d3.js中的node.path()函數用於返回源節點和目標節點之間的最短路徑。
用法:
node.path(target);
參數:此函數接受上麵給定並在下麵描述的單個參數:
- target:此參數接受目標節點。
返回值:該函數返回一個數組。
下麵給出的是上麵給出的函數的一些例子。
範例1:從根節點到任何其他節點的路徑。
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" path1tent=
"width=device-width, initial-scale = 1.0" />
<script src=
"https://d3js.org/d3.v4.min.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// Constructing a tree
var tree = {
name:"rootNode",
children:[
{
name:"child1"
},
{
name:"child2",
children:[
{
name:"grandchild1",
children:[
{ name:"grand granchild1" },
{ name:"grand granchild2" }
]
},
]
},
{
name:"child3",
children:[
{ name:"grandchild2" },
{ name:"grandchild3" },
{ name:"grandchild4" },
{ name:"grandchild5" }
]
}
]
};
var obj = d3.hierarchy(tree);
// Printing path from rootnode
// to grand granchild1
console.log(obj.path(obj.children[1].
children[0].children[0]));
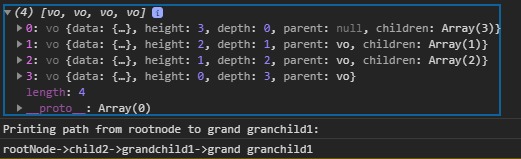
console.log("Printing path from rootnode"
+ "to grand granchild1:");
let path = obj.path(obj.children[1]
.children[0].children[0]);
console.log(path[0].data.name + "->"
+ path[1].data.name + "->"
+ path[2].data.name + "->"
+ path[3].data.name);
</script>
</body>
</html>輸出:
範例2:以下代碼演示了從任何節點到任何其他節點的路徑。
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" path1tent=
"width=device-width, initial-scale = 1.0" />
<script src=
"https://d3js.org/d3.v4.min.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// Constructing a tree
var tree = {
name:"rootNode",
children:[
{
name:"child1"
},
{
name:"child2",
children:[
{
name:"grandchild1",
children:[
{ name:"grand granchild1" },
{ name:"grand granchild2" }
]
},
]
},
{
name:"child3",
children:[
{ name:"grandchild2" },
{ name:"grandchild3" },
{ name:"grandchild4" },
{ name:"grandchild5" }
]
}
]
};
var obj = d3.hierarchy(tree);
// Printing path from any node to
// any other node
var grandchild3 = obj.children[2].children[1];
var child2 = obj.children[1];
console.log(grandchild3.path(child2));
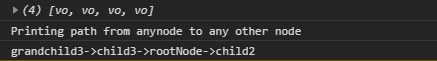
console.log("Printing path from anynode to"
+ " any other node ");
let path = grandchild3.path(child2);
console.log(path[0].data.name + "->"
+ path[1].data.name + "->"
+ path[2].data.name + "->"
+ path[3].data.name);
</script>
</body>
</html>輸出:
相關用法
- PHP imagecreatetruecolor()用法及代碼示例
- p5.js year()用法及代碼示例
- d3.js d3.utcTuesdays()用法及代碼示例
- PHP ImagickDraw getTextAlignment()用法及代碼示例
- PHP Ds\Sequence last()用法及代碼示例
- PHP array_udiff_uassoc()用法及代碼示例
- PHP geoip_continent_code_by_name()用法及代碼示例
- d3.js d3.map.set()用法及代碼示例
- PHP GmagickPixel setcolor()用法及代碼示例
- PHP opendir()用法及代碼示例
- PHP cal_to_jd()用法及代碼示例
- d3.js d3.bisectLeft()用法及代碼示例
- PHP stream_get_transports()用法及代碼示例
- PHP Ds\Deque pop()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自tarun007大神的英文原創作品 D3.js node.path() Function。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
