用法:
RandomState.logistic(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=None)從物流分布中抽取樣本。
從具有指定參數,位置(位置或均值,也為中位數)和比例(> 0)的對數分布中抽取樣本。
參數: - loc: : float 或 array_like of floats, 可選參數
分布參數。默認值為0。
- scale: : float 或 array_like of floats, 可選參數
分布參數。必須為非負數。默認值為1。
- size: : int 或 tuple of ints, 可選參數
輸出形狀。如果給定的形狀是
(m, n, k), 然後m * n * k抽取樣品。如果尺寸是None(默認),如果返回一個值loc和scale都是標量。除此以外,np.broadcast(loc, scale).size抽取樣品。
返回值: - out: : ndarray或標量
從參數化邏輯分布中抽取樣本。
注意:
Logistic分布的概率密度為
哪裏
=位置和
=比例。
Logistic分布用於極值問題,在流行病學中可以混合使用Gumbel分布,在世界象棋聯合會(FIDE)中也用於Elo排名係統,假設每個玩家的表現都是邏輯分布的隨機變量。
參考文獻:
[1] Reiss,R.-D.和Thomas M.(2001),“來自保險,金融,水文學和其他領域的極值統計分析”,Birkhauser Verlag,巴塞爾,第132-133頁。 [2] Weisstein,EricW。“物流配送”。來自MathWorld-A Wolfram Web資源。http://mathworld.wolfram.com/LogisticDistribution.html [3] 維基百科,“Logistic-distribution”,https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logistic_distribution 例子:
從分布中抽取樣本:
>>> loc, scale = 10, 1 >>> s = np.random.logistic(loc, scale, 10000) >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s, bins=50)#針對分布圖
>>> def logist(x, loc, scale): ... return np.exp((loc-x)/scale)/(scale*(1+np.exp((loc-x)/scale))**2) >>> lgst_val = logist(bins, loc, scale) >>> plt.plot(bins, lgst_val * count.max() / lgst_val.max()) >>> plt.show()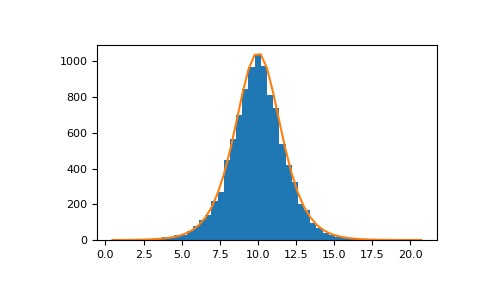
相關用法
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自 numpy.random.mtrand.RandomState.logistic。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
