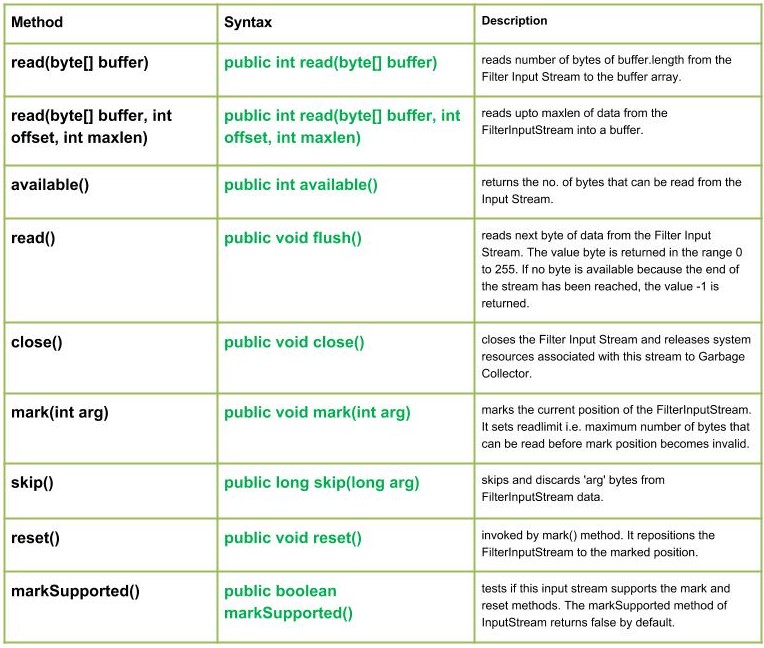
過濾流在讀取和寫入輸入流中的數據時過濾數據,過濾數據並將其傳遞到底層流。過濾流是
- FilterInputStream
- Java.io.FilterOutputStream
FilterInputStream:Java.io.FilterInputStream 類的工作方式與 Java 中的 InputStream 類幾乎類似,但它所做的隻是重寫 InputStream 類方法,將請求傳遞給 InputStream。 FilterInputStream 類的 read() 方法過濾數據並讀取數據,並將數據傳遞到底層流過濾,該過濾是根據流完成的。
聲明:
public class FilterInputStream extends InputStream
構造函數:
- 受保護的FilterInputStream(InputStream中):通過將參數分配給字段this.in來創建FilterInputStream,以便記住它以供以後使用。
方法:
- 讀取(字節[]緩衝區):java.io.FilterInputStream.read(byte[] 緩衝區)將 buffer.length 的字節數從過濾器輸入流讀取到緩衝區數組。
Syntax :public int read(byte[] buffer) Parameters : buffer : buffer to be read Return : reads number of bytes of buffer.length to the buffer else, -1 i.e. when end of file is reached. Exception : -> IOException : If I/O error occurs.
執行:
// Java program illustrating the working of read(byte[] buffer) method
import java.io.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
// LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initailly null
FilterInputStream geek_input = null;
InputStream geek = null;
try{
char c;
int a;
byte[] buffer = new byte[6];
// New InputStream : 'GEEKS' is created
geek = new FileInputStream("GEEKS.txt");
geek_input = new BufferedInputStream(geek);
a = geek.read(buffer);
// read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer
// '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream
int length = 1 ;
for(byte g : buffer)
{
// Since read() method returns Integer value
// So, we convert each integer value to char
c = (char)g;
System.out.println("At position " + length + " : " + c);
length++;
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{
// In case of error
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("ERROR Occurs ");
}
finally
{
// Closing the streams, Once the End of Input Stream is reached
if(geek != null)
geek.close();
if(geek_input != null)
geek_input.close();
}
}
} 注意:
以下 Java 代碼不會在這裏運行,因為我們無法訪問在線 IDE 上的任何文件。
因此,將該程序複製到您的係統並在那裏運行。
程序中使用的GEEKS.txt文件包含:
HelloGeeks
在給定的代碼中 buffer.length = 6 ,因此隻有 HelloG 會通過 read(byte[] buffer) 方法讀取
輸出:
At position 1 : H At position 2 : e At position 3 : l At position 4 : l At position 5 : o At position 6 : G
- 讀取(字節[]緩衝區,int偏移量,int maxlen):java.io.FilterInputStream.read(byte[] 緩衝區, int 偏移量, int maxlen)將 FilterInputStream 中最多 maxlen 的數據讀取到緩衝區中。
Syntax :public int read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen) Parameters : buffer : Destination buffer offset : start position to read maxlen : max. length of bytes to be read Return : total no. of bytes to be written else, -1 i.e. when end of Stream is reached. Exception : -> IOException : If I/O error occurs.
