AbstractQueueJava 中的類是Java集合框架並實施集合接口和AbstractCollection類。它提供了一些框架的實現隊列運營。當基本實現不允許空元素時,此類中的實現是合適的。 add、remove 和 element 方法分別基於 Offer、poll 和 peek,但會拋出異常,而不是通過 false 或 null 返返回指示失敗。
類層次結構:
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractCollection<E>
↳ Class AbstractQueue<E>
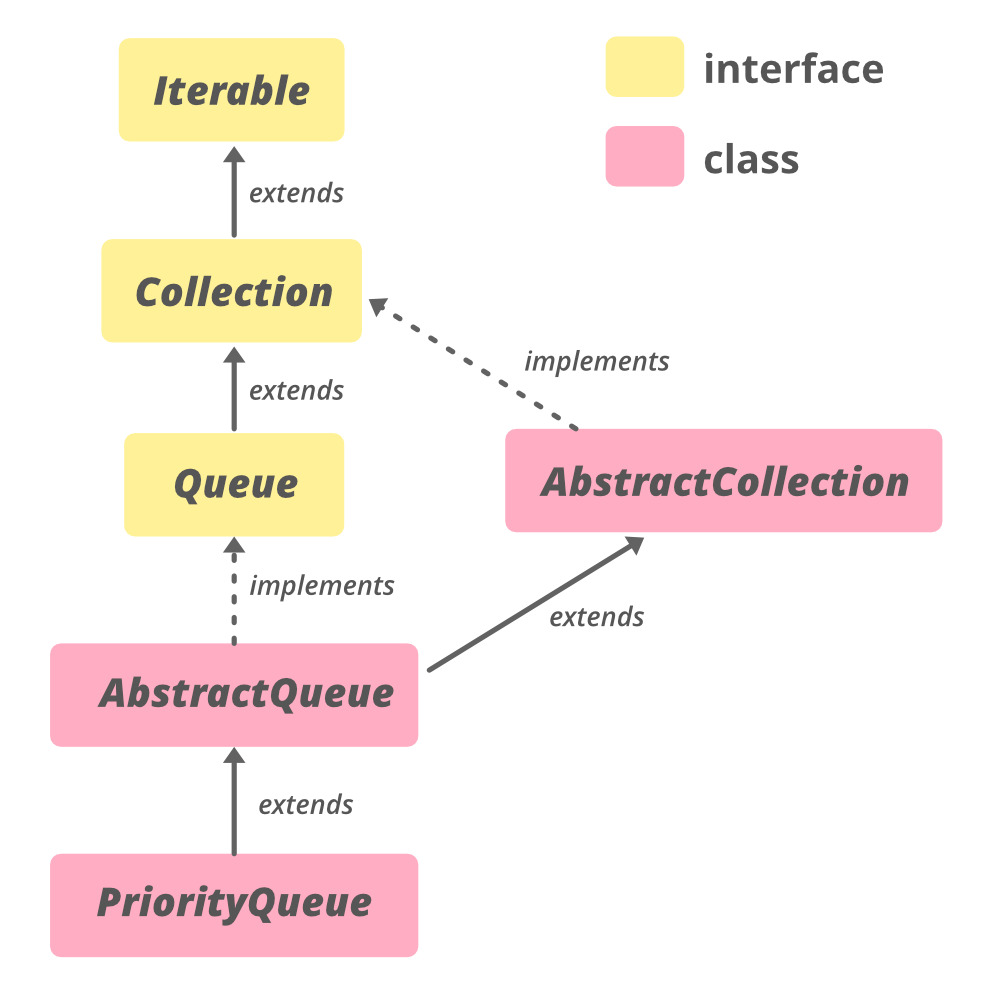
這個類實現了可迭代<E>,集合<E>,Queue接口和擴展AbstractCollection
聲明:
public abstract class AbstractQueue<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements Queue<E>
E - 由集合框架類或接口維護的元素類型。
Java 中的構造函數AbstractQueue
由於AbstractQueue是一個抽象類,因此它的實現由其子類提供。下麵顯示了可以提供實現的類的列表。要創建它,我們需要從 java.util.AbstractQueue 中獲取它。
受保護AbstractQueue():默認構造函數,但由於是抽象的,因此不允許創建AbstractQueue對象。該實現應該由其子類之一提供,例如ArrayBlockingQueue,ConcurrentLinkedQueue,DelayQueue Class,LinkedBlockingDeque,LinkedBlockingQueue,LinkedTransferQueue,PriorityBlockingQueue,PriorityQueue,SynchronousQueue.
