Matplotlib是Python中的一個庫,它是數字的-NumPy庫的數學擴展。軸類包含大多數圖形元素:Axis,Tick,Line2D,Text,Polygon等,並設置坐標係。 Axes實例通過callbacks屬性支持回調。
matplotlib.axes.Axes.hist()函數
matplotlib庫的axiss模塊中的Axes.hist()函數用於繪製直方圖。
用法: Axes.hist(self, x, bins=None, range=None, density=None, weights=None, cumulative=False, bottom=None, histtype=’bar’, align=’mid’, orientation=’vertical’, rwidth=None, log=False, color=None, label=None, stacked=False, normed=None, *, data=None, **kwargs)
參數:此方法接受以下描述的參數:
- x:此參數是數據序列。
- bins:此參數是可選參數,它包含整數,序列或字符串。
- range:此參數是可選參數,它是箱子的上下限。
- density:此參數是可選參數,它包含布爾值。
- weights:此參數是可選參數,並且是一個權重數組,與x的形狀相同。
- bottom:此參數是每個容器底部基線的位置。
- histtype:此參數是可選參數,用於繪製直方圖的類型。 {“ bar”,“ barstacked”,“ step”,“ stepfilled”}
- align:此參數是可選參數,它控製如何繪製直方圖。 {“左”,“中”,“右”}
- rwidth:此參數是可選參數,它是條形圖的相對寬度,是箱寬度的一部分
- log:此參數是可選參數,用於將直方圖軸設置為對數刻度
- color:此參數是一個可選參數,它是一個顏色規格或一係列顏色規格,每個數據集一個。
- label:此參數是可選參數,它是一個字符串或匹配多個數據集的字符串序列。
- normed:此參數是可選參數,包含布爾值,而是使用density關鍵字參數。
返回值:這將返回以下內容:
- n:這將返回直方圖箱的值。
- 垃圾桶:這將返回箱子的邊。
- 補丁:這將返回用於創建直方圖的單個補丁的列表。
以下示例說明了matplotlib.axes中的matplotlib.axes.Axes.hexbin()函數:
示例1:
# Implementation of matplotlib function
import matplotlib
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(10**7)
mu = 121
sigma = 21
x = mu + sigma * np.random.randn(1000)
num_bins = 100
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
n, bins, patches = ax.hist(x, num_bins,
density = 1,
color ='green',
alpha = 0.7)
y = ((1 / (np.sqrt(2 * np.pi) * sigma)) *
np.exp(-0.5 * (1 / sigma * (bins - mu))**2))
ax.plot(bins, y, '--', color ='black')
ax.set_xlabel('X-Axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y-Axis')
ax.set_title('matplotlib.axes.Axes.hist() Example')
plt.show()輸出:
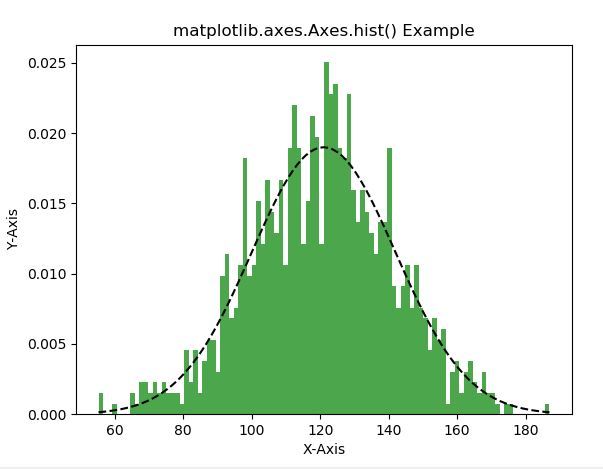
示例2:
# Implementation of matplotlib function
import matplotlib
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(10**7)
n_bins = 20
x = np.random.randn(10000, 3)
fig, [(ax0, ax1), (ax2, ax3)] = plt.subplots(nrows = 2,
ncols = 2)
colors = ['green', 'blue', 'lime']
ax0.hist(x, n_bins, density = True,
histtype ='bar',
color = colors,
label = colors)
ax0.legend(prop ={'size':10})
ax1.hist(x, n_bins, density = True,
histtype ='barstacked',
stacked = True,
color = colors)
ax2.hist(x, n_bins, histtype ='step',
stacked = True,
fill = False,
color = colors)
x_multi = [np.random.randn(n) for n in [100000,
80000,
1000]]
ax3.hist(x_multi, n_bins,
histtype ='stepfilled',
color = colors)
plt.show()輸出:
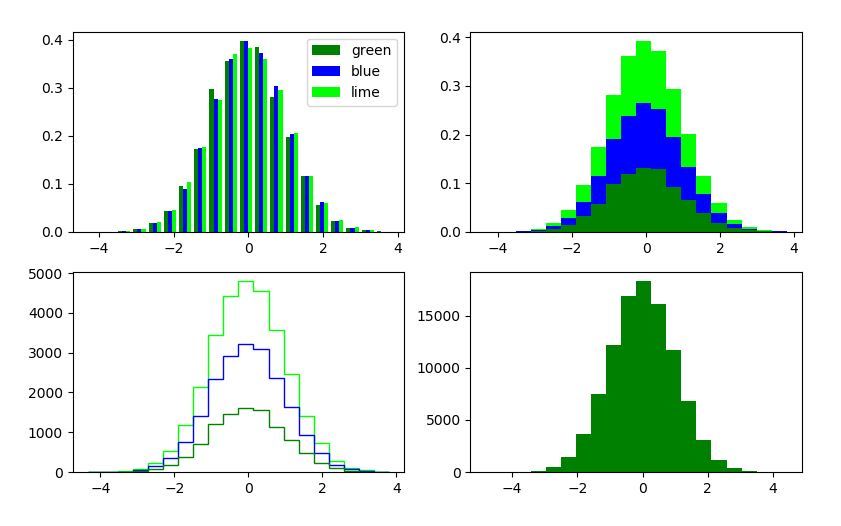
相關用法
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自SHUBHAMSINGH10大神的英文原創作品 Matplotlib.axes.Axes.hist() in Python。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
