Inheritance是OOP(Object Oriented Programming)的重要支柱。這是 Java 中的一種機製,允許一個類繼承另一個類的函數( fields 和 methods )。有兩種方法可以在繼承父類和子類的屬性的同時初始化對象。他們是:
- 子 c = 新Child():此初始化的用途是訪問父類和子類中存在的所有成員,因為我們繼承了屬性。
- 父 p = 新Child():這種類型的初始化僅用於訪問父類中存在的成員以及子類中重寫的方法。這是因為父類被向上轉換為子類。
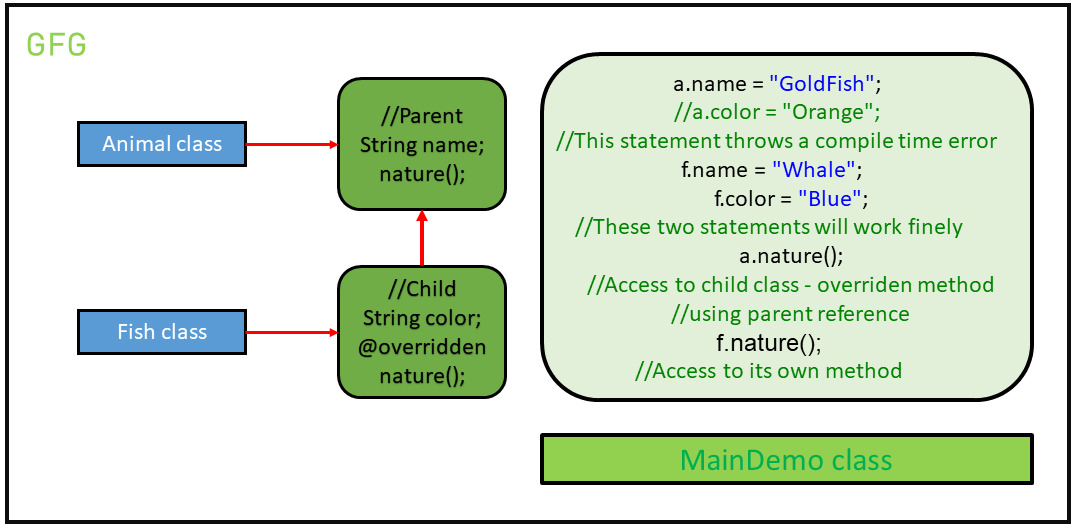
什麽是向上轉型?向上轉型是類型轉換子對象到父對象。向上轉換可以隱式完成。向上轉換使我們可以靈活地訪問父類成員,但使用此函數不可能訪問所有子類成員。我們可以訪問子類的一些指定成員,而不是所有成員。例如,我們可以訪問重寫方法.例子:讓有一個動物類。動物可以有許多不同的類別。其中一個類是魚。所以,我們假設魚類類擴展了動物類。因此,本例中的兩種繼承方式的實現方式為: 我們通過下麵的代碼來了解一下區別:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// the concept of upcasting
// Animal Class
class Animal {
String name;
// A method to print the
// nature of the class
void nature()
{
System.out.println("Animal");
}
}
// A Fish class which extends the
// animal class
class Fish extends Animal {
String color;
// Overriding the method to
// print the nature of the class
@Override
void nature()
{
System.out.println("Aquatic Animal");
}
}
// Demo class to understand
// the concept of upcasting
public class GFG {
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object to represent
// Parent p = new Child();
Animal a = new Fish();
// The object 'a' has access to
// only the parent's properties.
// That is, the colour property
// cannot be accessed from 'a'
a.name = "GoldFish";
// This statement throws
// a compile-time error
// a.color = "Orange";
// Creating an object to represent
// Child c = new Child();
Fish f = new Fish();
// The object 'f' has access to
// all the parent's properties
// along with the child's properties.
// That is, the colour property can
// also be accessed from 'f'
f.name = "Whale";
f.color = "Blue";
// Printing the 'a' properties
System.out.println("Object a");
System.out.println("Name: " + a.name);
// This statement will not work
// System.out.println("Fish1 Color" +a.color);
// Access to child class - overridden method
// using parent reference
a.nature();
// Printing the 'f' properties
System.out.println("Object f");
System.out.println("Name: " + f.name);
System.out.println("Color: " + f.color);
f.nature();
}
}輸出:
Object a Name: GoldFish Aquatic Animal Object f Name: Whale Color: Blue Aquatic Animal
- 從上麵的例子可以清楚地看出,即使是子類型,我們也不能使用父類引用來訪問子類成員。那是:
// This statement throws // a compile-time error a.color = "Orange";
- 從上麵的例子中,我們還可以觀察到我們能夠使用相同的父類引用對象來訪問父類成員和子類的重寫方法。那是:
// Access to child class // overridden method a.nature();
- 因此,我們可以得出結論,使用這兩種不同語法的主要目的是在訪問類中的各個成員時獲得變化。
相關用法
- Java UUID randomUUID()用法及代碼示例
- Java URI getAuthority()用法及代碼示例
- Java URI getHost()用法及代碼示例
- Java URI getPath()用法及代碼示例
- Java URI getQuery()用法及代碼示例
- Java URI getRawAuthority()用法及代碼示例
- Java URI getRawPath()用法及代碼示例
- Java URI getRawQuery()用法及代碼示例
- Java URI getRawUserInfo()用法及代碼示例
- Java URI getUserInfo()用法及代碼示例
- Java URL getAuthority()用法及代碼示例
- Java URL getDefaultPort()用法及代碼示例
- Java URL getFile()用法及代碼示例
- Java URL getHost()用法及代碼示例
- Java URL getPath()用法及代碼示例
- Java URL getPort()用法及代碼示例
- Java URL getProtocol()用法及代碼示例
- Java URL getQuery()用法及代碼示例
- Java URL getRef()用法及代碼示例
- Java URL getUserInfo()用法及代碼示例
- Java URL sameFile()用法及代碼示例
- Java URL toExternalForm()用法及代碼示例
- Java URL toURI()用法及代碼示例
- Java UUID clockSequence()用法及代碼示例
- Java UUID compareTo()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自sofiaa大神的英文原創作品 Upcasting in Java with Examples。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。