AbstractQueue<E> objName = new ArrayBlockingQueue<E>();
下麵是一個示例程序,用於說明 Java 中的AbstractQueue:
Java
// Java code to illustrate AbstractQueue
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
public class AbstractQueueExample {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception
{
// Creating object of AbstractQueue<Integer>
AbstractQueue<Integer> AQ = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>();
// Adding elements to the Queue
AQ.add(10);
AQ.add(20);
AQ.add(30);
AQ.add(40);
AQ.add(50);
// print the queue contents to the console
System.out.println("AbstractQueue contains: " + AQ);
}
}AbstractQueue contains: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
Basic Operations
1. 添加元素
為了向 AbstractQueue 添加元素,它提供了兩種方法。這AbstractQueue add()方法將指定的元素插入到此隊列中(如果可以立即執行此操作而不違反容量限製)。成功後返回 true 並拋出IllegalStateException如果當前沒有可用空間。這AbstractQueue addAll()方法將指定集合中的所有元素添加到此隊列中。
Java
// Java program to illustrate the
// adding elements to the AbstractQueue
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
public class AddingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception
{
// Since AbstractQueue is an abstract class
// create object using LinkedBlockingQueue
AbstractQueue<Integer> AQ1 = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>();
// Populating AQ
AQ1.add(10);
AQ1.add(20);
AQ1.add(30);
AQ1.add(40);
AQ1.add(50);
// print AQ
System.out.println("AbstractQueue contains : "
+ AQ1);
// Since AbstractQueue is an abstract class
// create object using LinkedBlockingQueue
AbstractQueue<Integer> AQ2 = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>();
// print AQ2 initially
System.out.println("AbstractQueue2 initially contains : " + AQ2);
// adds elements of AQ1 in AQ2
AQ2.addAll(AQ1);
System.out.println( "AbstractQueue1 after addition contains : " + AQ2);
}
}AbstractQueue contains : [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] AbstractQueue2 initially contains : [] AbstractQueue1 after addition contains : [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
2. 刪除元素
要從 AbstractQueue 中刪除元素,它提供了 remove() 和 clear() 方法。
Java
// Java program to illustrate the
// removal of elements from AbstractQueue
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
public class RemovingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception
{
// Since AbstractQueue is an abstract class
// create object using LinkedBlockingQueue
AbstractQueue<Integer> AQ1 = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>();
// Add elements using add method
AQ1.add(10);
AQ1.add(20);
AQ1.add(30);
AQ1.add(40);
AQ1.add(50);
// print the queue contents to the console
System.out.println("AbstractQueue1 contains : " + AQ1);
// Retrieves the head
int head = AQ1.remove();
// print the head element to the console
System.out.println("head : " + head);
// print the modified queue
System.out.println("AbstractQueue1 after removal of head : " + AQ1);
// remove all the elements
AQ1.clear();
// print the modified queue
System.out.println("AbstractQueue1 : " + AQ1);
}
}AbstractQueue1 contains : [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] head : 10 AbstractQueue1 after removal of head : [20, 30, 40, 50] AbstractQueue1 : []
3. 訪問元素
AbstractQueue 的 element() 方法檢索但不刪除該隊列的頭部。
Java
// Java program to illustrate the
// accessing element from AbstractQueue
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
public class AccessingElementExample {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception
{
// Since AbstractQueue is an abstract class
