在本教程中,我們將借助示例了解 Java String format() 方法。
format() 方法根據傳遞的參數返回格式化字符串。
示例
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "Java";
// format string
String formatStr = String.format("Language: %s", str);
System.out.println(formatStr);
}
}
// Output: Language: Java
format() 語法
用法:
String.format(String str, Object... args)
這裏,
format()是一個靜態方法。我們使用類名String調用format()方法。str是要格式化的字符串- 上麵代碼中的
...表示您可以將多個對象傳遞給format()。
參數:
format() 方法采用兩個參數。
- format- 格式字符串
- args- 0 個或多個參數
返回:
- 返回一個格式化的字符串
示例 1:Java 字符串 format()
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String language = "Java";
int number = 30;
String result;
// format object as a string
result = String.format("Language: %s", language);
System.out.println(result); // Language: Java
// format number as a hexadecimal number
result = String.format("Hexadecimal Number: %x", number); // 1e
System.out.println(result); // Hexadecimal Number: 1e
}
}
在上麵的程序中,注意代碼
result = String.format("Language: %s", language);
這裏,"Language: %s"是一個格式化字符串.
格式字符串中的 %s 替換為 language 的內容。 %s 是格式說明符。
類似地,%x 在 String.format("Number: %x", number) 中被替換為 number 的十六進製值。
格式說明符
以下是常用的格式說明符:
| 說明符 | 說明 |
|---|---|
%b , %B |
"true" 或 "false" 基於參數 |
%s , %S |
一個字符串 |
%c , %C |
一個 Unicode 字符 |
%d |
十進製整數(僅用於整數) |
%o |
八進製整數(僅用於整數) |
%x , %X |
十六進製整數(僅用於整數) |
%e , %E |
科學記數法(用於浮點數) |
%f |
十進製數(用於浮點數) |
示例 2:數字的字符串格式
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n1 = 47;
float n2 = 35.864f;
double n3 = 44534345.76d;
// format as an octal number
System.out.println(String.format("n1 in octal: %o", n1)); // 57
// format as hexadecimal numbers
System.out.println(String.format("n1 in hexadecimal: %x", n1)); // 2f
System.out.println(String.format("n1 in hexadecimal: %X", n1)); // 2F
// format as strings
System.out.println(String.format("n1 as string: %s", n1)); // 47
System.out.println(String.format("n2 as string: %s", n2)); // 35.864
// format in scientific notation
System.out.println(String.format("n3 in scientific notation: %g", n3)); // 4.45343e+07
}
}
輸出
n1 in octal: 57 n1 in hexadecimal: 2f n1 in hexadecimal: 2F n1 as string: 47 n2 as string: 35.864 n3 in scientific notation: 4.45343e+07
示例 3:具有多個格式說明符的字符串格式
您可以在格式字符串中使用多個格式說明符。
// using more than one format specifiers
// in a format string
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n1 = 47;
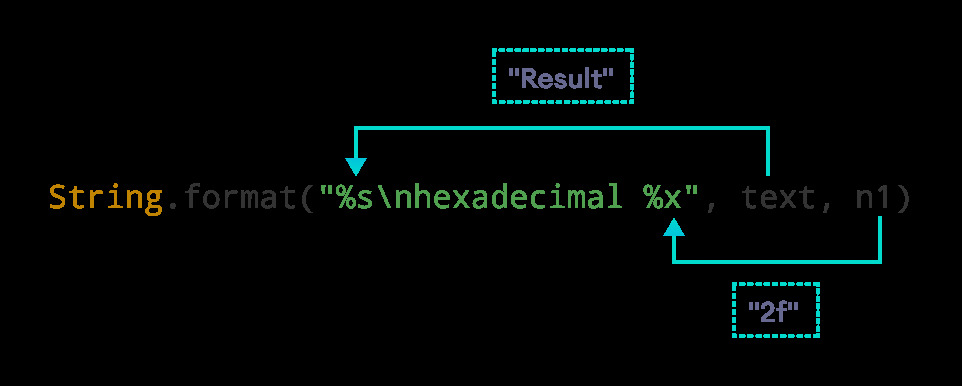
String text = "Result";
System.out.println(String.format("%s\nhexadecimal: %x", text, n1));
}
}
輸出
Result hexadecimal: 2f
在這裏,%s 被替換為 text 的值。同樣,%o 被替換為 n1 的十六進製值。
示例 4:十進製數的格式
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
float n1 = -452.534f;
double n2 = -345.766d;
// format floating-point as it is
System.out.println(String.format("n1 = %f", n1)); // -452.533997
System.out.println(String.format("n2 = %f", n2)); // -345.766000
// show up to two decimal places
System.out.println(String.format("n1 = %.2f", n1)); // -452.53
System.out.println(String.format("n2 = %.2f", n2)); // -345.77
}
}
輸出
n1 = -452.533997 n2 = -345.766000 n1 = -452.53 n2 = -345.77
注意:當我們格式化-452.534使用%f,我們得到-452.533997.這不是因為format()方法。 Java 不返回確切的浮點數的表示.
當使用%.2f 格式說明符時,format() 在小數點後給出兩個數字。
示例 5:用空格和 0 填充數字
// using more than one format specifiers
// in a format string
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n1 = 46, n2 = -46;
String result;
// padding number with spaces
// the length of the string will be 5
result = String.format("|%5d|", n1); // | 46|
System.out.println(result);
// padding number with numbers 0
// the length of the string will be 5
result = String.format("|%05d|", n1); // |00046|
System.out.println(result);
// using signs before numbers
result = String.format("%+d", n1); // +46
System.out.println(result);
result = String.format("%+d", n2); // -46
System.out.println(result);
// enclose negative number within parenthesis
// and removing the sign
result = String.format("%(d", n2); // (46)
System.out.println(result);
}
}
示例 6:在十六進製和八進製之前使用 0x 和 0
// using 0x before hexadecimal
// using 0 before octal
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 46;
System.out.println(String.format("%#o", n)); // 056
System.out.println(String.format("%#x", n)); // 0x2e
}
}
帶有語言環境的 Java 字符串 format()
如果您必須使用指定的 locale ,則 String format() 方法還有另一種語法。
String.format(Locale l,
String format,
Object... args)
示例 7:在 format() 中使用德語區域設置
// to use Locale
import java.util.Locale;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 8652145;
String result;
// using the current locale
result = String.format("Number: %,d", number);
System.out.println(result);
// using the GERMAN locale as the first argument
result = String.format(Locale.GERMAN, "Number in German: %,d", number);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
輸出
Number: 8,652,145 Number in German: 8.652.145
注意:在德國,整數由.代替,.
相關用法
- Java String format()用法及代碼示例
- Java String valueOf()用法及代碼示例
- Java String split()用法及代碼示例
- Java String strip()用法及代碼示例
- Java String getChars()用法及代碼示例
- Java String substring()用法及代碼示例
- Java String replace()用法及代碼示例
- Java String contains()用法及代碼示例
- Java String regionMatches()用法及代碼示例
- Java String copyValueOf()用法及代碼示例
- Java String isEmpty()用法及代碼示例
- Java String toString()用法及代碼示例
- Java String endsWith()用法及代碼示例
- Java String lines()用法及代碼示例
- Java String repeat()用法及代碼示例
- Java String hashCode()用法及代碼示例
- Java String lastIndexOf()用法及代碼示例
- Java String equals()用法及代碼示例
- Java String replaceAll()用法及代碼示例
- Java String startsWith()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自 Java String format()。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
