大多數時候,在java中處理數字時,我們使用原始數據類型。但是,Java還提供了各種數字包裝紙抽象類下的子類 Number 存在於java.lang包。主要有六Number 類下的子類。這些子類定義了一些在處理數字時經常使用的有用方法。
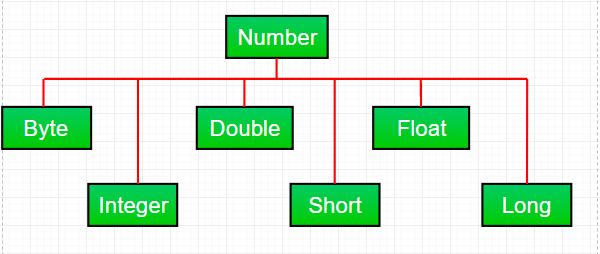
這些類“wrap”是相應對象中的原始數據類型。通常,包裝是由編譯器完成的。如果您在需要對象的地方使用原語,編譯器會為您將原語裝箱在其包裝類中。同樣,如果您在需要基元時使用 Number 對象,編譯器會為您取消裝箱該對象。這也稱為自動裝箱和拆箱。
為什麽要使用 Number 類對象而不是原始數據?
- 由數字類定義的常量(例如 MIN_VALUE 和 MAX_VALUE)非常有用,它們提供了數據類型的上限和下限。
- Number 類對象可以用作需要對象的方法的參數(通常在操作數字集合時使用)。
- 類方法可用於將值與其他基元類型相互轉換、與字符串相互轉換以及在數字係統(十進製、八進製、十六進製、二進製)之間進行轉換。
Number 的所有子類共有的方法:
- xxxxxxValue():這裏xxx代表原始數字數據類型(byte、short、int、long、float、double)。該方法用於將值轉換為這個Number 對象以原始數據類型指定。
Syntax : byte byteValue() short shortValue() int intValue() long longValue() float floatValue() double doubleValue() Parameters : ---- 返回: the numeric value represented by this object after conversion to specified type
Java
//Java program to demonstrate xxxValue() method
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a Double Class object with value "6.9685"
Double d = new Double("6.9685");
// Converting this Double(Number) object to
// different primitive data types
byte b = d.byteValue();
short s = d.shortValue();
int i = d.intValue();
long l = d.longValue();
float f = d.floatValue();
double d1 = d.doubleValue();
System.out.println("value of d after converting it to byte : " + b);
System.out.println("value of d after converting it to short : " + s);
System.out.println("value of d after converting it to int : " + i);
System.out.println("value of d after converting it to long : " + l);
System.out.println("value of d after converting it to float : " + f);
System.out.println("value of d after converting it to double : " + d1);
}
}輸出:
value of d after converting it to byte : 6 value of d after converting it to short : 6 value of d after converting it to int : 6 value of d after converting it to long : 6 value of d after converting it to float : 6.9685 value of d after converting it to double : 6.9685
注意:轉換時,可能會發生精度損失。例如,我們可以看到,從 Double 對象轉換為 int 數據類型時,小數部分(“.9685”)已被省略。
- intcompareTo(NumberSubClass 參考名稱):這個方法是用來比較的這個指定參數的數字對象。但是,無法比較兩種不同的類型,因此調用該方法的參數和 Number 對象應該是同一類型。referenceName 可以是 Byte、Double、Integer、Float、Long 或 Short。
Syntax : public int compareTo( NumberSubClass referenceName ) Parameters : referenceName - any NumberSubClass type value 返回: the value 0 if the Number is equal to the argument. the value 1 if the Number is less than the argument. the value -1 if the Number is greater than the argument.
Java
//Java program to demonstrate compareTo() method
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// creating an Integer Class object with value "10"
Integer i = new Integer("10");
// comparing value of i
System.out.println(i.compareTo(7));
System.out.println(i.compareTo(11));
System.out.println(i.compareTo(10));
}
}輸出:
1 -1 0
- 布爾等於(對象 obj):該方法判斷是否這個Number 對象等於參數。
Syntax : public boolean equals(Object obj) Parameters : obj - any object 返回: The method returns true if the argument is not null and is an object of the same type and with the same numeric value, otherwise false.
Java
//Java program to demonstrate equals() method
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// creating a Short Class object with value "15"
Short s = new Short("15");
// creating a Short Class object with value "10"
Short x = 10;
// creating an Integer Class object with value "15"
Integer y = 15;
// creating another Short Class object with value "15"
Short z = 15;
//comparing s with other objects
System.out.println(s.equals(x));
System.out.println(s.equals(y));
System.out.println(s.equals(z));
}
}輸出:
false false true
- int parseInt(字符串 s,int 基數):該方法用於獲取a的原始數據類型String。 Radix 用於返回十進製 (10)、八進製 (8) 或十六進製 (16) 等表示形式作為輸出。
Syntax : static int parseInt(String s, int radix) Parameters : s - any String representation of decimal radix - any radix value 返回: the integer value represented by the argument in decimal. Throws : NumberFormatException : if the string does not contain a parsable integer.