// create object using LinkedBlockingQueue
AbstractQueue<Integer> AQ1 = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>();
// Populating AQ1 using add method
AQ1.add(10);
AQ1.add(20);
AQ1.add(30);
AQ1.add(40);
AQ1.add(50);
// print AQ to the console
System.out.println("AbstractQueue1 contains : " + AQ1);
// access the head element
System.out.println("head : " + AQ1.element());
}
}AbstractQueue1 contains : [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] head : 10
AbstractQueue的方法
|
METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | 如果可以在不違反容量限製的情況下立即將指定元素插入此隊列,則成功時返回 true,如果當前沒有可用空間,則拋出 IllegalStateException。 |
| addAll(集合 <? 擴展 E> c) | 將指定集合中的所有元素添加到此隊列中。 |
| clear() | 從此隊列中刪除所有元素。 |
| element() | 檢索但不刪除此隊列的頭部。 |
| remove() | 檢索並刪除此隊列的頭部。 |
類 java.util.AbstractCollection 中聲明的方法
|
METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| contains(Object o) | 如果此集合包含指定元素,則返回 true。 |
| containsAll(集合<?> c) | 如果此集合包含指定集合中的所有元素,則返回 true。 |
| isEmpty() | 如果此集合不包含任何元素,則返回 true。 |
| iterator() | 返回此集合中包含的元素的迭代器。 |
| remove(Object o) | 從此集合中刪除指定元素的單個實例(如果存在)(可選操作)。 |
| 移除全部(集合<?> c) | 刪除指定集合中也包含的所有該集合的元素(可選操作)。 |
| keepAll(集合<?> c) | 僅保留此集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可選操作)。 |
| toArray() | 返回一個包含此集合中所有元素的數組。 |
| toArray(T[] a) | 返回一個包含該集合中所有元素的數組;返回數組的運行時類型是指定數組的運行時類型。 |
| toString() | 返回此集合的字符串表示形式。 |
接口 java.util.Collection 中聲明的方法
|
METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| contains(Object o) | 如果此集合包含指定元素,則返回 true。 |
| containsAll(集合<?> c) | 如果此集合包含指定集合中的所有元素,則返回 true。 |
| equals(Object o) | 比較指定對象與此集合是否相等。 |
| hashCode() | 返回此集合的哈希碼值。 |
| isEmpty() | 如果此集合不包含任何元素,則返回 true。 |
| iterator() | 返回此集合中元素的迭代器。 |
| parallelStream() | 返回一個可能並行的 Stream 並以此集合作為其源。 |
| remove(Object o) | 從此集合中刪除指定元素的單個實例(如果存在)(可選操作)。 |
| 移除全部(集合<?> c) | 刪除指定集合中也包含的所有該集合的元素(可選操作)。 |
| removeIf(Predicate<? super E> 過濾器) | 刪除此集合中滿足給定謂詞的所有元素。 |
| keepAll(集合<?> c) | 僅保留此集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可選操作)。 |
| size() | 返回此集合中的元素數量。 |
| spliterator() | 在此集合中的元素上創建一個 Spliterator。 |
| stream() | 返回以此集合作為源的順序 Stream。 |
| toArray() | 返回一個包含此集合中所有元素的數組。 |
| toArray(IntFunction<T[]> 生成器) | 返回一個包含此集合中所有元素的數組,使用提供的生成器函數分配返回的數組。 |
| toArray(T[] a) | 返回一個包含該集合中所有元素的數組;返回數組的運行時類型是指定數組的運行時類型。 |
接口 java.lang.Iterable 中聲明的方法
|
METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Iterable forEach() | 對 Iterable 的每個元素執行給定的操作,直到處理完所有元素或該操作引發異常。 |
接口 java.util.Queue 中聲明的方法
|
METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Queue offer() | 如果可以在不違反容量限製的情況下立即執行此操作,則將指定元素插入此隊列。 |
| Queue peek() | 檢索但不刪除此隊列的頭部,如果此隊列為空,則返回 null。 |
| Queue poll() | 檢索並刪除此隊列的頭部,如果此隊列為空,則返回 null。 |
參考: https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/docs/api/java.base/java/util/AbstractQueue.html
解釋
在Java中,抽象隊列是一種遵循先進先出(First-In-First-Out)原則的數據結構,這意味著添加到隊列中的第一個元素是第一個被刪除的元素。抽象隊列是一個抽象類,它作為Java中各種隊列實現的基類。
抽象隊列提供了一組所有隊列實現都通用的方法,例如向隊列後麵添加元素、從隊列前麵刪除元素以及在不進行任何操作的情況下查看隊列前麵的元素。刪除它。這些方法在抽象類中定義,可以被具體隊列實現覆蓋。
抽象隊列類提供的一些常用方法是:
add():該方法用於向隊列末尾添加一個元素。如果隊列已滿,則會拋出異常。
offer():該方法用於向隊列末尾添加一個元素。如果隊列已滿,則返回 false。
remove():該方法用於移除並返回隊列前麵的元素。如果隊列為空,則會拋出異常。
poll():該方法用於移除並返回隊列前麵的元素。如果隊列為空,則返回null。
element():該方法用於查看隊列前麵的元素而不刪除它。如果隊列為空,則會拋出異常。
peek():該方法用於查看隊列前麵的元素而不刪除它。如果隊列為空,則返回null。
Java中抽象隊列的一些具體實現是:
LinkedList:Java中的LinkedList類實現了Queue接口,並提供了抽象隊列的具體實現。
ArrayDeque:Java中的ArrayDeque類提供了抽象隊列的resizable-array實現。
PriorityQueue:Java中的PriorityQueue類提供了一個基於優先級堆的無界優先級隊列。
Java 中的抽象隊列在各種需要按照添加順序處理元素的應用程序中非常有用。它用於以下情況:
在消息係統中實現消息隊列。
在多線程應用程序中實現任務隊列。
在流係統中實現數據處理的緩衝區。
