函數malloc()在 C++ 中用於分配請求的字節大小,並返回指向已分配內存的第一個字節的指針。 Amalloc()在C++中是一個在運行時分配內存的函數,因此,malloc()是一種動態內存分配技術。如果失敗則返回空指針。
用法:
pointer_name = (cast-type*) malloc(size);
這裏,size是一個無符號整數值(轉換為size_t),它表示以字節為單位的內存塊
malloc()在 C++ 中 分配 size 字節的內存塊,返回指向塊開頭的指針。新分配的內存塊的內容未初始化,保留不確定的值。 Malloc 函數存在於 <cstdlib> 頭文件中。
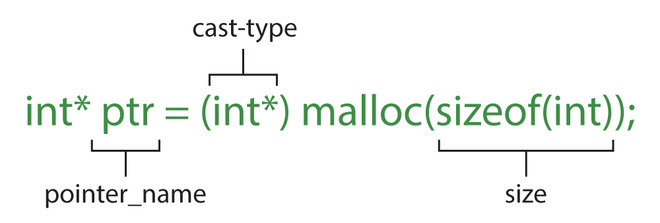
malloc() 的語法
malloc() 的返回類型
如果大小為零,則返回值取決於特定的庫實現(它可能是也可能不是空指針),但返回的指針不應被取消引用。
- 空指針用於函數分配的未初始化、已初始化的內存塊
- 空指針如果分配失敗
內存塊的工作和分配使用malloc()
示例 1:
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate working of malloc()
// cstdlib is used to use malloc function
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// size_t is an integer data type which can assign
// greater than or equal to 0 integer values
size_t s = 0; // s is SIZE
// malloc declaration/initialization
int* ptr = (int*)malloc(s);
// return condition if the memory block is not
// initialized
if (ptr == NULL) {
cout << "Null pointer has been returned";
}
// condition printing the message if the memory is
// initialized
else {
cout << "Memory has been allocated at address "
<< ptr << endl;
}
free(ptr);
return 0;
}輸出
Memory has been allocated at address 0x8cae70
free() 函數 在C++中用於動態地de-allocate memory 。
示例 2:
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate working of malloc()
#include <iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// variable declaration
int var_len = 10;
// pointer variable declaration
int *ptr;
// allocating memory to the pointer variable using malloc()
ptr = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int)*var_len);
for(int i=0;i<var_len;i++)
{
cout << "Enter a number : " << endl;
cin >> *(ptr+i);
}
cout << "Entered elements are : " << endl;
for(int i=0;i<var_len;i++)
{
cout << *(ptr+i) << endl;
}
free(ptr);
return 0;
}輸出:
malloc()初始化的輸出
Malloc應該用在什麽地方?
1. 動態內存分配
動態內存分配幫助我們根據用戶的需求分配一塊內存。它返回一個指向該內存開頭的指針,可以像數組一樣對待它。
2.堆內存
malloc() 在堆上分配內存位置,並在堆棧上返回一個指針,指向正在分配的數組類型內存的起始地址,而靜態數組大小對程序在任一時刻可以處理的數據量設置了硬性上限時間,無需重新編譯。
3. 更長的使用壽命
使用 malloc 創建的變量或數組將存在終生,直到被清除為止。這對於 linked lists 、 binary heap 等各種數據結構非常重要。
新和malloc()之間的區別
| 新的 | 分配內存 |
|---|---|
| 新是一個操作符 | malloc() 是函數 |
| 新調用構造函數 | malloc()不調用構造函數 |
| 新返回確切的數據類型 | malloc()返回空白* |
| 新的永遠不會返回NULL(失敗時會拋出) | malloc() 返回 NULL |
| new 不處理內存的重新分配 | 內存的重新分配可以通過malloc來處理 |
| 新的分配內存並調用構造函數 | 僅分配內存分配內存 |
相關用法
- C++ malloc()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map at()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map begin()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map cbegin()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map cend()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map clear()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map crbegin()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map crend()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map empty()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map end()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map size()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map swap()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map::max_size()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map count()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map emplace()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map emplace_hint()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map equal_range()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map erase()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map find()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map insert()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map key_comp()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map lower_bound()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map max_size()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map rbegin()用法及代碼示例
- C++ map upper_bound()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自harsh_shokeen大神的英文原創作品 C++ malloc()。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
