erf() 函數計算傳遞給函數的參數的誤差函數值。
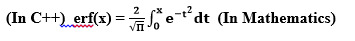
用法
假設一個數字是 'x':
float erf( float x);
double erf( double x);
long double erf( long double x);
double erf( integral x);參數
x: 它是一個浮點值。
返回值
它返回 x 的誤差函數值。
| 參數 | 返回值 | |
|---|---|---|
| x=±0 | ±0 | |
| x=±無窮大 | ±1 | |
| x=nan | nan |
例子1
讓我們看一個簡單的例子。
#include <iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double x= 6.2;
cout<<"Value of x is:"<<x<<'\n';
cout<<"erf(x):"<<erf(x);
return 0;}輸出:
Value of x is:6.2 erf(x):1
在上麵的例子中,x 的值為 6.2。 erf() 函數返回值,即 1。
例子2
讓我們看一個簡單的例子,當 x 的值是無窮大時。
#include <iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double x= 1.0/0.0;
cout<<"Value of x is:"<<x<<'\n';
cout<<"erf(x):"<<erf(x);
return 0;
}輸出:
Value of x is:inf erf(x):1
在上麵的例子中,x 的值是無限的。因此,函數 erf() 返回值 1。
例子3
讓我們看看 x 的值為零時的簡單示例。
#include <iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float x= 0.0;
cout<<"Value of x is:"<<x<<'\n';
cout<<"erf(x):"<<erf(x);
return 0;
}輸出:
Value of x is:0 erf(x):0
在上麵的例子中,x 的值為零。因此,函數 erf() 返回 0 值。
示例 4
讓我們看一個簡單的例子,當 x 的值為 nan 時。
#include <iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float x= 0.0/0.0;
cout<<"Value of x is:"<<x<<'\n';
cout<<"erf(x):"<<erf(x);
return 0;
}輸出:
Value of x is:-nan erf(x):-nan
在上麵的例子中,x 的值為 nan。因此,函數 erf() 返回 nan。
相關用法
- C++ Math erfc()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math exp()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math expm1()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math exp2()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math scalbn()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math acosh()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math asinh()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math isgreater()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math fabs()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math islessgreater()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math log2()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math nearbyint()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math tan()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math log()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math nextafter()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math fdim()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math isfinite()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math sinh()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math scalbln()用法及代碼示例
- C++ Math cosh()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自 C++ Math erf()。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