總的來說,Java 中的抽象隊列是一個通用且強大的工具,用於以先進先出的方式管理數據集合。
程序
Java
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class QueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new queue
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// Add elements to the queue
queue.add("Alice");
queue.add("Bob");
queue.add("Charlie");
queue.add("David");
// Print the elements in the queue
System.out.println("Queue: " + queue);
// Remove the first element from the queue
String first = queue.remove();
System.out.println("Removed element: " + first);
// Print the remaining elements in the queue
System.out.println("Queue: " + queue);
// Peek at the first element in the queue
String peeked = queue.peek();
System.out.println("Peeked element: " + peeked);
// Print the remaining elements in the queue
System.out.println("Queue: " + queue);
}
}Queue: [Alice, Bob, Charlie, David] Removed element: Alice Queue: [Bob, Charlie, David] Peeked element: Bob Queue: [Bob, Charlie, David]
在此示例中,我們使用具體實現 LinkedList 創建一個新隊列。然後,我們將四個元素添加到隊列中,並使用 System.out.println() 語句打印這些元素。
然後,我們使用 remove() 方法從隊列中刪除第一個元素並打印刪除的元素。我們使用 System.out.println() 語句再次打印隊列中的剩餘元素。
然後,我們使用 peek() 方法查看隊列中的第一個元素並打印查看的元素。最後,我們使用 System.out.println() 語句打印隊列中的剩餘元素。
時間和空間複雜度
Java 中抽象隊列的時間和空間複雜度取決於所使用的具體實現。在這個例子中,我們使用LinkedList來實現隊列。
對LinkedList的各種操作的時間複雜度如下:
添加(元素):O(1)
remove():O(1)
peek():O(1)
因此,向隊列添加一個元素、從隊列中刪除一個元素以及查看隊列中的第一個元素的時間複雜度都是 O(1)。
使用 LinkedList 實現的隊列的空間複雜度為 O(n),其中 n 是隊列中元素的數量。這是因為 LinkedList 內部使用動態數組來存儲其元素,當添加或刪除元素時可能需要調整該數組的大小。但是,確切的空間複雜度可能取決於LinkedList 類的實現細節。
綜上所述,使用 LinkedList 實現的抽象隊列中添加、刪除和查看元素的時間複雜度為 O(1),空間複雜度為 O(n)
相關用法
- Java AbstractQueue add()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractQueue addAll()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractQueue clear()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractQueue element()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractQueue remove()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractCollection add()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractCollection addAll()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractCollection clear()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractCollection contains()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractCollection containsAll()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractCollection isEmpty()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractCollection remove()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractCollection removeAll()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractCollection retainAll()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractCollection size()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractCollection toArray()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractCollection toString()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractList addAll()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractList clear()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractList equals()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractList get()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractList hashCode()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractList indexOf()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractList iterator()用法及代碼示例
- Java AbstractList lastIndexOf()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自RishabhPrabhu大神的英文原創作品 AbstractQueue in Java with Examples。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
