth(15)
// Use of weight function
.weight(48888)
.x(function(d) { return x(d.x); })(data)
svg.selectAll("path")
.data(density)
.enter()
.append("path")
.attr("d", d3.geoPath())
.attr("fill", "none")
.attr("stroke", "green")
});
// Data for csv file
// x, y, group
// 9.45, 14.14, H
// 9.1, 14.14, H
// 9.9, 9.9, H
// 9.6, 14.5, H
// 9.1, 9.7, H
// 14.7, 9.5, H
// 7.9, 9.6, H
// 14.7, 9.7, H
// 9.45, 14.14, H
// 12.1, 9.14, H
// 7.5, 9, H
// 14.5, 14.5, H
// 9.45, 9.7, H
// 14.45, 9.6, H
// 9.5, 7.6, H
// 9, 9.45, H
// 14.7, 12, H
// 9.7, 9.7, H
// 9.6, 9, H
// 12, 9, H
// 9.45, 14.5, H
// 9.9, 14.6, H
// 12.7, 9.9, H
// 9, 12.14, H
// 9, 14.9, H
// 9.5, 9.7, H
// 9.7, 14.7, H
// 9.9, 14.5, H
// 14, 14.5, H
// 7.9, 9, H
// 9.9, 9.45, H
// 9, 14.14, H
// 14.7, 9.7, H
// 14.5, 9.9, H
</script>
</body>
</html> 输出:
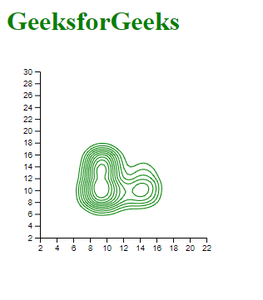
相关用法
- PHP imagecreatetruecolor()用法及代码示例
- p5.js year()用法及代码示例
- d3.js d3.utcTuesdays()用法及代码示例
- PHP ImagickDraw getTextAlignment()用法及代码示例
- PHP Ds\Sequence last()用法及代码示例
- PHP array_udiff_uassoc()用法及代码示例
- PHP geoip_continent_code_by_name()用法及代码示例
- d3.js d3.map.set()用法及代码示例
- PHP GmagickPixel setcolor()用法及代码示例
- PHP opendir()用法及代码示例
- PHP cal_to_jd()用法及代码示例
- d3.js d3.bisectLeft()用法及代码示例
- PHP stream_get_transports()用法及代码示例
- PHP Ds\Deque pop()用法及代码示例
注:本文由纯净天空筛选整理自tarun007大神的英文原创作品 D3.js density.weight() Function。非经特殊声明,原始代码版权归原作者所有,本译文未经允许或授权,请勿转载或复制。