執行:
// Java program illustrating the working of
// read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen) method
import java.io.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
// LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initailly null
FilterInputStream geek_input = null;
InputStream geek = null;
try{
char c;
int a;
byte[] buffer = new byte[4];
// New InputStream : 'ABC' is created
geek = new FileInputStream("ABC.txt");
geek_input = new BufferedInputStream(geek);
// Offset = 1(*), Maxlen = 3 (MOH)
a = geek.read(buffer, 1, 3);
// read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer
// '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream
for(byte g : buffer)
{
// Since read() method returns Integer value
// So, we convert each integer value to char
c = (char)g;
if(g == 0)
c = '*';
System.out.print(c);
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{
// In case of error
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("ERROR Occurs ");
}
finally
{
// Closing the streams, Once the End of Input Stream is reached
if(geek != null)
geek.close();
if(geek_input != null)
geek_input.close();
}
}
} 注意:
以下 Java 代碼不會在這裏運行,因為我們無法訪問在線 IDE 上的任何文件。
因此,將該程序複製到您的係統並在那裏運行。
程序中使用的ABC.txt文件包含:
MOHIT
偏移 = 1 即 * 且 Maxlen = 3 即 MOH
輸出:
*MOH
- available():java.io.FilterInputStream.available()返回編號。可以從輸入流讀取的字節數。
Syntax :public int available() Parameters : ------- Return : returns the no. of bytes that can be read from the FilterInputStream. Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
執行:
// Java program illustrating the working of available() method
import java.io.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
// FilterInputStream & FileInputStream initailly null
FilterInputStream geek_input = null;
InputStream geek = null;
try{
char c;
int a, b;
// New InputStream : 'ABC' is created
geek = new FileInputStream("ABC.txt");
geek_input = new BufferedInputStream(geek);
while((a = geek_input.read()) != -1)
{
// So, we convert each integer value to char
c = (char)a;
// Use of available method : return no. of bytes that can be read
a = geek_input.available();
System.out.println(c + " Bytes available : " + a);
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{
// In case of error
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("ERROR Occurs ");
}
finally
{
// Closing the streams, Once the End of FilterInputStream is reached
if(geek != null)
geek.close();
if(geek_input != null)
geek_input.close();
}
}
} 注意:
以下 Java 代碼不會在這裏運行,因為我們無法訪問在線 IDE 上的任何文件。
因此,將該程序複製到您的係統並在那裏運行。
程序中使用的ABC.txt文件包含:
MOHIT
輸出:
M Bytes available : 4 O Bytes available : 3 H Bytes available : 2 I Bytes available : 1 T Bytes available : 0
- read():java.io.FilterInputStream.read()從過濾器輸入流讀取下一個數據字節。返回的字節值範圍為 0 到 255。如果由於已到達流末尾而沒有可用字節,則返回值 -1。
Syntax :public int read() Parameters : ------ Return : Reads next data else, -1 i.e. when end of Stream is reached. Exception : -> IOException : If I/O error occurs.
- close():java.io.FilterInputStream.close()關閉過濾器輸入流並將與該流關聯的係統資源釋放到垃圾Collector。
Syntax :public void close() Parameters : ------ Return : void Exception : -> IOException : If I/O error occurs.
