在討論差異之前,讓我們快速回顧一下這三種方法
- Java - File getPath()用法及代碼示例 方法
- Java - File getAbsolutePath()用法及代碼示例 方法
- Java - File getCanonicalPath()用法及代碼示例方法
1. Java - File getPath()用法及代碼示例 方法
getPath()是URL類的一種方法,它將給定的抽象路徑名轉換為路徑名字符串。結果字符串使用默認的name-separator字符分隔名稱序列中的名稱。
返回值:抽象路徑名的字符串形式
例
Java
// Java Program illustrating the getPath() method
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Class for getPath method()
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a new file onject in which input is
// absoute path as in argument from the user
File path1 = new File(
"C:/Users/ASPIRE/Desktop/Java/Notes/Chapter one/demo.txt");
// Print the display the path string for
// absolute path using getPath() method
System.out.println(
"Output for given absolute path:"
+ path1.getPath());
// Creating another object of File and this time
// relative path is provided as an input
File path2 = new File("Notes/../demo.txt");
// Print the display the path string for
// relative path using getPath() method
System.out.println(
"Output for given relative path:"
+ path2.getPath());
}
}輸出:
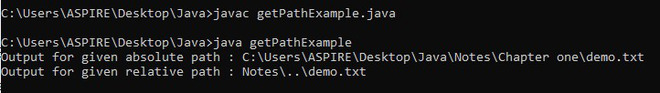
2. Java - File getAbsolutePath()用法及代碼示例 方法
getAbsolutePath()返回表示給定路徑的絕對路徑的路徑對象。如果給定的路徑名已經是絕對的,則僅通過getPath()方法返回路徑名字符串。如果此抽象路徑名是空的抽象路徑名,則返回由係統屬性用戶“ .dir”()命名的當前用戶目錄的路徑名字符串。否則,將以system-dependent的方式解析此路徑名。
返回值:絕對路徑名字符串,表示與此抽象路徑名相同的文件或目錄
- On Unix’s System:通過針對當前用戶目錄解析相對路徑名,可以使該路徑為絕對路徑。
- On Microsoft System:通過將相對路徑名與由路徑名命名的驅動器的當前目錄(如果有)解析,可以使它成為絕對路徑。如果不是,則針對當前用戶目錄進行解析。
例:
Java
// Java Program illustrating the getAbsolutePath() Method
// Importing all input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Class to get getAbsolutePath
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a file object where
// relatie path is provided as in paarameter
File path = new File("Notes/../demo.txt");
// Print and display the string representing
// absolute path of the file
System.out.println("Output:"
+ path.getAbsolutePath());
}
}輸出:
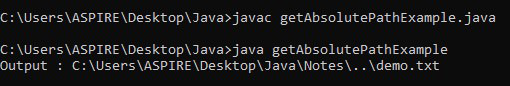
3。Java - File getCanonicalPath()用法及代碼示例方法
此方法返回給定抽象路徑名的規範路徑名字符串。規範路徑名是絕對的,也是唯一的。如有必要,此方法首先將路徑名轉換為絕對格式,就像調用getAbsolutePath()方法一樣,然後以system-dependent方式將其映射為唯一格式。
返回值:規範路徑名字符串,表示與抽象路徑名相同的文件或目錄。
Java
// Java Program illustrating the getCanonicalPath() method
// Importing all input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Class for showcasing getCanonicalPath method
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
// Creating a new File object and
// providing it relative path as in argumennts
File path = new File("Notes/../demo.txt");
// Print an display the the canonical path
// name string
System.out.println("Output:"
+ path.getCanonicalPath());
}
}輸出:
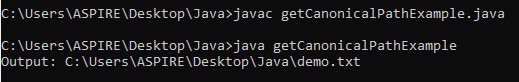
輸出說明:為了更好地解釋這些CMD輸出或硬編碼輸出,使用的java文件的指定位置如下
:C:\Users\ASPIRE\Desktop\Java\getPathExample or getAbsoltePathExample or getCanonicalPathExample
demo.txt文件的位置
:C:\Users\ASPIRE\Desktop\Java\Notes\Chapter one\demo.txt
現在,在討論了它們各自之後,讓我們深入研究getPath(),getAbsolutePath()和getCanonicalPath()之間的差異,如下所示:
| getPath() | getAbsolutePath() | getCononicalPath() |
|---|---|---|
| 此方法返回一個字符串,該字符串表示文件對象表示的文件的(絕對或相對)路徑名。 | 此方法返回抽象文件路徑名的絕對路徑名字符串。 | 此方法返回給定抽象路徑名的規範路徑名字符串。 |
| 如果使用相對路徑創建文件對象,則返回的路徑是相對路徑。 | 如果抽象路徑名是相對的,則以system-dependent的方式解析。 | 如果文件對象是使用相對路徑創建的,則此方法首先將路徑名轉換為絕對路徑並將其映射為唯一形式。 |
| 如果使用絕對路徑創建文件對象,則返回的路徑為絕對路徑。 | 如果抽象路徑名已經是絕對路徑,則返回相同的路徑名字符串。 | 如果使用相對路徑創建文件對象,則返回的路徑將采用唯一形式。 |
| 此方法不解析路徑名。 | 此方法僅解析當前目錄的相對路徑。速記表示形式(例如“.”和“..”)不再得到解決。 | 此方法涉及從路徑名中刪除冗餘名稱(例如“.”和“..”),解析符號鏈接(在Unix平台上)以及將驅動器號轉換為標準大小寫(在Microsoft window平台上)。 |
|
例 在視窗係統上 文件路徑=新文件(“Notes/../demo.txt”); 輸出: Notes \ .. \ demo.txt 在Unix係統上 文件路徑=新文件(“ Notes /../demo.txt”) 輸出: 注釋/../demo.txt |
例 視窗係統 文件路徑=新文件(“Notes/../demo.txt”); 輸出: C:\ Users \ ASPIRE \ Desktop \ Java \ Notes \ .. \ demo.txt 在Unix係統上 文件路徑=新文件(“ Notes /../demo.txt”) 輸出: 主頁/pooja /桌麵/便箋/../demo.txt |
例 在Window係統上 文件路徑=新文件(“Notes/../demo.txt”); 輸出: C:\ Users \ ASPIRE \ Desktop \ Java \ demo.txt 在Unix係統上 文件路徑=新文件(“ Notes /../demo.txt”) 輸出: /home/pooja/Desktop/Java/demo.txt |
相關用法
- Java getPath()和getAbsolutePath()的區別用法及代碼示例
- Java getPath()和getCanonicalPath()的區別用法及代碼示例
- Java URL getPath()用法及代碼示例
- Java URI getPath()用法及代碼示例
- Java File getPath()用法及代碼示例
- Java super()和this()的區別用法及代碼示例
- Java throw和throws的區別用法及代碼示例
- Java notify()和notifyAll()的區別用法及代碼示例
- Java Stream.of()和Arrays.stream()的區別用法及代碼示例
- Java LinkedList和LinkedHashSet的區別用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自poojavichare1810大神的英文原創作品 Difference between getPath() and getCononicalPath() in Java。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
