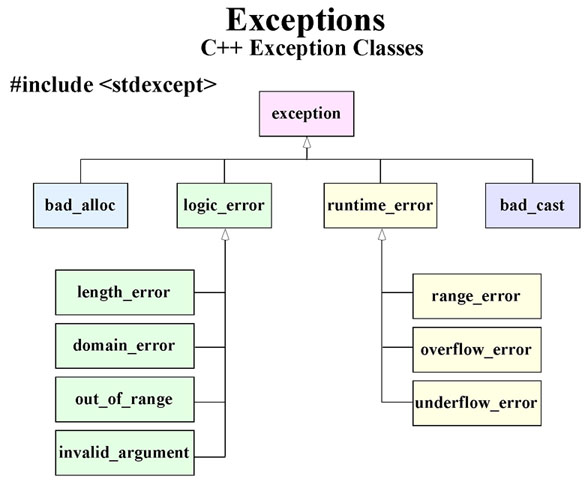
本文收集了有關C++異常的常用實例,附精簡代碼。
關鍵詞:C++異常 C++ Exception try/catch throw
- 異常捕獲:使用try/catch捕獲異常。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stdexcept>
int main() {
std::string str("foo");
try {
str.at(10); // access element, may throw std::out_of_range
} catch (const std::out_of_range& e) {
// what() is inherited from std::exception and contains an explanatory message
std::cout << e.what();
}
}
- 連續多個異常捕獲
std::string str("foo");
try {
str.reserve(2); // reserve extra capacity, may throw std::length_error
str.at(10); // access element, may throw std::out_of_range
} catch (const std::length_error& e) {
std::cout << e.what();
} catch (const std::out_of_range& e) {
std::cout << e.what();
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cout << e.what();
}
- 捕獲任意異常/捕獲所有異常,或者叫匿名捕獲異常
try {
throw 10;
} catch (...) {
std::cout << "caught an exception";
}- 異常捕獲最佳實踐:拋出異常值,捕獲異常值的引用,可以避免不必要的開銷。
try {
// throw new std::runtime_error("Error!");
// Don't do this!
// This creates an exception object
// on the heap and would require you to catch the
// pointer and manage the memory yourself. This can
// cause memory leaks! throw std::runtime_error("Error!");
} catch (const std::runtime_error& e) {
std::cout << e.what() << std::endl;
}
- 將異常簡單處理之後,繼續拋出
try {
... // some code here
} catch (const SomeException& e) {
std::cout << "caught an exception";
throw;
}- 自定義C++異常
#include <exception>
class Except: virtual public std::exception {
protected:
int error_number; ///< Error number
int error_offset; ///< Error offset
std::string error_message; ///< Error message
public:
/** Constructor (C++ STL string, int, int).
* @param msg The error message
* @param err_num Error number
* @param err_off Error offset
*/
explicit Except(const std::string& msg, int err_num, int err_off):
error_number(err_num), error_offset(err_off),error_message(msg) {}
/** Destructor.
* Virtual to allow for subclassing.
*/
virtual ~Except() throw () {}
/** Returns a pointer to the (constant) error description.
* @return A pointer to a const char*. The underlying memory
* is in possession of the Except object. Callers must
* not attempt to free the memory.
*/
virtual const char* what() const throw () {
return error_message.c_str();
}
/** Returns error number.
* @return #error_number
*/
virtual int getErrorNumber() const throw() { return error_number; }
/**Returns error offset.
* @return #error_offset
*/
virtual int getErrorOffset() const throw() { return error_offset; }
}; - 拋出上述自定義異常
try {
throw(Except("Couldn't do what you were expecting", -12, -34));
} catch (const Except& e) {
std::cout<<e.what() <<"
Error number: "<<e.getErrorNumber() <<"
Error offset: "<<e.getErrorOffset();
}