Java
//Java program to demonstrate Integer.parseInt() method
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// parsing different strings
int z = Integer.parseInt("654",8);
int a = Integer.parseInt("-FF", 16);
long l = Long.parseLong("2158611234",10);
System.out.println(z);
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(l);
// run-time NumberFormatException will occur here
// "Geeks" is not a parsable string
int x = Integer.parseInt("Geeks",8);
// run-time NumberFormatException will occur here
// (for octal(8),allowed digits are [0-7])
int y = Integer.parseInt("99",8);
}
}輸出:
428
-255
2158611234
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "Geeks"
at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:65)
at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:580)
at Test.main(Test.java:17)
- int parseInt(字符串):此方法是上述方法的另一種變體,默認基數為 10(十進製)。
Syntax : static int parseInt(String s) Parameters : s - any String representation of decimal 返回: the integer value represented by the argument in decimal. Throws : NumberFormatException : if the string does not contain a parsable integer.
Java
//Java program to demonstrate Integer.parseInt() method
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// parsing different strings
int z = Integer.parseInt("654");
long l = Long.parseLong("2158611234");
System.out.println(z);
System.out.println(l);
// run-time NumberFormatException will occur here
// "Geeks" is not a parsable string
int x = Integer.parseInt("Geeks");
// run-time NumberFormatException will occur here
// (for decimal(10),allowed digits are [0-9])
int a = Integer.parseInt("-FF");
}
}輸出:
654
2158611234
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "Geeks"
at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:65)
at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:580)
at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:615)
at Test.main(Test.java:15)
- 字符串toString():toString() 方法有兩種變體。它們用於獲取數字的字符串表示形式。這些方法的其他變體是整數.toBinaryString(int i),Integer.toHexString(int i),整數.toOctalString(int i)它將分別返回指定整數(i)的二進製、hexa-decimal、八進製字符串表示形式。
Syntax : String toString() String toString(int i) Parameters : String toString() - no parameter String toString(int i) - i: any integer value 返回: String toString() - returns a String object representing the value of the Number object on which it is invoked. String toString(int i) - returns a decimal String object representing the specified integer(i)
Java
//Java program to demonstrate Integer.toString()
//and Integer.toString(int i) method
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// demonstrating toString() method
Integer x = 12;
System.out.println(x.toString());
// demonstrating toString(int i) method
System.out.println(Integer.toString(12));
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(152));
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(152));
System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(152));
}
}輸出:
12 12 10011000 98 230
- 整數valueOf():valueOf()方法有三種變體。所有這三個方法都返回一個包含原始整數值的 Integer 對象。
Syntax : Integer valueOf(int i) Integer valueOf(String s) Integer valueOf(String s, int radix) Parameters : i - any integer value s - any String representation of decimal radix - any radix value 返回: valueOf(int i) : an Integer object holding the valuerepresented by the int argument. valueOf(String s) : an Integer object holding value represented by the string argument. valueOf(String s, int radix) : an Integer object holding the value represented by the string argument with base radix. Throws : valueOf(String s) - NumberFormatException : if the string does not contain a parsable integer. valueOf(String s, int radix) - NumberFormatException : if the string does not contain a parsable integer.
Java
// Java program to demonstrate valueOf() method
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// demonstrating valueOf(int i) method
System.out.println("Demonstrating valueOf(int i) method");
Integer i =Integer.valueOf(50);
Double d = Double.valueOf(9.36);
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(d);
// demonstrating valueOf(String s) method
System.out.println("Demonstrating valueOf(String s) method");
Integer n = Integer.valueOf("333");
Integer m = Integer.valueOf("-255");
System.out.println(n);
System.out.println(m);
// demonstrating valueOf(String s,int radix) method
System.out.println("Demonstrating (String s,int radix) method");
Integer y = Integer.valueOf("333",8);
Integer x = Integer.valueOf("-255",16);
Long l = Long.valueOf("51688245",16);
System.out.println(y);
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(l);
// run-time NumberFormatException will occur in below cases
Integer a = Integer.valueOf("Geeks");
Integer b = Integer.valueOf("Geeks",16);
}
}輸出:
Demonstrating valueOf(int i) method
50
9.36
Demonstrating valueOf(String s) method
333
-255
Demonstrating (String s,int radix) method
219
-597
1365803589
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "Geeks"
at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:65)
at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:580)
at java.lang.Integer.valueOf(Integer.java:766)
at Test.main(Test.java:28)
練習題:
給定的java代碼的輸出是什麽?
Java
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Integer i = Integer.parseInt("Kona", 27);
System.out.println(i);
}
}選項:
A) NumberFormatException at run-time B) NumberFormatException at compile-time C) 411787
回答:
C) 411787
解釋:
由於基數為 27,因此字符串文字中允許的字符為 [0-9]、[A-Q](10 到 26)。因此其值將計算如下:
=> a*(27^0) + n*(27^1) + o*(27^2) + k*(27^3)
=> 10*1 + 23*27 + 24*27*27 + 20*27*27*27
=> 10 + 621 + 17496 + 393660
=> 411787
相關用法
- Java Java.lang.Number.byteValue()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Number.doubleValue()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Number.floatValue()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Number.intValue()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Number.longValue()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Number.shortValue()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Boolean.booleanValue()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Boolean.compareTo()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Boolean.equals()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Boolean.getBoolean()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Boolean.hashCode()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Boolean.parseBoolean()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Boolean.toString()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Boolean.valueOf()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Byte.byteValue()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Byte.compareTo()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Byte.decode()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Byte.doubleValue()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Byte.equals()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Byte.floatValue()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Byte.hashCode()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Byte.intValue()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Byte.longValue()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Byte.parseByte()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.lang.Byte.shortValue()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自佚名大神的英文原創作品 Java.lang.Number Class in Java。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