- 標記(int arg):java.io.FilterInputStream.mark(int arg)標記 FilterInputStream 的當前位置。它設置讀取限製,即標記位置無效之前可以讀取的最大字節數。
Syntax :public void mark(int arg) Parameters : arg : integer specifying the read limit of the input Stream Return : void
- skip():java.io.FilterInputStream.skip(長參數)跳過並丟棄FilterInputStream 數據中的‘arg’ 字節。
Syntax :public long skip(long arg) Parameters : arg : no. of bytes of FilterInputStream data to skip. Return : no. of bytes to be skipped Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
- reset():java.io.FilterInputStream.reset()由mark()方法調用。它將 FilterInputStream 重新定位到標記位置。
Syntax :public void reset() Parameters : ---- Return : void Exception : -> IOException : If I/O error occurs.
- markSupported():java.io.FilterInputStream.markSupported()方法測試此輸入流是否支持標記和重置方法。 InputStream 的 markSupported 方法默認返回 false。
Syntax :public boolean markSupported() Parameters : ------- Return : true if input stream supports the mark() and reset() method else,false
Java程序講解:markSupported()、close()、reset()、mark()、read()、skip()方法
// Java program illustrating the working of FilterInputStream method
// mark(), read(), skip()
// markSupported(), close(), reset()
import java.io.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
InputStream geek = null;
// FilterInputStream initialised to null here
FilterInputStream geek_input = null;
try {
geek = new FileInputStream("GEEKS.txt");
geek_input = new BufferedInputStream(geek);
// read() method : reading and printing Characters
// one by one
System.out.println("Char : " + (char)geek_input.read());
System.out.println("Char : " + (char)geek_input.read());
System.out.println("Char : " + (char)geek_input.read());
// mark() : read limiing the 'geek' input stream
geek_input.mark(0);
// skip() : it results in redaing of 'e' in G'e'eeks
geek_input.skip(1);
System.out.println("skip() method comes to play");
System.out.println("mark() method comes to play");
System.out.println("Char : " + (char)geek_input.read());
System.out.println("Char : " + (char)geek_input.read());
System.out.println("Char : " + (char)geek_input.read());
boolean check = geek_input.markSupported();
if (geek_input.markSupported())
{
// reset() method : repositioning the stream to
// marked positions.
geek_input.reset();
System.out.println("reset() invoked");
System.out.println("Char : " + (char)geek_input.read());
System.out.println("Char : " + (char)geek_input.read());
}
else
System.out.println("reset() method not supported.");
System.out.println("geek_input.markSupported() supported"
+ " reset() : " + check);
}
catch(Exception excpt)
{
// in case of I/O error
excpt.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
// releasing the resources back to the
// GarbageCollector when closes
if (geek != null)
{ // Use of close() : closing the file
// and releasing resources
geek.close();
}
if(geek_input != null)
geek_input.close();
}
}
} 注意:
此代碼不會在在線 IDE 上運行,因為此處不存在此類文件。
您可以在係統上運行此代碼來檢查工作情況。
GEEKS.txt代碼中使用的文件有
HelloGeeks
輸出:
Char : H Char : e Char : l skip() method comes to play mark() method comes to play Char : o Char : G Char : e reset() invoked Char : l Char : o geek_input.markSupported() supported reset() : true
相關用法
- Java Java.io.FilterInputStream.available()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterInputStream.mark()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterInputStream.markSupported()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterInputStream.read()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterInputStream.reset()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterInputStream.skip()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterOutputStream.Close()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterOutputStream.flush()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterOutputStream.write()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterReader.close()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterReader.mark()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterReader.markSupported()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterReader.read()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterReader.ready()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterReader.reset()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterReader.skip()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterWriter.close()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterWriter.flush()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterWriter.write()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterWriter.available()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterWriter用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterReader用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.FilterOutputStream用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.File.canExecute()用法及代碼示例
- Java Java.io.File.canRead()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自佚名大神的英文原創作品 Java.io.FilterInputStream Class in Java。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。