問題:實現一個棧,要求含有函數push, pop, min,並且他們的時間複雜度都是O(1)。
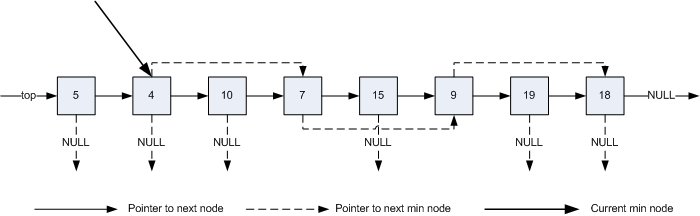
解決思路:如圖1所示,在普通棧的基礎上,增加當前最小節點的指針currentMinNode,以及指向下一個最小節點的指針
nextMinNode。當push元素到棧裏麵時,如果新元素小於棧中的currentMinNode,需要更新當前最小元素指針currentMinNode,
使它指向新元素;如果新元素不小於currentMinNode,和普通棧一樣直接添加新節點。當從棧中POP元素時,如果當前棧頂
節點的nextMinNode為空,則和普通棧一樣直接刪除棧頂節點;如果當前棧頂節點的nextMinNode不為空,則更新currentMinNode
指向棧頂節點的nextMinNode,然後再刪除棧頂節點。本文主要說明求棧中最小值的情形,實際上,這裏的處理思路可以很方便的遷移到求棧中最大值的情形。
圖1 含有MIN函數的棧的結構
含有MIN函數的棧的C語言實現源碼如下,這裏棧中可存儲的數據是簡單的INT類型。
/*
* File: stack.h
* Purpose: implementation of stack which having MIN function in c
* Author: puresky
*/
#ifndef _STACK_H
#define _STACK_H
typedef struct StackNodeStruct StackNode;
struct StackNodeStruct
{
int _data;
struct StackNodeStruct *_next;
struct StackNodeStruct *_nextMinNode;
};
typedef struct StackStruct Stack;
struct StackStruct
{
StackNode *_top;
StackNode *_currentMinNode;
int _count;
};
Stack *stack_new();
void stack_free(Stack *st);
void stack_push(Stack *st, int data);
int stack_top(Stack *st);
int stack_pop(Stack *st);
int stack_min(Stack *st);
int stack_size(Stack *st);
int stack_empty(Stack *st);
void stack_print(Stack *st);
#endif
/*
* File: stack.c
* Purpose: implementation of stack in c
* Author: puresky
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "stack.h"
StackNode *stack_node_new(int data)
{
StackNode *stn = (StackNode *)malloc(sizeof(StackNode));
stn->_data = data;
stn->_next = NULL;
stn->_nextMinNode = NULL;
return stn;
}
void stack_node_free(StackNode *stn)
{
if(stn)
{
free(stn);
}
}
Stack *stack_new()
{
Stack *st = (Stack *)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
st->_count = 0;
st->_top = NULL;
st->_currentMinNode = NULL;
return st;
}
void stack_free(Stack *st)
{
StackNode *stn;
StackNode *iter;
if(st)
{
iter = st->_top;
while(iter)
{
stn = iter;
iter = iter->_next;
stack_node_free(stn);
}
}
}
void stack_push(Stack *st, int data)
{
StackNode *stn = stack_node_new(data);
stn->_next = st->_top;
st->_top = stn;
st->_count++;
if(st->_currentMinNode == NULL)
{
st->_currentMinNode = stn;
}
else if(stn->_data < st->_currentMinNode->_data)
{
stn->_nextMinNode = st->_currentMinNode;
st->_currentMinNode = stn;
}
else
{
stn->_nextMinNode = NULL;
}
printf("push %d\n", data);
}
int stack_top(Stack *st)
{
if(st->_top)
{
return st->_top->_data;
}
fprintf(stderr, "top error : stack is empty!\n");
return -1;
}
int stack_pop(Stack *st)
{
int ret;
StackNode *stn;
if(st->_top)
{
if(st->_top->_nextMinNode)
{
st->_currentMinNode = st->_top->_nextMinNode;
}
ret = st->_top->_data;
stn = st->_top;
st->_top = st->_top->_next;
stack_node_free(stn);
st->_count--;
printf("pop %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
fprintf(stderr, "pop error : stack is empty!\n");
return -1;
}
int stack_min(Stack *st)
{
if(st->_top)
{
return st->_currentMinNode->_data;
}
fprintf(stderr, "min error : stack is emtpy!\n");
return -1;
}
int stack_size(Stack *st)
{
return st->_count;
}
int stack_empty(Stack *st)
{
if(st->_top == NULL)
return 1;
return 0;
}
void stack_print(Stack *st)
{
StackNode *ptr = st->_top;
printf("--------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("stack size:%d\n", st->_count);
printf("stack min:%d\n", st->_currentMinNode->_data);
while(ptr)
{
printf("%d ", ptr->_data);
ptr = ptr->_next;
}
printf("\n--------------------------------------------------\n\n");
}
/*
* File: main.c
* Purpose: To test the stack
* Author: puresky
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "stack.h"
#define MAX_NUM 20
#define N 10
void init_stack(Stack *st, int size)
{
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
j = rand() % MAX_NUM;
stack_push(st, j);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
Stack *st = stack_new();
srand(time(NULL));
init_stack(st, N);
stack_print(st);
stack_pop(st);
stack_pop(st);
stack_pop(st);
stack_pop(st);
stack_pop(st);
stack_print(st);
stack_free(st);
system("pause");
return 0;
}